жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
йҡҸзқҖдёҡеҠЎзҡ„йЈһйҖҹеҸ‘еұ•пјҢAPIжҺҘеҸЈи¶ҠжқҘи¶ҠеӨҡпјҢи·Ҝз”ұз®ЎзҗҶж–Ү件д»ҺеҮ еҚҒеҸ·еҸҳжҲҗеҮ зҷҫдёҠеҚғиЎҢпјҢдё”жҜҸж¬ЎдёҠж–°жңҚеҠЎпјҢйңҖиҰҒеңЁдҝ®ж”№и·Ҝз”ұж–Ү件代з ҒпјҢеёҰжқҘдёҖе®ҡзҡ„йЈҺйҷ©гҖӮ
еҲ¶е®ҡеҜ№еә”规еҲҷпјҢи·Ҝз”ұйҖҡиҝҮAPIж–Ү件еҗҚж №жҚ®дёҖе®ҡзҡ„规еҲҷеҜ№еә”зұ»еҗҚпјҢ然еҗҺиҮӘеҠЁеҜје…ҘеҜ№еә”е®һзҺ°зұ»пјҢжіЁеҶҢеҲ°WebжЎҶжһ¶дёӯгҖӮ
дёӢйқўиҝҷеҘ—规еҲҷеҸӘжҳҜе…¶дёӯдёҖз§Қж–№жЎҲпјҢеҸҜд»Ҙй’ҲеҜ№йЎ№зӣ®жғ…еҶөеҲ¶е®ҡеҜ№еә”зҡ„规еҲҷпјҢ然еҗҺе®һзҺ°зӣёе…ід»Јз ҒпјҢдҪҶжҳҜж•ҙдҪ“жҖқи·Ҝеҹәжң¬дёҖж ·гҖӮ
д»Јз Ғзӣ®еҪ•з»“жһ„пјҢеҲ—дёҖдёӢз®ҖеҚ•зҡ„йЎ№зӣ®ж–Ү件зӣ®еҪ•пјҢдёӢйқўд»ҘflaskжЎҶжһ¶дёәдҫӢ: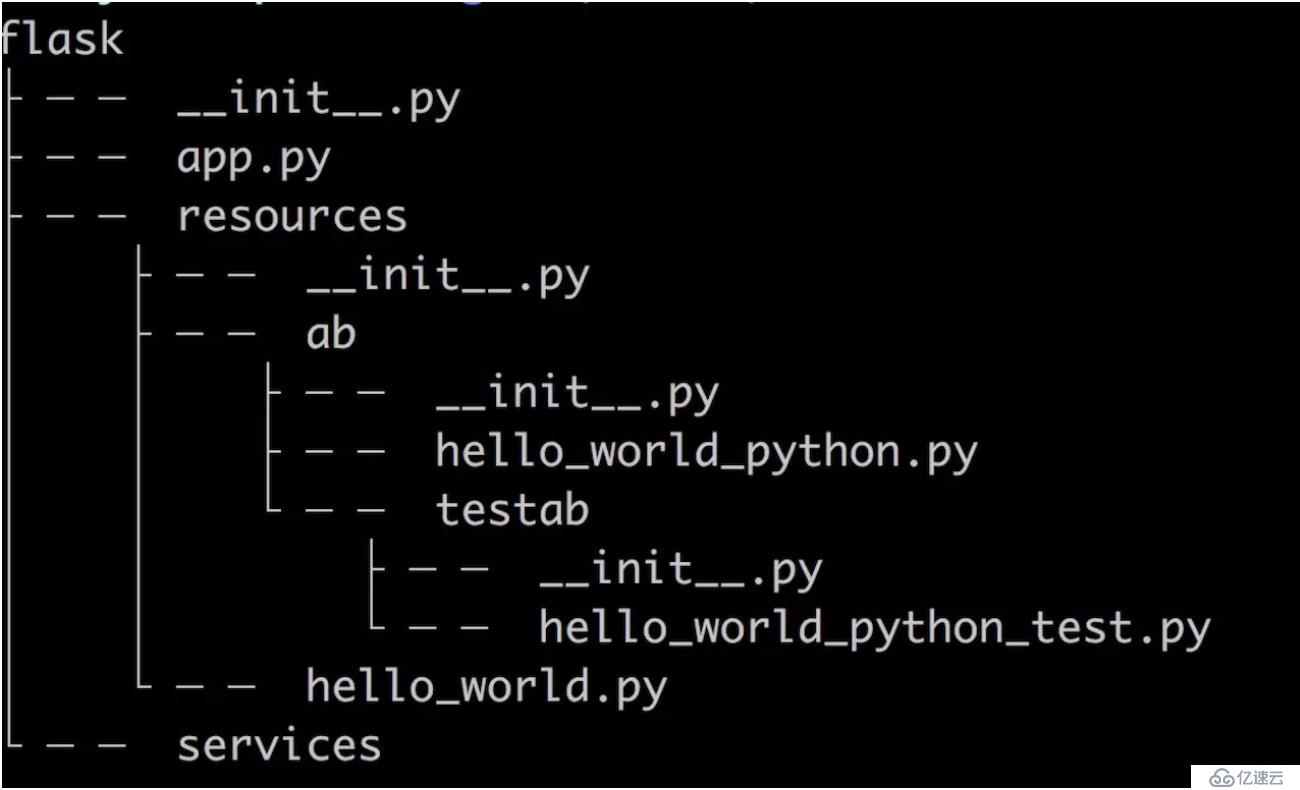
app.pyжҳҜеҗҜеҠЁж–Ү件гҖӮ
resourcesжҳҜAPIжҺҘеҸЈд»Јз Ғж–Ү件еӨ№гҖӮ
servicesжҳҜдёәAPIжҺҘеҸЈжңҚеҠЎзҡ„еҮҪж•°е°ҒиЈ…ж–Ү件еӨ№гҖӮ
еҰӮжһңйЎ№зӣ®иҝҳжңүдҫқиө–ж–Ү件пјҢд№ҹеҸҜд»ҘеҚ•зӢ¬еҶҚе»әе…¶д»–ж–Ү件еӨ№гҖӮ
йЎ№зӣ®зҡ„APIжҺҘеҸЈд»Јз ҒеқҮж”ҫеңЁresourcesж–Ү件еӨ№дёӢпјҢдё”жӯӨж–Ү件еӨ№еҸӘиғҪеҶҷжҺҘеҸЈAPIжңҚеҠЎд»Јз ҒгҖӮ
жҺҘеҸЈеҗҚз§°е‘ҪеҗҚд»Ҙ_иҝһжҺҘеҚ•иҜҚпјҢиҖҢеҜ№еә”ж–Ү件йҮҢзҡ„зұ»еҗҚж–Ү件еҗҚз§°зҡ„еҚ•иҜҚпјҢдёҚиҝҮжҚўжҲҗжҳҜй©јеі°еҶҷжі•гҖӮ
规еҲҷдёҫдҫӢеҰӮдёӢпјҡ
еҰӮдёҠеӣҫпјҢresourcesдёӢжңүдёҖдёӘhello_worldжҺҘеҸЈпјҢиҝҳжңүдёҖдёӘabйЎ№зӣ®ж–Ү件еӨ№пјҢabдёӢйқўиҝҳжңүдёҖдёӘhello_world_pythonжҺҘеҸЈд»ҘеҸҠеӯҗйЎ№зӣ®ж–Ү件еӨ№testab, testabдёӢйқўд№ҹжңүдёҖдёӘhello_world_python.
жҺҘеҸЈж–Ү件зҡ„ж–Ү件еҗҚе‘ҪеҗҚ规иҢғпјҡ
ж–Ү件еҗҚе‘ҪеҗҚеқҮдёәе°ҸеҶҷпјҢеӨҡдёӘеҚ•иҜҚд№Ӣй—ҙдҪҝз”Ё'_'йҡ”ејҖпјҢжҜ”еҰӮhello_world.py е‘ҪеҗҚжӯЈзЎ®пјҢhelloWorld.pyе‘ҪеҗҚй”ҷиҜҜгҖӮ


и·Ҝз”ұе…ҘеҸЈж–Ү件дјҡиҮӘеҠЁжҳ е°„пјҢжҳ 射规еҲҷдёә:
еүҚзјҖ / йЎ№зӣ®ж–Ү件еӨ№[...] / ж–Ү件еҗҚ
е…¶дёӯ еүҚзјҖдёәж•ҙдёӘйЎ№зӣ®зҡ„и·Ҝз”ұеүҚзјҖпјҢеҸҜд»Ҙе®ҡд№үпјҢд№ҹеҸҜд»ҘдёҚе®ҡд№үпјҢжҜ”еҰӮapi-abйЎ№зӣ®пјҢеҸҜд»Ҙе®ҡд№үж•ҙдёӘйЎ№зӣ®зҡ„и·Ҝз”ұеүҚзјҖдёә ab/
resourceдёӢйқўйЎ№зӣ®ж–Ү件еӨ№еҰӮжһңжңүпјҢеҲҷдјҡиҮӘеҠЁжӢјжҺҘпјҢеҰӮжһңжІЎжңүпјҢеҲҷдёҚдјҡиҜ»еҸ–гҖӮ
дёҫдҫӢпјҡ
еүҚзјҖдёәз©әпјҢдёҠеӣҫresourcesдёӯзҡ„дёүдёӘжҺҘеҸЈеҜ№еә”зҡ„и·Ҝз”ұдёәпјҡ
hello_world.py ==> /hello_world
ab/hello_world_python.py ==> /ab/hello_world_python
ab/testab/hello_world_python.py ==> /ab/testab/hello _world_pythonеүҚзјҖдёәab/пјҢдёҠеӣҫresourcesдёӯзҡ„дёүдёӘжҺҘеҸЈеҜ№еә”зҡ„и·Ҝз”ұдёәпјҡ
hello_world.py ==> ab/hello_world
ab/hello_world_python.py ==> ab/ab/hello_world_python
ab/testab/hello_world_python.py ==> ab/ab/testab/hello_world_pythonpythonеҫҲеӨҡжЎҶжһ¶зҡ„еҗҜеҠЁе’Ңи·Ҝз”ұз®ЎзҗҶйғҪеҫҲзұ»дјјпјҢжүҖд»ҘиҝҷеҘ—规еҲҷйҖӮеҗҲеҫҲеӨҡжЎҶжһ¶пјҢжөӢиҜ•иҝҮзЁӢдёӯжңүеҢ…жӢ¬flask, tornado, sanic, japrontoгҖӮ д»ҘеүҚе№ҙд»Јд№…иҝңзҡ„web.pyд№ҹжҳҜж”ҜжҢҒзҡ„гҖӮ
е®Ңж•ҙд»Јз Ғең°еқҖ:
https://github.com/CrystalSkyZ/PyAutoApiRoute
е®һзҺ°дёӢеҲ’зәҝе‘ҪеҗҚ иҪ¬ й©јеі°е‘ҪеҗҚ еҮҪж•°пјҢд»Јз Ғжј”зӨә:
def underline_to_hump(underline_str):
'''
дёӢеҲ’зәҝеҪўејҸеӯ—з¬ҰдёІиҪ¬жҲҗй©јеі°еҪўејҸпјҢйҰ–еӯ—жҜҚеӨ§еҶҷ
'''
sub = re.sub(r'(_\w)', lambda x: x.group(1)[1].upper(), underline_str)
if len(sub) > 1:
return sub[0].upper() + sub[1:]
return subе®һзҺ°ж №жҚ®еӯ—з¬ҰдёІеҜје…ҘжЁЎеқ—еҮҪж•°, д»Јз Ғжј”зӨә:
йҖҡиҝҮpythonеҶ…зҪ®еҮҪж•°__import__еҮҪж•°е®һзҺ°еҠ иҪҪзұ»
def import_object(name):
"""Imports an object by name.
import_object('x') is equivalent to 'import x'.
import_object('x.y.z') is equivalent to 'from x.y import z'.
"""
if not isinstance(name, str):
name = name.encode('utf-8')
if name.count('.') == 0:
return __import__(name, None, None)
parts = name.split('.')
obj = __import__('.'.join(parts[:-1]), None, None, [parts[-1]], 0)
try:
return getattr(obj, parts[-1])
except AttributeError:
raise ImportError("No module named %s" % parts[-1])importlib.import_module(name)дёҠйқў2з§Қж–№жі•йғҪеҸҜд»ҘпјҢgithubдёҠд»Јз ҒйҮҢ2з§Қж–№жі•йғҪжңүжөӢиҜ•гҖӮ
жЈҖзҙўresourcesж–Ү件еӨ№пјҢз”ҹжҲҗи·Ҝз”ұжҳ е°„пјҢ并еҜје…ҘеҜ№еә”е®һзҺ°зұ»пјҢ д»Јз Ғжј”зӨәеҰӮдёӢ:
def route(route_file_path,
resources_name="resources",
route_prefix="",
existing_route=None):
route_list = []
def get_route_tuple(file_name, route_pre, resource_module_name):
"""
:param file_name: API file name
:param route_pre: route prefix
:param resource_module_name: resource module
"""
nonlocal route_list
nonlocal existing_route
route_endpoint = file_name.split(".py")[0]
#module = importlib.import_module('{}.{}'.format(
# resource_module_name, route_endpoint))
module = import_object('{}.{}'.format(
resource_module_name, route_endpoint))
route_class = underline_to_hump(route_endpoint)
real_route_endpoint = r'/{}{}'.format(route_pre, route_endpoint)
if existing_route and isinstance(existing_route, dict):
if real_route_endpoint in existing_route:
real_route_endpoint = existing_route[real_route_endpoint]
route_list.append((real_route_endpoint, getattr(module, route_class)))
def check_file_right(file_name):
if file_name.startswith("_"):
return False
if not file_name.endswith(".py"):
return False
if file_name.startswith("."):
return False
return True
def recursive_find_route(route_path, sub_resource, route_pre=""):
nonlocal route_prefix
nonlocal resources_name
file_list = os.listdir(route_path)
if config.DEBUG:
print("FileList:", file_list)
for file_item in file_list:
if file_item.startswith("_"):
continue
if file_item.startswith("."):
continue
if os.path.isdir(route_path + "/{}".format(file_item)):
recursive_find_route(route_path + "/{}".format(file_item), sub_resource + ".{}".format(file_item), "{}{}/".format(route_pre, file_item))
continue
if not check_file_right(file_item):
continue
get_route_tuple(file_item, route_prefix + route_pre, sub_resource)
recursive_find_route(route_file_path, resources_name)
if config.DEBUG:
print("RouteList:", route_list)
return route_listд»ҘflaskжЎҶжһ¶дёәдҫӢпјҢе…¶дҪҷжЎҶжһ¶иҜ·зңӢgithubдёӯзҡ„д»Јз Ғжј”зӨәгҖӮ
app.py дёӯд»Јз Ғ
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
# APi route and processing functions
exist_route = {"/flask/hello_world": "/hello_world"}
route_path = "./resources"
route_list = route(
route_path,
resources_name="resources",
route_prefix="flask/",
existing_route=exist_route)
for item in route_list:
api.add_resource(item[1], item[0])
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=int(parse_args.port), debug=config.DEBUG)иҝҗиЎҢapp.pyд№ӢеҗҺпјҢи·Ҝз”ұжү“еҚ°еҰӮдёӢ:
RouteList: [
('/hello_world', <class'resources.hello_world.HelloWorld'>),
('/flask/ab/testab/hello_world_python_test', \
<class 'resources.ab.testab.hello_world_python_test.HelloWorldPythonTest'>),
('/flask/ab/hello_world_python', <class 'resources.ab.hello_world_python.HelloWorldPython'>)
]е…ғ组第дёҖдёӘе…ғзҙ еҲҷжҳҜи·Ҝз”ұпјҢ第дәҢдёӘе…ғзҙ жҳҜеҜ№еә”зҡ„е®һзҺ°зұ»гҖӮ
жҖ»з»“:
иҮіжӯӨпјҢйҖҡиҝҮеҲ¶е®ҡдёҖе®ҡ规еҲҷпјҢи§Јж”ҫи·Ҝз”ұз®ЎзҗҶж–Ү件方жЎҲе®ҢжҲҗгҖӮ ж¬ўиҝҺеҗ„дҪҚдёҖиө·и®Ёи®әе…¶дҪҷжҜ”иҫғеҘҪзҡ„ж–№жЎҲпјҢжӣҙеӨҡж–№жЎҲи®Ёи®әеҸҜд»Ҙе…іжіЁеҫ®дҝЎе…¬дј—еҸ·пјҡ еӨ©жҫ„зҡ„жҠҖжңҜ笔记 гҖӮ 
е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ