导入自定义镜像时选择Customized Linux的方法?这个问题可能是我们日常学习或工作经常见到的。希望通过这个问题能让你收获颇深。下面是小编给大家带来的参考内容,让我们一起来看看吧!
定制 Linux 自定义镜像
当您的镜像操作系统不在阿里云所支持的已有平台类型中,亦不能安装 cloud-init 时,您可以在导入自定义镜像时选择 Customized Linux(定制版镜像)。阿里云将定制版 Linux 镜像当作无法识别的操作系统类型,缺少初次启动ECS实例时所必要的标准配置信息,需要您导入镜像前根据本文描述在定制版镜像中添加解析脚本,便于初次启动时自动化配置实例。
限制条件
Customized Linux 镜像的第一个分区必须可以被写入。
Customized Linux 镜像的第一个分区类型支持 FAT32、EXT2、EXT3、EXT4 或 UFS。
Customized Linux 镜像的虚拟文件大小必须大于 5 GiB。
Customized Linux 镜像有如下安全要求:
不能存在可被远程利用的高危漏洞。
使用控制台的 管理终端 登录实例时,如果存在初始默认密码,必须在首次登录时修改,修改密码之前不允许进入实例做任何操作。
不支持默认 SSH 密钥对,初始 SSH 密钥对必须由阿里云随机生成。
配置方法
在镜像的第一个分区的根目录下新建目录 aliyun_custom_image。
使用该 Customized Linux 镜像所创建的实例初次启动时,阿里云会在 aliyun_custom_image 目录的 os.conf 文件中写入实例相关配置信息。如果不存在 os.conf 文件,系统则自动创建。
在镜像中创建一份解析脚本,用以解析 os.conf 文件的系统配置。参阅 解析脚本注意事项 和 解析脚本示例编写脚本。
os.conf 文件示例
经典网络类型实例
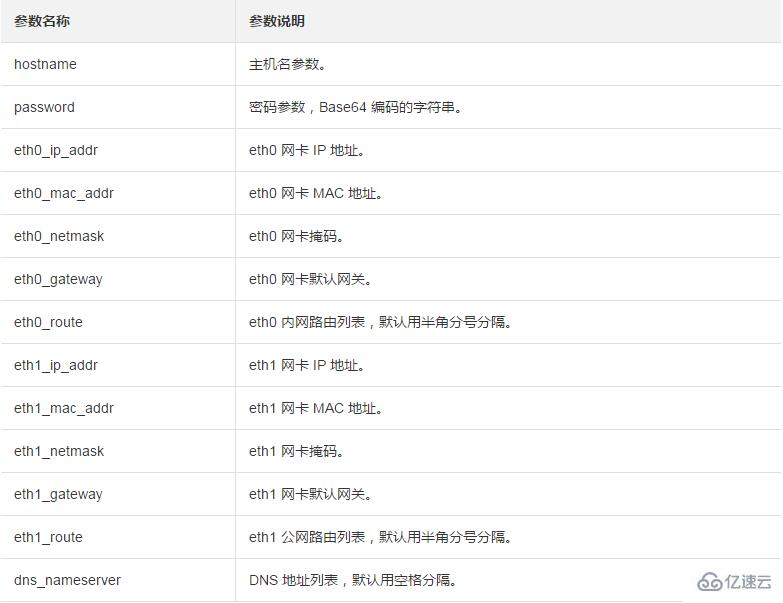
hostname=iZ23r29djmjZ
password=cXdlcjEyMzQK
eth0_ip_addr=10.171.254.123
eth0_mac_addr=00:8c:fa:5e:14:23
eth0_netmask=255.255.255.0
eth0_gateway=10.171.254.1
eth0_route="10.0.0.0/8 10.171.254.1;172.16.0.0/12 10.171.254.1"
eth2_ip_addr=42.120.74.105
eth2_mac_addr=00:8c:fa:5e:14:24
eth2_netmask=255.255.255.0
eth2_gateway=42.120.74.1
eth2_route="0.0.0.0/0 42.120.74.1"
dns_nameserver="7.7.7.7 8.8.8.8"参数说明如下表所示:
专有网络 VPC 类型实例
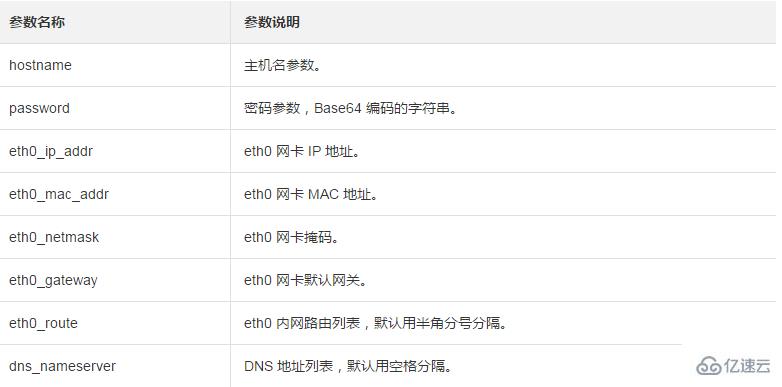
hostname=iZ23r29djmjZ
password=cXdlcjEyMzQK
eth0_ip_addr=10.171.254.123
eth0_mac_addr=00:8c:fa:5e:14:23
eth0_netmask=255.255.255.0
eth0_gateway=10.171.254.1
eth0_route="0.0.0.0/0 10.171.254.1"
dns_nameserver="7.7.7.7 8.8.8.8"参数说明如下表所示:
解析脚本注意事项
实例初次启动时,正常情况下阿里云自动将配置项的相关信息写入第一个分区的根目录下 aliyun_custom_image 目录的 os.conf 文件中。配置 Customized Linux 镜像必须要在镜像中创建预定义解析脚本,用以从 os.conf 文件中读取实例配置信息并完成实例配置。以下为解析脚本需要满足的条件。
开机启动:解析脚本需要设置成开机自启动,例如,将解析脚本存放在 /etc/init.d/ 目录下。
配置项取值规则:如 os.conf 文件示例 的配置项所述,VPC 与经典网络实例的配置项数量和部分配置项的取值规则均有所不同。
配置文件读取路径:Customized Linux 镜像在创建 I/O 优化实例或非 I/O 优化实例时,为第一个分区所分配的设备名默认不一样。所以在解析脚本中最好可以用 uuid 或 label 识别第一个分区的设备。用户密码为 Base64 编码的字符串,设置密码时需要做相关处理。
判断 VPC 或经典网络:解析脚本判断该网络类型时,可以查看是否存在 eth2_route 或其他 eth2 相关的配置项。判断出当前实例的网络类型后再有针对性地解析和处理。
VPC 类型实例在 os.conf 文件的 eth0_route 参数中配置默认公网路由。
经典网络类型实例在 os.conf 文件的 eth2_route 参数中配置默认公网路由,内网路由配置在 eth0_route 中。
配置优化:os.conf 文件中的配置在实例的整个生命周期中执行一次即可,解析脚本执行成功后建议删除 os.conf 文件。同时解析脚本如果没有读取到 os.conf 文件配置,则不执行文件中的配置。
自定义镜像处理:根据 Customized Linux 镜像创建的实例再制作自定义镜像时,镜像中也会包含这个开机启动脚本。阿里云会在实例第一次启动时写入 os.conf 配置,解析脚本在检测到该配置时即可执行相关配置。
修改相关配置时的处理:当实例的配置信息通过阿里云的控制台或 API 发生变更时,阿里云将相关信息写入到 os.conf 文件中,解析脚本将被再次执行从而下发这些更改。
解析脚本示例
以下为以 CentOS 操作系统为例的解析脚本示例,仅供参考,您需要根据实际的操作系统类型调整脚本内容。在使用脚本前,务必在镜像中调试脚本,并保证调试通过。
#!/bin/bash
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: os-conf
# Required-Start: $local_fs $network $named $remote_fs
# Required-Stop:
# Should-Stop:
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: The initial os-conf job, config the system.
### END INIT INFO
first_partition_dir='/boot/'
os_conf_dir=${first_partition_dir}/aliyun_custom_image
os_conf_file=${os_conf_dir}/os.conf
load_os_conf() {
if [[ -f $os_conf_file ]]; then
. $os_conf_file
return 0
else
return 1
fi
}
cleanup() {
# ensure $os_conf_file is deleted, to avoid repeating config system
rm $os_conf_file >& /dev/null
# ensure $os_conf_dir is exitst
mkdir -p $os_conf_dir
}
config_password() {
if [[ -n $password ]]; then
password=$(echo $password | base64 -d)
if [[ $? == 0 && -n $password ]]; then
echo "root:$password" | chpasswd
fi
fi
}
config_hostname() {
if [[ -n $hostname ]]; then
sed -i "s/^HOSTNAME=.*/HOSTNAME=$hostname/" /etc/sysconfig/network
hostname $hostname
fi
}
config_dns() {
if [[ -n $dns_nameserver ]]; then
dns_conf=/etc/resolv.conf
sed -i '/^nameserver.*/d' $dns_conf
for i in $dns_nameserver; do
echo "nameserver $i" >> $dns_conf
done
fi
}
is_classic_network() {
# vpc: eth0
# classic: eth0 eth2
grep -q 'eth2' $os_conf_file
}
config_network() {
/etc/init.d/network stop
config_interface eth0 ${eth0_ip_addr} ${eth0_netmask} ${eth0_mac_addr}
config_route eth0 ${eth0_route}
if is_classic_network ; then
config_interface eth2 ${eth2_ip_addr} ${eth2_netmask} ${eth2_mac_addr}
config_route eth2 ${eth2_route}
fi
/etc/init.d/network start
}
config_interface() {
local interface=$1
local ip=$2
local netmask=$3
local mac=$4
inteface_cfg="/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-${interface}"
cat << EOF > $inteface_cfg
DEVICE=$interface
IPADDR=$ip
NETMASK=$netmask
HWADDR=$mac
ONBOOT=yes
BOOTPROTO=static
EOF
}
config_default_gateway() {
local gateway=$1
sed -i "s/^GATEWAY=.*/GATEWAY=$gateway/" /etc/sysconfig/network
}
config_route() {
local interface=$1
local route=$2
route_conf=/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-${interface}
> $route_conf
echo $route | sed 's/;/\n/' | \
while read line; do
dst=$(echo $line | awk '{print $1}')
gw=$(echo $line | awk '{print $2}')
if ! grep -q "$dst" $route_conf 2> /dev/null; then
echo "$dst via $gw dev $interface" >> $route_conf
fi
if [[ "$dst" == "0.0.0.0/0" ]]; then
config_default_gateway $gw
fi
done
}
################## sysvinit service portal ####################
start() {
if load_os_conf ; then
config_password
config_network
config_hostname
config_dns
cleanup
return 0
else
echo "not load $os_conf_file"
return 0
fi
}
RETVAL=0
case "$1" in
start)
start
RETVAL=$?
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start}"
RETVAL=3
;;
esac
exit $RETVAL感谢各位的阅读!看完上述内容,你们对导入自定义镜像时选择Customized Linux的方法大概了解了吗?希望文章内容对大家有所帮助。如果想了解更多相关文章内容,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。