我们之前学习了二叉树相关的概念,那么我们今天来分析下二叉树中的一些经典面试题。
1、单度结点的删除
-- 编写一个函数用于删除二叉树中的所有单度结点;
-- 要求:结点删除后,其唯一的子结点替代它的位置。
示例如下
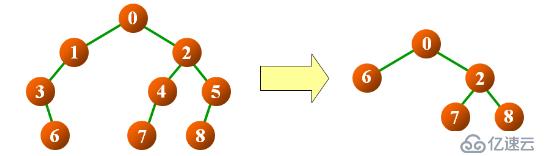
a> 那么在我们的结点中包含指向父结点的指针。定义功能:delOld1(node),删除 node 为根结点的二叉树中的单度结点;
实现思路如下

我们来看看具体代码怎么写
#include <iostream>
#include "BTree.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
template < typename T >
BTreeNode<T>* createTree()
{
static BTreeNode<int> ns[9];
for(int i=0; i<9; i++)
{
ns[i].value = i;
ns[i].parent = NULL;
ns[i].left = NULL;
ns[i].right = NULL;
}
ns[0].left = &ns[1];
ns[0].right = &ns[2];
ns[1].parent = &ns[0];
ns[2].parent = &ns[0];
ns[1].left = &ns[3];
ns[1].right = NULL;
ns[3].parent = &ns[1];
ns[2].left = &ns[4];
ns[2].right = &ns[5];
ns[4].parent = &ns[2];
ns[5].parent = &ns[2];
ns[3].left = NULL;
ns[3].right = &ns[6];
ns[6].parent = &ns[3];
ns[4].left = &ns[7];
ns[4].right = NULL;
ns[7].parent = &ns[4];
ns[5].left = &ns[8];
ns[5].right = NULL;
ns[8].parent = &ns[5];
return ns;
}
template < typename T >
void printInOrder(BTreeNode<T>* node)
{
if( node != NULL )
{
printInOrder(node->left);
cout << node->value << " ";
printInOrder(node->right);
}
}
template < typename T >
void printDualList(BTreeNode<T>* node)
{
BTreeNode<T>* g = node;
cout << "head -> tail: " << endl;
while( node != NULL )
{
cout << node->value << " ";
g = node;
node = node->right;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "tail -> head: " << endl;
while( g != NULL )
{
cout << g->value << " ";
g = g->left;
}
cout << endl;
}
template< typename T >
BTreeNode<T>* delOld1(BTreeNode<T>* node)
{
BTreeNode<T>* ret = NULL;
if( node != NULL )
{
if( ((node->left != NULL) && (node->right == NULL)) ||
((node->left == NULL) && (node->right != NULL)) )
{
BTreeNode<T>* parent = dynamic_cast<BTreeNode<T>*>(node->parent);
BTreeNode<T>* node_child = (node->left != NULL) ? node->left : node->right;
if( parent != NULL )
{
BTreeNode<T>*& parent_child = (parent->left == node) ? parent->left : parent->right;
parent_child = node_child;
node_child->parent = parent;
}
else
{
node_child->parent = NULL;
}
if( node->flag() )
{
delete node;
}
ret = delOld1(node_child);
}
else
{
delOld1(node->left);
delOld1(node->right);
ret = node;
}
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
BTreeNode<int>* ns = createTree<int>();
printInOrder(ns);
cout << endl;
ns = delOld1(ns);
printInOrder(ns);
cout << endl;
int a[] = {6, 7, 8};
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
TreeNode<int>* n = ns + a[i];
while( n != NULL )
{
cout << n->value << " ";
n = n->parent;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}我们在其中构建的是上图中的二叉树,来运行看看结果
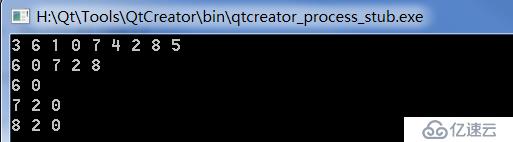
我们看到运行的结果和我们想象的是一致的,前序遍历完后的结果为 6 0 7 2 8。
b> 结点中只包含左右孩子指针。定义功能:delOld2(node) // node 为结点指针的引用;删除 node 为根结点的二叉树中的单度结点;
实现思路如下图所示

我们来看看具体的源码编写
template< typename T >
void delOld2(BTreeNode<T>*& node)
{
if( node != NULL )
{
if( ((node->left != NULL) && (node->right == NULL)) ||
((node->left == NULL) && (node->right != NULL)) )
{
BTreeNode<T>* node_child = (node->left != NULL) ? node->left : node->right;
if( node->flag() )
{
delete node;
}
node = node_child;
delOld2(node);
}
else
{
delOld2(node->left);
delOld2(node->right);
}
}
}测试代码如下
int main()
{
BTreeNode<int>* ns = createTree<int>();
printInOrder(ns);
cout << endl;
delOld2(ns);
printInOrder(ns);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}我们来看看运行结果
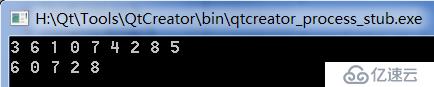
结果还是和之前的是一样的,证明我们写的是正确的。
2、中序线索化二叉树
-- 编写一个函数用于中序线索化二叉树
-- 要求:不允许使用其他数据结构
示例如下
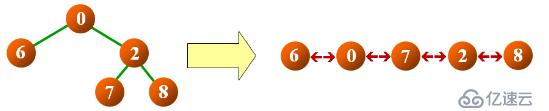
a> 在中序遍历的同时进行线索化
思路:使用辅助指针,在中序遍历时指向当前结点的前驱结点;访问当前结点时,连接与前驱结点的先后次序;
示例如下
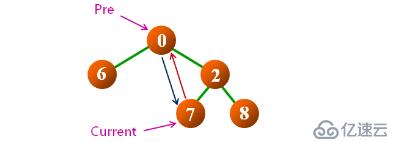
定义功能:inOrderThread(node, pre) ,node 为根结点,也是中序访问的结点;pre 为中序遍历时的前驱结点指针。
实现思路如下

我们来看看具体源码是怎么写的
template < typename T >
void inOrderThread(BTreeNode<T>* node, BTreeNode<T>*& pre)
{
if( node != NULL )
{
inOrderThread(node->left, pre);
node->left = pre;
if( pre != NULL )
{
pre->right = node;
}
pre = node;
inOrderThread(node->right, pre);
}
}
template < typename T >
BTreeNode<T>* inOrderThread1(BTreeNode<T>* node)
{
BTreeNode<T>* pre = NULL;
inOrderThread(node, pre);
while( (node != NULL) && (node->left != NULL) )
{
node = node->left;
}
return node;
} 测试代码如下
int main()
{
BTreeNode<int>* ns = createTree<int>();
printInOrder(ns);
cout << endl;
ns = inOrderThread1(ns);
printDualList(ns);
return 0;
}运行结果如下
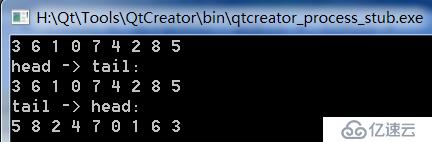
b> 中序遍历的结案次序正好是结点的水平次序
思路:使用辅助指针,指向转换后双向链表的头结点和尾结点;跟结点与左右子树转换的双向链表连接,成为完整的双向链表。
示例如下
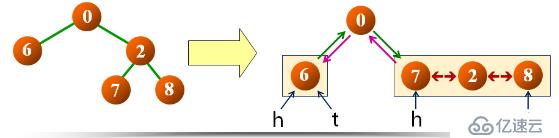
定义功能:inOrderThread(node, head, tail); node 为根结点,也是中序访问的结点;head 为转换成功后指向双向链表的首结点;tail 为转换成功后指向双向链表的尾结点。
实现思路如下

具体源码实现
template < typename T >
void inOrderThread(BTreeNode<T>* node, BTreeNode<T>*& head, BTreeNode<T>*& tail)
{
if( node != NULL )
{
BTreeNode<T>* h = NULL;
BTreeNode<T>* t = NULL;
inOrderThread(node->left, h, t);
node->left = t;
if( t != NULL )
{
t->right = node;
}
head = (h != NULL) ? h : node;
h = NULL;
t = NULL;
inOrderThread(node->right, h, t);
node->right = h;
if( h != NULL )
{
h->left = node;
}
tail = (t != NULL) ? t : node;
}
}
template < typename T >
BTreeNode<T>* inOrderThread2(BTreeNode<T>* node)
{
BTreeNode<T>* head = NULL;
BTreeNode<T>* tail = NULL;
inOrderThread(node, head, tail);
return head;
}测试代码
int main()
{
BTreeNode<int>* ns = createTree<int>();
printInOrder(ns);
cout << endl;
ns = inOrderThread2(ns);
printDualList(ns);
return 0;
}运行结果如下
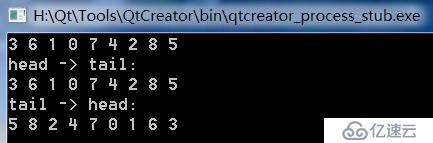
我们看到两中算法的遍历结果是一样的。关于二叉树的面试题分析,我们就到这了,后面继续学习相关的数据结构。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。