朴素贝叶斯(Naive Bayes)算法的核心思想是:分别计算给定样本属于每个分类的概率,然后挑选概率最高的作为猜测结果。
假定样本有2个特征x和y,则其属于分类1的概率记作p(C1|x,y),它的值无法直接分析训练样本得出,需要利用公式间接求得。
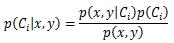
p(x,y)表示满足2个特征的样本概率,它等于第1特征等于x且第2特征等于y的样本数除以样本总数。可以发现p(x,y)与当前在计算哪个分类概率是无关的,因此实际计算中可以忽略它,不会影响结果。
p(x,y|Ci)表示Ci分类中满足2个特征的样本概率,在朴素贝叶斯算法中,认为x与y是相互独立的,因此p(x,y|Ci)=p(x|Ci)*p(y|Ci),其中p(x|Ci)表示Ci分类的样本中第1个特征等于x的概率。
上面的例子中只给定了2维的情况,实际可以扩展到N维,由于假定各特征相互独立,因此p(w|Ci)总是可以分解求得的。
上C#代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace MachineLearning
{
/// <summary>
/// 朴素贝叶斯
/// </summary>
public class NaiveBayes
{
private List<DataVector<string>> m_TrainingSet;
/// <summary>
/// 训练
/// </summary>
/// <param name="trainingSet"></param>
public void Train(List<DataVector<string>> trainingSet)
{
m_TrainingSet = trainingSet;
}
/// <summary>
/// 分类
/// </summary>
/// <param name="vector"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public string Classify(DataVector<string> vector)
{
var classProbDict = new Dictionary<string, double>();
//得到所有分类
var typeDict = new Dictionary<string, int>();
foreach(var item in m_TrainingSet)
typeDict[item.Label] = 0;
//为每个分类计算概率
foreach(string type in typeDict.Keys)
classProbDict[type] = GetClassProb(vector, type);
//找最大值
double max = double.NegativeInfinity;
string label = string.Empty;
foreach(var type in classProbDict.Keys)
{
if(classProbDict[type] > max)
{
max = classProbDict[type];
label = type;
}
}
return label;
}
/// <summary>
/// 分类(快速)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="vector"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public string ClassifyFast(DataVector<string> vector)
{
var typeCount = new Dictionary<string, int>();
var featureCount = new Dictionary<string, Dictionary<int, int>>();
//首先通过一次遍历,得到所需要的各种数量
foreach(var item in m_TrainingSet)
{
if(!typeCount.ContainsKey(item.Label))
{
typeCount[item.Label] = 0;
featureCount[item.Label] = new Dictionary<int, int>();
for(int i = 0;i < vector.Dimension;++i)
featureCount[item.Label][i] = 0;
}
//累加对应分类的样本数
typeCount[item.Label]++;
//遍历每个维度(特征),累加对应分类对应特征的计数
for(int i = 0;i < vector.Dimension;++i)
{
if(string.Equals(vector.Data[i], item.Data[i]))
featureCount[item.Label][i]++;
}
}
//然后开始计算概率
double maxProb = double.NegativeInfinity;
string bestLabel = string.Empty;
foreach(string type in typeCount.Keys)
{
//计算p(Ci)
double classProb = typeCount[type] * 1.0 / m_TrainingSet.Count;
//计算p(F1|Ci)
double featureProb = 1.0;
for(int i = 0;i < vector.Dimension;++i)
featureProb = featureProb * (featureCount[type][i] * 1.0 / typeCount[type]);
//计算p(Ci|w),忽略p(w)部分
double typeProb = featureProb * classProb;
//保留最大概率
if(typeProb > maxProb)
{
maxProb = typeProb;
bestLabel = type;
}
}
return bestLabel;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取指定分类的概率
/// </summary>
/// <param name="vector"></param>
/// <param name="type"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private double GetClassProb(DataVector<string> vector, string type)
{
double classProb = 0.0;
double featureProb = 1.0;
//统计训练样本中属于此分类的数量,用于计算p(Ci)
int typeCount = m_TrainingSet.Count(p => string.Equals(p.Label, type));
//遍历每个维度(特征)
for(int i = 0;i < vector.Dimension;++i)
{
//统计此分类下符合本特征的样本数,用于计算p(Fn|Ci)
int featureCount = m_TrainingSet.Count(p => string.Equals(p.Data[i], vector.Data[i]) && string.Equals(p.Label, type));
//计算p(Fn|Ci)
featureProb = featureProb * (featureCount * 1.0 / typeCount);
}
//计算p(Ci|w),忽略p(w)部分
classProb = featureProb * (typeCount * 1.0 / m_TrainingSet.Count);
return classProb;
}
}
}代码中Classify方法以最直接直观的方式实现算法,易于理解,但是由于遍历次数太多,在训练样本较多时效率不佳。ClassifyFast方法减少了遍历次数,效率有一定提升。两者的基础算法是一致的,结果也一致。
需要注意实际运行中有可能遇到多个分类概率相同或者每种分类概率都是0的情况,此时一般是随便选取一个分类作为结果。但有时要小心对待,比如用贝叶斯识别垃圾邮件时,如果概率相同,甚至是两个概率相差不大时,都要按非垃圾邮件来处理,这是因为没识别出垃圾邮件造成的影响远小于把正常邮件识别成垃圾造成的影响。
还是用上回的毒蘑菇数据进行一下测试,这回减少点数据量,选取2000个样本进行训练,然后选取500个测试错误率。
public void TestBayes()
{
var trainingSet = new List<DataVector<string>>();
var testSet = new List<DataVector<string>>();
var file = new StreamReader("agaricus-lepiota.txt", Encoding.Default);
//读取数据
string line = string.Empty;
for(int i = 0;i < 2500;++i)
{
line = file.ReadLine();
if(line == null)
break;
var parts = line.Split(',');
var p = new DataVector<string>(22);
p.Label = parts[0];
for(int j = 0;j < p.Dimension;++j)
p.Data[j] = parts[j + 1];
if(i < 2000)
trainingSet.Add(p);
else
testSet.Add(p);
}
file.Close();
//检验
var bayes = new NaiveBayes();
bayes.Train(trainingSet);
int error = 0;
foreach(var p in testSet)
{
var label = bayes.ClassifyFast(p);
if(label != p.Label)
++error;
}
Console.WriteLine("Error = {0}/{1}, {2}%", error, testSet.Count, (error * 100.0 / testSet.Count));
}测试结果是错误率是0%,有点出乎意料。改变训练样本与测试样本,错误率会有变化,比如与上一篇相同条件时(7000个训练样本+1124个测试样本),测试出的错误率是4.18%,与随机猜测50%的错误率相比,已经相当精确了。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。