小编给大家分享一下Python中顺序表怎么实现,相信大部分人都还不怎么了解,因此分享这篇文章给大家参考一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后大有收获,下面让我们一起去了解一下吧!
顺序表python版的实现(部分功能未实现)
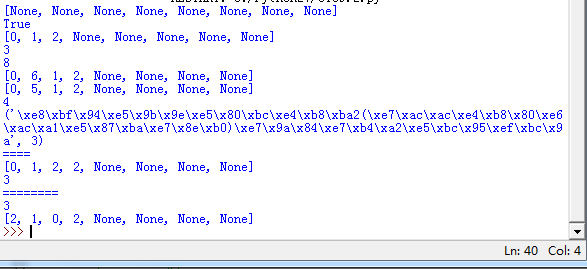
结果展示:
代码示例:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class SeqList(object):
def __init__(self, max=8):
self.max = max #创建默认为8
self.num = 0
self.date = [None] * self.max
#list()会默认创建八个元素大小的列表,num=0,并有链接关系
#用list实现list有些荒谬,全当练习
#self.last = len(self.date)
#当列表满时,扩建的方式省略
def is_empty(self):
return self.num is 0
def is_full(self):
return self.num is self.max
#获取某个位置的元素
def __getitem__(self, key):
if not isinstance(key, int):
raise TypeError
if 0<= key < self.num:
return self.date[key]
else:
#表为空或者索引超出范围都会引发索引错误
raise IndexError
#设置某个位置的元素
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
if not isinstance(key, int):
raise TypeError
#只能访问列表里已有的元素,self.num=0时,一个都不能访问,self.num=1时,只能访问0
if 0<= key < self.num:
self.date[key] = value #该位置无元素会发生错误
else:
raise IndexError
def clear(self):
self.__init__()
def count(self):
return self.num
def __len__(self):
return self.num
#加入元素的方法 append()和insert()
def append(self,value):
if self.is_full():
#等下扩建列表
print("list is full")
return
else:
self.date[self.num] = value
self.num += 1
def insert(self,key,value):
if not isinstance(key, int):
raise TypeError
if key<0: #暂时不考虑负数索引
raise IndexError
#当key大于元素个数时,默认尾部插入
if key>=self.num:
self.append(value)
else:
#移动key后的元素
for i in range(self.num, key, -1):
self.date[i] = self.date[i-1]
#赋值
self.date[key] = value
self.num += 1
#删除元素的操作
def pop(self,key=-1):
if not isinstance(key, int):
raise TypeError
if self.num-1 < 0:
raise IndexError("pop from empty list")
elif key == -1:
#原来的数还在,但列表不识别他
self.num -= 1
else:
for i in range(key,self.num-1):
self.date[i] = self.date[i+1]
self.num -= 1
def index(self,value,start=0):
for i in range(start, self.num):
if self.date[i] == value:
return i
#没找到
raise ValueError("%d is not in the list" % value)
#列表反转
def reverse(self):
i,j = 0, self.num - 1
while i<j:
self.date[i], self.date[j] = self.date[j], self.date[i]
i,j = i+1, j-1
if __name__=="__main__":
a = SeqList()
print(a.date)
#num == 0
print(a.is_empty())
a.append(0)
a.append(1)
a.append(2)
print(a.date)
print(a.num)
print(a.max)
a.insert(1,6)
print(a.date)
a[1] = 5
print(a.date)
print(a.count())
print("返回值为2(第一次出现)的索引:", a.index(2, 1))
print("====")
t = 1
if t:
a.pop(1)
print(a.date)
print(a.num)
else:
a.pop()
print(a.date)
print(a.num)
print("========")
print(len(a))
a.reverse()
print(a.date)
"""
print(a.is_full())
a.clear()
print(a.date)
print(a.count())
"""以上是“Python中顺序表怎么实现”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。