这篇文章主要介绍了Spring Bean初始化及销毁多种实现方式,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友可以参考下
一、前言
日常开发过程有时需要在应用启动之后加载某些资源,或者在应用关闭之前释放资源。Spring 框架提供相关功能,围绕 Spring Bean 生命周期,可以在 Bean 创建过程初始化资源,以及销毁 Bean 过程释放资源。Spring 提供多种不同的方式初始化/销毁 Bean,如果同时使用这几种方式,Spring 如何处理这几者之间的顺序?
二、姿势剖析
首先我们先来回顾一下 Spring 初始化/销毁 Bean 几种方式,分别为:
PS: 其实还有一种方式,就是继承 Spring Lifecycle 接口。不过这种方式比较繁琐,这里就不再分析。
2.1、init-method/destroy-method
这种方式在配置文件文件指定初始化/销毁方法。XML 配置如下
<bean id="demoService" class="com.dubbo.example.provider.DemoServiceImpl" destroy-method="close" init-method="initMethod"/>或者也可以使用注解方式配置:
@Configurable
public class AppConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "init", destroyMethod = "destroy")
public HelloService hello() {
return new HelloService();
}
}还记得刚开始接触学习 Spring 框架,使用就是这种方式。
2.2、InitializingBean/DisposableBean
这种方式需要继承 Spring 接口 InitializingBean/DisposableBean,其中 InitializingBean 用于初始化动作,而 DisposableBean 用于销毁之前清理动作。使用方式如下:
@Service
public class HelloService implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("hello destroy...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("hello init....");
}
}2.3、@PostConstruct/@PreDestroy
这种方式相对于上面两种方式来说,使用方式最简单,只需要在相应的方法上使用注解即可。使用方式如下:
@Service
public class HelloService {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("hello @PostConstruct");
}
@PreDestroy
public void PreDestroy() {
System.out.println("hello @PreDestroy");
}
}这里踩过一个坑,如果使用 JDK9 之后版本 ,@PostConstruct/@PreDestroy 需要使用 maven 单独引入 javax.annotation-api,否者注解不会生效。
2.4、ContextStartedEvent/ContextClosedEvent
这种方式使用 Spring 事件机制,日常业务开发比较少见,常用与框架集成中。Spring 启动之后将会发送 ContextStartedEvent 事件,而关闭之前将会发送 ContextClosedEvent 事件。我们需要继承 Spring ApplicationListener 才能监听以上两种事件。
@Service
public class HelloListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if(event instanceof ContextClosedEvent){
System.out.println("hello ContextClosedEvent");
}else if(event instanceof ContextStartedEvent){
System.out.println("hello ContextStartedEvent");
}
}
}也可以使用 @EventListener注解,使用方式如下:
public class HelloListenerV2 {
@EventListener(value = {ContextClosedEvent.class, ContextStartedEvent.class})
public void receiveEvents(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent) {
System.out.println("hello ContextClosedEvent");
} else if (event instanceof ContextStartedEvent) {
System.out.println("hello ContextStartedEvent");
}
}
}PS:只有调用 ApplicationContext#start 才会发送 ContextStartedEvent。若不想这么麻烦,可以监听 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件代替。一旦 Spring 容器初始化完成,就会发送 ContextRefreshedEvent。
三、综合使用
回顾完上面几种方式,这里我们综合使用上面的四种方式,来看下 Spring 内部的处理顺序。在看结果之前,各位读者大人可以猜测下这几种方式的执行顺序。
public class HelloService implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("hello @PostConstruct");
}
@PreDestroy
public void PreDestroy() {
System.out.println("hello @PreDestroy");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("bye DisposableBean...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("hello InitializingBean....");
}
public void xmlinit(){
System.out.println("hello xml-init...");
}
public void xmlDestory(){
System.out.println("bye xmlDestory...");
}
@EventListener(value = {ContextClosedEvent.class, ContextStartedEvent.class})
public void receiveEvents(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent) {
System.out.println("bye ContextClosedEvent");
} else if (event instanceof ContextStartedEvent) {
System.out.println("hello ContextStartedEvent");
}
}
}xml 配置方式如下:
<context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="com.dubbo.example.demo"/>
<bean class="com.dubbo.example.demo.HelloService" init-method="xmlinit" destroy-method="xmlDestory"/>应用启动方法如下:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/dubbo-provider.xml");
context.start();
context.close();程序输出结果如下所示:
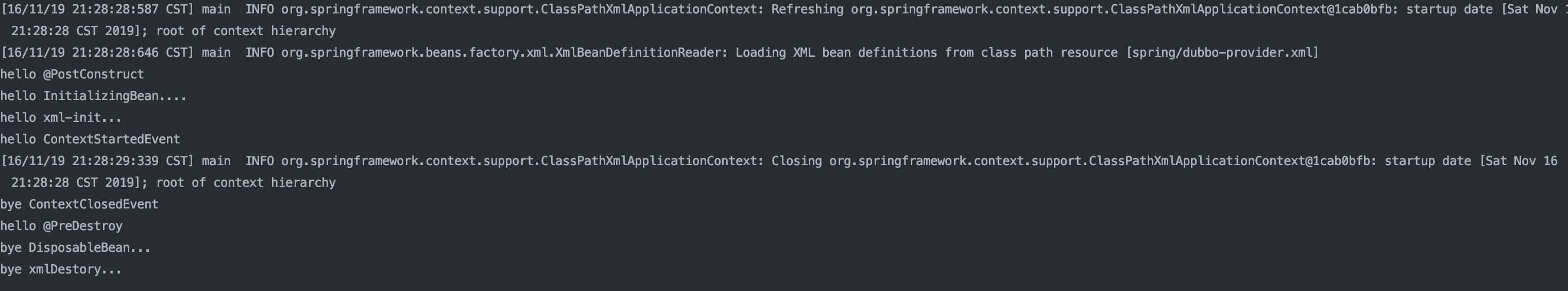
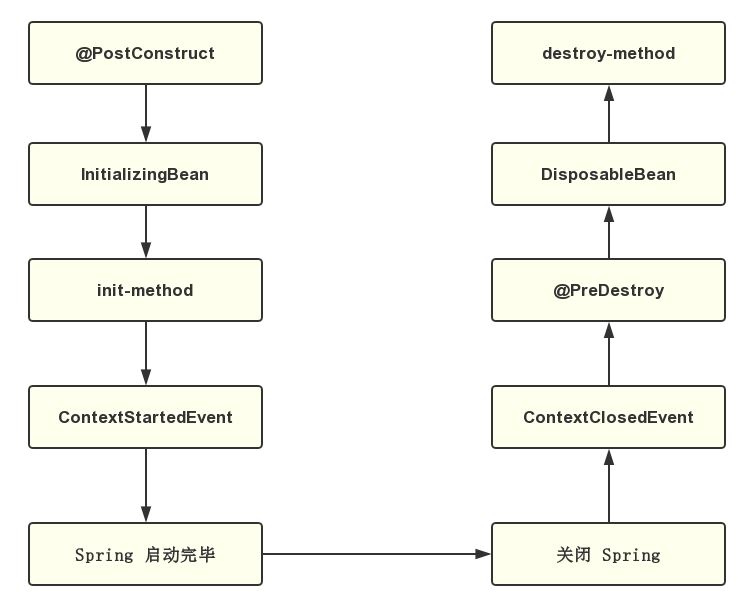
最后采用图示说明总结以上结果:
四、源码解析
不知道各位读者有没有猜对这几种方式的执行顺序,下面我们就从源码角度解析 Spring 内部处理的顺序。
4.1、初始化过程
使用 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 启动 Spring 容器,将会调用 refresh 方法初始化容器。初始化过程将会创建 Bean 。最后当一切准备完毕,将会发送 ContextRefreshedEvent。当容器初始化完毕,调用 context.start() 就发送 ContextStartedEvent 事件。
refresh 方法源码如下:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//... 忽略无关代码
// 初始化所有非延迟初始化的 Bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 发送 ContextRefreshedEvent
finishRefresh();
//... 忽略无关代码
}
}一路跟踪 finishBeanFactoryInitialization 源码,直到 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean,源码如下:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 调用 BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 初始化 Bean
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
}BeanPostProcessor 将会起着拦截器的作用,一旦 Bean 符合条件,将会执行一些处理。这里带有 @PostConstruct 注解的 Bean 都将会被 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 类拦截,内部将会触发 @PostConstruct 标注的方法。
接着执行 invokeInitMethods ,方法如下:
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
// 省略无关代码
// 如果是 Bean 继承 InitializingBean,将会执行 afterPropertiesSet 方法
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
if (mbd != null) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
// 执行 XML 定义 init-method
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}如果 Bean 继承 InitializingBean 接口,将会执行 afterPropertiesSet 方法,另外如果在 XML 中指定了 init-method ,也将会触发。
上面源码其实都是围绕着 Bean 创建的过程,当所有 Bean 创建完成之后,调用 context#start 将会发送 ContextStartedEvent 。这里源码比较简单,如下:
public void start() {
getLifecycleProcessor().start();
publishEvent(new ContextStartedEvent(this));
}4.2、销毁过程
调用 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext#close 方法将会关闭容器,具体逻辑将会在 doClose 方法执行。
doClose 这个方法首先发送 ContextClosedEvent,然再后开始销毁 Bean。
灵魂拷问:如果我们颠倒上面两者顺序,结果会一样吗?
doClose 源码如下:
protected void doClose() {
if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// 省略无关代码
try {
// Publish shutdown event.
publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", ex);
}
// 销毁 Bean
destroyBeans();
// 省略无关代码
}
}destroyBeans 最终将会执行 DisposableBeanAdapter#destroy,@PreDestroy、DisposableBean、destroy-method 三者定义的方法都将会在内部被执行。
首先执行 DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeDestruction,这里方法类似与上面 BeanPostProcessor。
@PreDestroy 注解将会被 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 拦截,这里类同时也继承了 DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor。
最后如果 Bean 为 DisposableBean 的子类,将会执行 destroy 方法,如果在 xml 定义了 destroy-method 方法,该方法也会被执行。
public void destroy() {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.beanPostProcessors)) {
for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this.beanPostProcessors) {
processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this.bean, this.beanName);
}
}
if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {
// 省略无关代码
// 如果 Bean 继承 DisposableBean,执行 destroy 方法
((DisposableBean) bean).destroy();
}
if (this.destroyMethod != null) {
// 执行 xml 指定的 destroy-method 方法
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod);
}
else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) {
Method methodToCall = determineDestroyMethod();
if (methodToCall != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(methodToCall);
}
}
}五、总结
init-method/destroy-method 这种方式需要使用 XML 配置文件或单独注解配置类,相对来说比较繁琐。而InitializingBean/DisposableBean 这种方式需要单独继承 Spring 的接口实现相关方法。@PostConstruct/@PreDestroy 这种注解方式使用方式简单,代码清晰,比较推荐使用这种方式。
另外 ContextStartedEvent/ContextClosedEvent 这种方式比较适合在一些集成框架使用,比如 Dubbo 2.6.X 优雅停机就是用改机制。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持亿速云。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。