这篇文章主要介绍了python中tkinter图形界面代码统计工具的示例分析,具有一定借鉴价值,感兴趣的朋友可以参考下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后大有收获,下面让小编带着大家一起了解一下。
具体内容如下
#encoding=utf-8
import os,sys,time
from collections import defaultdict
from tkinter import *
import tkinter.messagebox
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter import scrolledtext
root= Tk()
root.title("有效代码统计工具") #界面的title
def code_count(path,file_types):
if os.path.exists(path):
os.chdir(path)
else:
#messagebox.showwarning("您输入的路径不存在!")
print("您输入的路径不存在!")
#sys.exit()
files_path=[]
file_types=file_types.split()
line_count=0
space_count=0
annotation_count=0
file_lines_dict=dict()
for root,dirs,files in os.walk(path):
for f in files:
files_path.append(os.path.join(root,f))
for file_path in files_path:
#print(os.path.splitext(file_path)[1][1:])
file_type=os.path.splitext(file_path)[1][1:]
if file_type in file_types:
if file_type.lower()=="java":
line_num,space_num,annotation_num=count_javafile_lines(file_path)
line_count+=line_num
space_count+=space_num
annotation_count+=annotation_num
file_lines_dict[file_path]=line_num,space_num,annotation_num
if file_type.lower()=="py":
line_num,space_num,annotation_num=count_py_lines(file_path)
line_count+=line_num
space_count+=space_num
annotation_count+=annotation_num
file_lines_dict[file_path]=line_num,space_num,annotation_num
#file_info=file_show(line_num,space_num,annotation_num)
#print(file_info[0])
return line_count,file_lines_dict,space_count,annotation_count
def count_py_lines(file_path):
line_count = 0
space_count=0
annotation_count=0
flag =True
try:
fp = open(file_path,"r",encoding="utf-8")
encoding_type="utf-8"
for i in fp:
pass
fp.close()
except:
#print(file_path)
encoding_type="gbk"
with open(file_path,"r",encoding=encoding_type,errors="ignore") as fp:
#print(file_path)
"""try:
fp.read()
except:
fp.close()"""
for line in fp:
if line.strip() == "":
space_count+=1
else:
if line.strip().endswith("'''") and flag == False:
annotation_count+=1
#print(line)
flag = True
continue
if line.strip().endswith('"""') and flag == False:
annotation_count+=1
#print('结尾双引',line)
flag = True
continue
if flag == False:
annotation_count+=1
#print("z",line)
continue
"""if flag == False:
annotation_count+=1
print("z",line)"""
if line.strip().startswith("#encoding") \
or line.strip().startswith("#-*-"):
line_count += 1
elif line.strip().startswith('"""') and line.strip().endswith('"""') and line.strip() != '"""':
annotation_count+=1
#print(line)
elif line.strip().startswith("'''") and line.strip().endswith("'''") and line.strip() != "'''":
annotation_count+=1
#print(line)
elif line.strip().startswith("#"):
annotation_count+=1
#print(line)
elif line.strip().startswith("'''") and flag == True:
flag = False
annotation_count+=1
#print(line)
elif line.strip().startswith('"""') and flag == True:
flag = False
annotation_count+=1
#print('开头双引',line)
else:
line_count += 1
return line_count,space_count,annotation_count
#path=input("请输入您要统计的绝对路径:")
#file_types=input("请输入您要统计的文件类型:")
#print("整个%s有%s类型文件%d个,共有%d行代码"%(path,file_types,len(code_dict),codes))
#print("代码最多的是%s,有%d行代码"%(max_code[1],max_code[0]))
def count_javafile_lines(file_path):
line_count = 0
space_count=0
annotation_count=0
flag =True
#read_type=''
try:
fp = open(file_path,"r",encoding="utf-8")
encoding_type="utf-8"
for i in fp:
pass
fp.close()
except:
#print(file_path)
encoding_type="gbk"
with open(file_path,"r",encoding=encoding_type) as fp:
#print(file_path)
for line in fp:
if line.strip() == "":
space_count+=1
else:
if line.strip().endswith("*/") and flag == False:
flag = True
annotation_count+=1
continue
if flag == False:
annotation_count+=1
continue
elif line.strip().startswith('/*') and line.strip().endswith('*/'):
annotation_count+=1
elif line.strip().startswith('/**') and line.strip().endswith('*/'):
annotation_count+=1
elif line.strip().startswith("//") and flag == True:
flag = False
continue
else:
line_count += 1
return line_count,space_count,annotation_count
def show(): #当按钮被点击,就调用这个方法
pathlist=e1.get() #调用get()方法得到在文本框中输入的内容
file_types=e2.get().lower()
file_types_list=["py","java"]
if not pathlist:
tkinter.messagebox.showwarning('提示',"请输入文件路径!")
return None
if not file_types:
tkinter.messagebox.showwarning('提示',"请输入要统计的类型!")
return None
#print(type(file_types),file_types)
if '\u4e00'<=file_types<='\u9fa5' or not file_types in file_types_list: #判断文件类型输入的是否是中文
tkinter.messagebox.showwarning('错误',"输入统计类型有误!")
return None
text.delete(1.0,END) #删除显示文本框中,原有的内容
for path in pathlist.split(";"):
path=path.strip()
codes,code_dict,space,annotation=code_count(path,file_types) #将函数返回的结果赋值给变量,方便输出
max_code=max(zip(code_dict.values(),code_dict.keys()))
#print(codes,code_dict)
#print("整个%s有%s类型文件%d个,共有%d行代码"%(path,file_types,len(code_dict),codes))
#print("代码最多的是%s,有%d行代码"%(max_code[1],max_code[0]))
for k,v in code_dict.items():
text.insert(INSERT,"文件%s 有效代码数%s\n"%(k,v[0])) #将文件名和有效代码输出到文本框中
text.insert(INSERT,"整个%s下有%s类型文件%d个,共有%d行有效代码\n"%(path,file_types,len(code_dict),codes)) #将结果输出到文本框中
text.insert(INSERT,"共有%d行注释\n"%(annotation))
text.insert(INSERT,"共有%d行空行\n"%(space))
text.insert(INSERT,"代码最多的是%s,有%s行有效代码\n\n"%(max_code[1],max_code[0][0]))
frame= Frame(root) #使用Frame增加一层容器
frame.pack(padx=50,pady=40) #设置区域
label= Label(frame,text="路径:",font=("宋体",15),fg="blue").grid(row=0,padx=10,pady=5,sticky=N) #创建标签
label= Label(frame,text="类型:",font=("宋体",15),fg="blue").grid(row=1,padx=10,pady=5)
e1= Entry(frame,foreground = 'blue',font = ('Helvetica', '12')) #创建文本输入框
e2= Entry(frame,font = ('Helvetica', '12', 'bold'))
e1.grid(row=0,column=1,sticky=W) #布置文本输入框
e2.grid(row=1,column=1,sticky=W,)
labeltitle=Label(frame,text="输入多个文件路径请使用';'分割",font=("宋体",10,'bold'),fg="red")
labeltitle.grid(row=2,column=1,sticky=NW)
frame.bind_all("<F1>",lambda event:helpinf())
frame.bind_all("<Return>",lambda event:show())
frame.bind_all("<Alt-F4>",lambda event:sys.exit())
frame.bind_all("<Control-s>",lambda event:save())
#print(path,file_types)
hi_there= Button(frame ,text=" 提交 ",font=("宋体",13),width=10,command=show).grid(row=3,column=0,padx=15,pady=5) #创建按钮
hi_there= Button(frame ,text=" 退出 ",font=("宋体",13),width=10,command=root.quit).grid(row=3,column=1,padx=15,pady=5)
#self.hi_there.pack()
text = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(frame,width=40,height=10,font=("宋体",15)) #创建可滚动的文本显示框
text.grid(row=4,column=0,padx=40,pady=15,columnspan=2) #放置文本显示框
def save():
#print(text.get("0.0","end"))
if not text.get("0.0","end").strip(): #获取文本框内容,从开始到结束
tkinter.messagebox.showwarning('提示',"还没有统计数据!")
return None
savecount=''
nowtime=time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()) #获取当前时间并格式化输出
savecount=nowtime+"\n"+text.get("0.0","end")
with open("e:\\save.txt",'w') as fp:
fp.write(savecount)
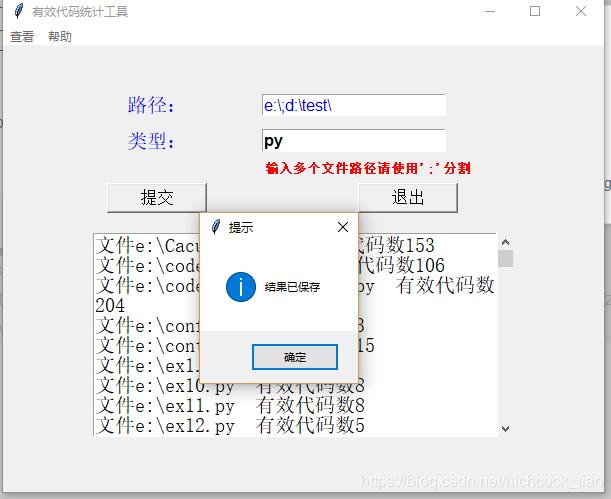
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示',"结果已保存")
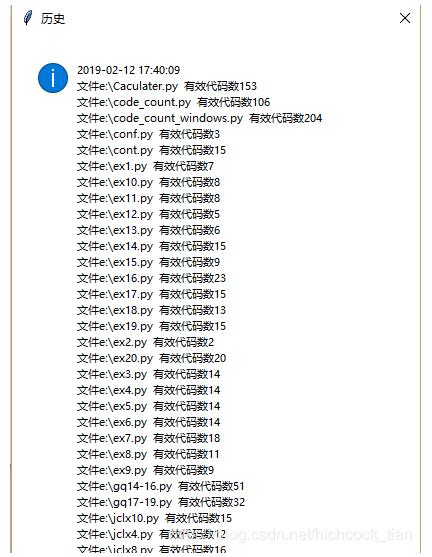
def history():
if os.path.exists("e:\\save.txt"):
with open("e:\\save.txt",'r') as fp:
historytxt=fp.read()
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('历史',historytxt)
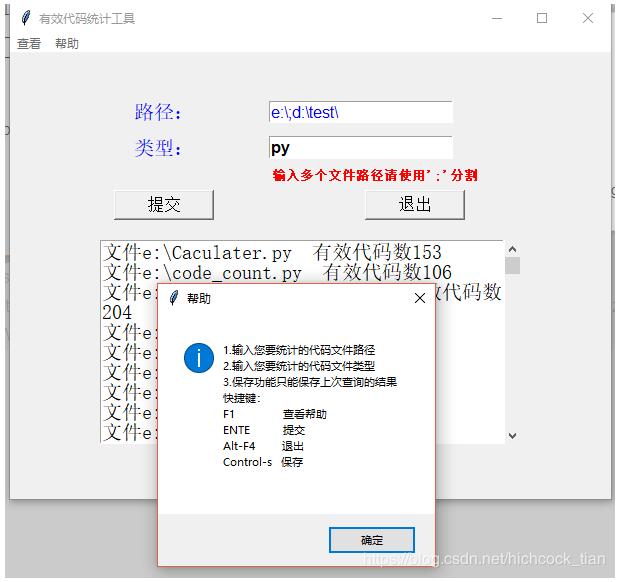
def helpinf():
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('帮助',"""1.输入您要统计的代码文件路径
2.输入您要统计的代码文件类型
3.保存功能只能保存上次查询的结果
快捷键:
F1 查看帮助
ENTE 提交
Alt-F4 退出
Control-s 保存
""")
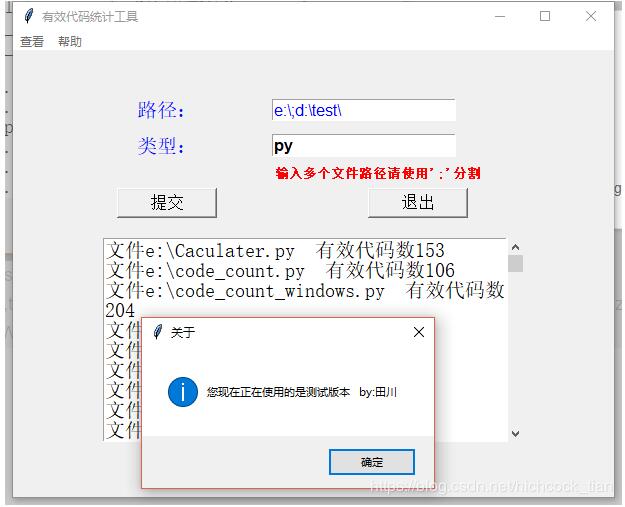
def aboutinf():
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('关于',"您现在正在使用的是测试版本 by:田川")
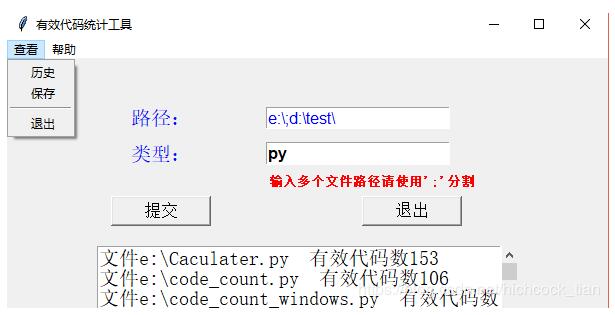
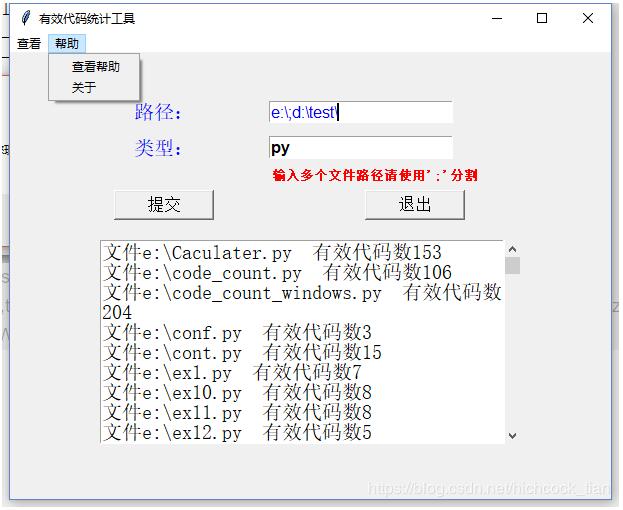
menu=Menu(root)
submenu1=Menu(menu,tearoff=0)
menu.add_cascade(label='查看',menu=submenu1)
submenu1.add_command(label='历史',command=history)
submenu1.add_command(label='保存',command=save)
submenu1.add_separator()
submenu1.add_command(label='退出', command=root.quit)
submenu2=Menu(menu,tearoff=0)
menu.add_cascade(label='帮助',menu=submenu2)
submenu2.add_command(label='查看帮助',command=helpinf)
submenu2.add_command(label='关于',command=aboutinf)
root.config(menu=menu)
#以上都是菜单栏的设置
"""
def caidan(root):
menu=tkinter.Menu(root)
submenu1=tkinter.Menu(menu,tearoff=0)
menu.add_cascade(label='查看',menu=submenu1)
submenu2 = tkinter.Menu(menu, tearoff=0)
submenu2.add_command(label='复制')
submenu2.add_command(label='粘贴')
menu.add_cascade(label='编辑',menu=submenu2)
submenu = tkinter.Menu(menu, tearoff=0)
submenu.add_command(
='查看帮助')
submenu.add_separator()
submenu.add_command(label='关于计算机')
menu.add_cascade(label='帮助',menu=submenu)
root.config(menu=menu)
caidan(root)"""
root.mainloop() #执行tk!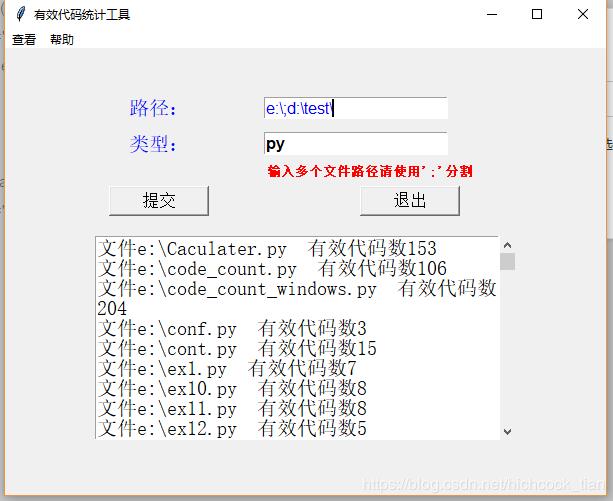
感谢你能够认真阅读完这篇文章,希望小编分享的“python中tkinter图形界面代码统计工具的示例分析”这篇文章对大家有帮助,同时也希望大家多多支持亿速云,关注亿速云行业资讯频道,更多相关知识等着你来学习!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。