参见:http://www.cnblogs.com/leiOOlei/p/3725911.html
参见:http://www.cnblogs.com/aurawing/articles/1887030.html
简单说一下new和nested的区别。
使用new的时候,外层事务的提交或回滚,与new的事务没有关系。而使用nested时,内层事务最终是提交还是回滚,需要依赖于外层事务。参见下表。
| 事务传播配置 | 外层事务(set a=1) | 内层事务(set b=2) | 最终结果 |
|---|---|---|---|
| new | 提交 | 提交 | a=1 && b=2 |
| new | 提交 | 回滚 | a=1 |
| new | 回滚 | 提交 | b=2 |
| new | 回滚 | 回滚 | 什么都不变 |
| nested | 提交 | 提交 | a=1 && b=2 |
| nested | 提交 | 回滚 | a=1(这种情况需要增加一个配置:<property name="globalRollbackOnParticipationFailure" value="false" />) |
| nested | 回滚 | 提交 | 什么都不变 |
| nested | 回滚 | 回滚 | 什么都不变 |
参见:Isolation Level(事务隔离等级):
我们知道并行可以提高数据库的吞吐量和效率,但是并不是所有的并发事务都可以并发运行,这需要查看数据库教材的可串行化条件判断了。
这里就不阐述了。
我们首先说并发中可能发生的3中不讨人喜欢的事情
| -- | Dirty reads | non-repeatable reads | phantom reads |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serializable | 不会 | 不会 | 不会 |
| REPEATABLE READ | 不会 | 不会 | 会 |
| READ COMMITTED | 不会 | 会 | 会 |
| Read Uncommitted | 会 | 会 | 会 |
| DEFALT(使用底层数据库的默认隔离级别) | ? | ? | ? |
标记事务只读。只读事务会被优化;但是“只读”事务中其实可以写数据。
事务超时时间
标记哪些异常会引发回滚。默认情况下,所有RuntimeException都会引发回滚;所有其它异常(checked-exception)都不引发回滚。如果需要针对某种checked-exception进行回滚,则需要为事务配置rollbackFor或者rollbackForClassName
标记哪些异常不会引发回滚。默认情况下,所有RuntimeException都会引发回滚;所有其它异常(checked-exception)都不引发回滚。如果需要使得某种RuntimeException不进行回滚,则需要为事务配置noRollbackFor/noRollbackForClassName。
无论配置方式,还是注解方式,spring都是基于spring aop来进行事务管理。
即,在事务切入点处,生成一个动态代理。在代理中管理事务(开启、传播、提交或回滚等)。可参见下面两张图: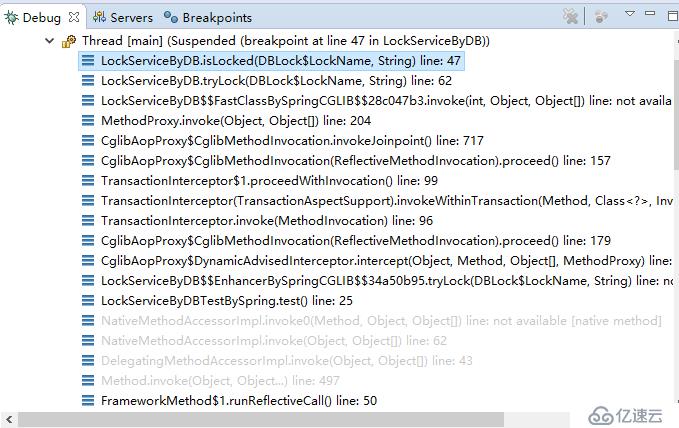
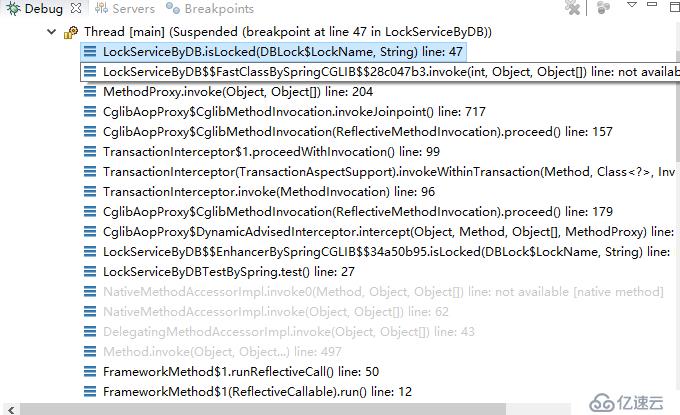
两张图都是调用isLocked()方法时的线程栈。可以看到,第二章图是通过动态代理来调用isLocked()方法的,而第一张图则不是。
动态代理的方式简化了代码的开发;但是也引入了一些小问题。后面会提。
spring会将事务相关的有状态数据(数据库连接、hibernate的session等)放在线程上下文中(ThreadLocal)。因此,事务间的传播关系、事务开启和关闭的时机,与线程中的方法调用栈很相似。
另外,由于事务与线程相关,因此目前spring的事务管理无法让多个子线程在同一事务内运行。
首先来看看如何确定运行时是否使用了事务、事务是如何传播的。
首先在log4j中加入以下配置。严格说只要记录了org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager的日志即可。另一个logger是为了记录SQL的,也可以将它替换成其它logger。
<Logger name="org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager" level="DEBUG" additivity="false">
<AppenderRef ref="Console" />
<AppenderRef ref="AuditAsyncAppender" />
</Logger>
<Logger name="org.hibernate.SQL" level="TRACE" additivity="false">
<AppenderRef ref="Console" />
<AppenderRef ref="AuditAsyncAppender" />
</Logger>然后运行事务相关代码:
@Testpublic void test() {
// 这个方法使用默认的传播方式(REQUIRED)
this.lockServiceByDB.tryLock(LockName.EVENT_LOAN, "23424");
// 这个方法使用REQUIRES_NEW的传播方式
this.lockServiceByDB.isLocked(LockName.EVENT_LOAN, "23424");
}可以找到如下日志:
2016-07-06 18:01:10,969 DEBUG AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.getTransaction Creating new transaction with name[cn.youcredit.thread.bizaccount.service.impl.LockServiceByDBTestBySpring.test]: PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,ISOLATION_DEFAULT; '',-cn.youcredit.thread.common.exception.ServiceException
【中略】
2016-07-06 18:01:11,297 DEBUG AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.handleExistingTransaction Participating in existing transaction
2016-07-06 18:01:11,309 DEBUG SqlStatementLogger.logStatement
select count(1) as col_00 from dblocks dblock0 where dblock0.lockName=? and dblock0.uniKey=?
2016-07-06 18:01:11,325 DEBUG SqlStatementLogger.logStatement
insert into db_locks (lockName, lockTimeAsLong, uniKey) values (?, ?, ?)
【中略】
2016-07-06 18:01:11,331 DEBUG AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.handleExistingTransaction Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [cn.youcredit.thread.bizaccount.service.impl.LockServiceByDB.isLocked]
【中略】
2016-07-06 18:01:11,335 DEBUG SqlStatementLogger.logStatement
select count(1) as col_00 from dblocks dblock0 where dblock0.lockName=? and dblock0.uniKey=?
2016-07-06 18:01:11,337 DEBUG AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.processCommit Initiating transaction commit
2016-07-06 18:01:11,337 DEBUG HibernateTransactionManager.doCommit Committing Hibernate transaction on Session [SessionImpl(PersistenceContext[entityKeys=[],collectionKeys=[]];ActionQueue[insertions=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@1a9ea4d9 updates=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@59ca0db6 deletions=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@33293dac orphanRemovals=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@384841e3 collectionCreations=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@571f925f collectionRemovals=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@5eb192b7 collectionUpdates=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@248f1090 collectionQueuedOps=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@5eb20abb unresolvedInsertDependencies=UnresolvedEntityInsertActions[]])]
【中略】
2016-07-06 18:01:11,339 DEBUG AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.cleanupAfterCompletion Resuming suspended transaction after completion of inner transaction
2016-07-06 18:01:11,340 DEBUG AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.proce***ollback Initiating transaction rollback
2016-07-06 18:01:11,340 DEBUG HibernateTransactionManager.doRollback Rolling back Hibernate transaction on Session [SessionImpl(PersistenceContext[entityKeys=[EntityKey[cn.youcredit.thread.common.model.auth.UserInfo#system], EntityKey[cn.youcredit.thread.bizaccount.bean.DBLock#139], EntityKey[cn.youcredit.thread.common.model.auth.UserGroupInfo#500]],collectionKeys=[]];ActionQueue[insertions=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@2f90ad92 updates=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@4710332d deletions=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@7930de44 orphanRemovals=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@52891a77 collectionCreations=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@785fd189 collectionRemovals=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@3e900cf4 collectionUpdates=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@412d379c collectionQueuedOps=org.hibernate.engine.spi.ExecutableList@5b6dc76c unresolvedInsertDependencies=UnresolvedEntityInsertActions[]])]
从日志中可以清楚的看到事务操作、传播的过程:
spring的事务注解只对public方法生效,对protcted、friendly(默认)、private方法无效。如果在后面这些方法上标记事务注解,其效果等于没有标记。
Java注解的基本继承关系如下。spring的Transactional注解上有Inherited的元注解。
| - | 未写@Inherited: | 写了@Inherited的 |
|---|---|---|
| 子类的类上能否继承到父类的类上的注解? | 否 | 能 |
| 子类方法,实现了父类上的抽象方法,这个方法能否继承到注解? | 否 | 否 |
| 子类方法,继承了父类上的方法,这个方法能否继承到注解? | 能 | 能 |
| 子类方法,覆盖了父类上的方法,这个方法能否继承到注解? | 否 | 否 |
例如下面的代码中,虽然Son在类级别上声明了事务,但是它的tryLocked()方法并不会启动新的事务。因为它在父类中没有声明事务。
public class Father{
public void tryLocked(){}
}
@Transactional(REQUIRES_NEW)
public class Son extends Father{
}对于spring aop的动态代理来说,被代理实例和方法是一个“黑盒”。只有在“黑盒”之外才能进行事务管理。而this调用是黑盒内部的调用逻辑,代理无法感知。
因此,像下文这样的代码中,isLocked()方法并不会启动新的事务。
@Transactional(REQUIRES_NEW)
public void isLocked(){
……
}
@Transactional()
public void tryLock(){
this.isLocked();
……
}虽然查询操作并不更新数据,但是查询也需要事务。尤其对hibernate来说。
hibernate操作数据库时,需要获取到一个hibernate的session。而这个session也由HibernateTransactionManager来管理。管理的方式与其它有状态数据一样,都是放在ThreadLocal中。如果线程上没有事务管理器,那么就拿不到session。hibernate做查询时就会报错:
org.hibernate.HibernateException: Could not obtain transaction-synchronized Session for current thread
at org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.SpringSessionContext.currentSession(SpringSessionContext.java:134) ~[spring-orm-4.2.2.RELEASE.jar:4.2.2.RELEASE]
有时候明明没有写事务注解,也能执行查询,那么多半是在某个地方默认、或者“偷偷”开了事务。比如继承SpringTestCase的单元测试会默认开启事务。或者web环境下,线程池中的线程上遗留了以前绑定的事务管理器。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。