这篇文章给大家分享的是有关JS对象之浅克隆和深克隆的案例分析的内容。小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考。一起跟随小编过来看看吧。
浅克隆
先看代码:
/**
* 浅克隆 克隆传入对象,只克隆一层
* @param {any} source
*/
function shallowClone(source) {
var tiaget = createEctype(source); //创建一个副本
// 将原对象的所有属性值赋值到新对象上
for (var property in source) {
if (source.hasOwnProperty(property)) {
tiaget[property] = source[property];
}
}
/**
* 创建副本
* @param {any} source
*/
function createEctype(source) {
var newObject = {};
if (Array.isArray(source))
newObject = [];
return newObject;
}
return tiaget;
}执行测试:
var a={a1:1,a2:2,a3:[1,2,3]};
var b={b1:1,b2:2,b3:[4,5,6]}
a.b=b;
b.a=a;
a.a4=[a,b];
b.b4=[a,b];
a.fn=function(){console.log(this.b);};
var newa=shallowClone(a);测试代码定义了一个自我引用的对象
a===a.a4[0]; // true
a===a.b.a; // true执行 shallowClone 方法获得了一个对象a的副本 newa
a === newa; // false
newa === newa.a4[0]; // false
newa === newa.b.a; // false
a === newa.a4[0]; // true
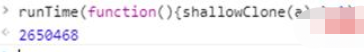
a === newa.b.a; // true测试执行速度:
/**
获取传入方法在规定时间内执行次数
示例:
var test = function(){
};
runTime(test,1)
表示test方法 在1秒中执行了6819005次
**/
/**
* 获取传入方法在规定时间内执行次数
* @param {any} fn 执行的方法
* @param {any} time 规定的时间,单位为秒
*/
function runTime(fn, time) {
var startTime = Date.now();
var count = 0;
while (Date.now() - startTime < time * 1000) {
fn.call();
count++;
}
return count;
}
深度克隆
代码:
/**
* 深克隆
*
* 示例:
* var a={a1:1,a2:2,a3:[1,2,3]};
* var b={b1:1,b2:2,b3:[4,5,6]}
* a.b=b;
* b.a=a;
* a.a4=[a,b];
* b.b4=[a,b];
* a.fn=function(){console.log(this.b);return this.b;};
*
* var newa=deepClone(a);
* newa.a1=123;
* newa.fn();
*/
function deepClone(source) {
this.objKeyCache = []; // 对象缓存
this.objValueCache = []; // 对象克隆缓存
this.clone = function (source) {
var target = createEctype.call(this, source);
for (var property in source) {
if (source.hasOwnProperty(property)) {
var value = source[property];
if (typeof value === "number"
|| typeof value === "boolean"
|| typeof value === "symbol"
|| typeof value === "string"
|| typeof value === "function"
|| typeof value === "undefined"
|| value === null)
target[property] = value;
else if (typeof value === "object") {
// 如果源对象在对象缓存中存在,就用对象克隆缓存中的值赋值
var index = this.objKeyCache.indexOf(value);
if (index >= 0)
target[property] = this.objValueCache[index];
else {
target[property] = this.clone( value);
}
}
else
throw "未知数据类型" + (typeof value);
}
}
return target;
};
/**
* 创建副本
* @param {any} source
*/
function createEctype(source) {
var target = {};
if (Array.isArray(source))
target = [];
this.objKeyCache.push(source);
this.objValueCache.push(target);
return target;
}
var newObject = this.clone(source);
// 释放缓存,防止内存溢出
this.objKeyCache = [];
this.objValueCache = [];
return newObject;
}执行测试:
var a={a1:1,a2:2,a3:[1,2,3]};
var b={b1:1,b2:2,b3:[4,5,6]}
a.b=b;
b.a=a;
a.a4=[a,b];
b.b4=[a,b];
a.fn=function(){console.log(this.b);return this.b;};
var newa=deepClone(a);a === newa; // false
newa === newa.a4[0] // true
newa === newa.b.a; // true
a === newa.a4[0]; // false
a === newa.b.a; // false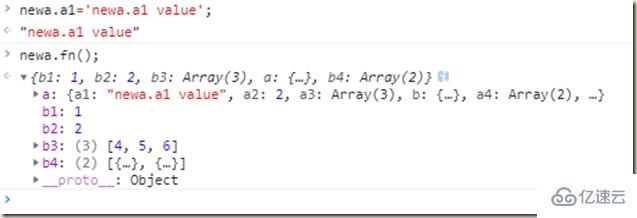
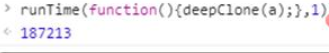
测试执行速度:
感谢各位的阅读!关于JS对象之浅克隆和深克隆的案例分析就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,让大家可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到吧!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。