document.write()怎么在JavaScript中使用?针对这个问题,这篇文章详细介绍了相对应的分析和解答,希望可以帮助更多想解决这个问题的小伙伴找到更简单易行的方法。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset=" utf-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function(){
document.write("重温 JavaScript");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>Hello JavaScript</div>
</body>
</html>从以上代码的可以看出document.write()函数将原来的文档内容清空了,下面介绍一下出现此种情况的原因:
window.onload事件是在文档内容完全加载完毕再去执行事件处理函数,当然文档流已经关闭了,这个时候执行doucment.writ()函数会自动调用document.open()函数创建一个新的文档流,并写入新的内容,再通过浏览器展现,这样就会覆盖原来的内容。不过很多朋友还有会这样的疑问,为什么类似下面的情况,原来网页中的内容不会被覆盖,代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset=" utf-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.write("重温 JavaScript");
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>Hello JavaScript</div>
</body>
</html>在以上代码中,原来的文档内容并没有被清空,这是因为当前文档流是由浏览器所创建,并且document.wirte()函数身处其中,也就是执行此函数的时候文档流并没有被关闭,这个时候不会调用document.open()函数创建新文档流,所以也就不会被覆盖了。可能还有朋友会问为什么下面的方式还是不行,代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset=" utf-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.close();
document.write("重温 JavaScript");
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>Hello JavaScript</div>
</body>
</html>上面使用document.close()关闭文档流了,为什么还是不能够覆盖原来的内容的,很遗憾,文档流是由浏览器创建,无权限手动关闭,document.close()函数只能够关闭由document.open()函数创建的文档流。看下面的代码实例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset=" utf-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function create(){
var newWindow=window.open("","Document","_blank");
newWindow.document.write("Hello JavaScript");
newWindow.document.close();
newWindow.document.write("覆盖后的输出");
}
window.onload=function(){
var obt=document.getElementById("bt");
obt.onclick=function(){
create();
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="print">Hello JavaScript</div>
<input type="button" id="bt" value="查看效果"/>
</body>
</html>由doucment.open()创建的文档流就可以由document.close()关闭,那么第二个document.write()输出的内容会覆盖掉第一个输出的内容。
异步引用外部JavaScript时,必须先运行document.open()清空文档,然后才能运行document.write(),参数写在body内容的开头。
如果不先运行document.open(),直接运行document.write(),则无效且Chrome有如下提示:
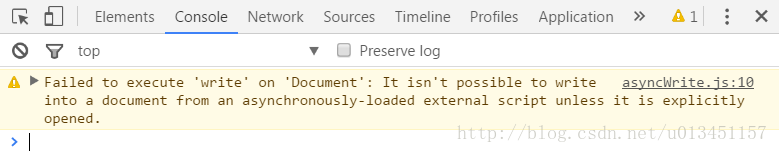
// asyncWrite.js
document.open();
document.write('<p>test</p>');
document.close();
<!-- asyncWrite.html -->
<!-- 运行前 -->
<body>
<script src="asyncWrite.js" async></script>
</body>
<!-- 运行后 -->
<body>
<p>test</p>
</body>document.write()也能写入含有script标签的字符串,但是需要转义。写入的script标签中的内容会正常运行。
<!-- 运行前 -->
<script>
document.write('<script>document.write("<p>test</p>");<\/script>');
</script>
<!-- 运行后 -->
<script>
document.write('<script>document.write("<p>test</p>");<\/script>');
</script>
<script>document.write("<p>test</p>");</script>
<p>test</p>document.write()可以传入多个参数。
<!-- 运行前 -->
<body>
<script>
document.write('<h3>multiArgument</h3>','<p>test</p>');
</script>
</body>
<!-- 运行后 -->
<body>
<script>
document.write('<h3>multiArgument</h3>','<p>test</p>');
</script>
<h3>multiArgument</h3>
<p>test</p>
</body>关于document.write()怎么在JavaScript中使用问题的解答就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,如果你还有很多疑惑没有解开,可以关注亿速云行业资讯频道了解更多相关知识。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。