这篇文章给大家分享的是有关JavaWeb如何读取配置文件的内容。小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,一起跟随小编过来看看吧。
方式一:采用ServletContext读取
获取配置文件的realpath,然后通过文件流读取出来或者通过方法getReasurceAsStream()。
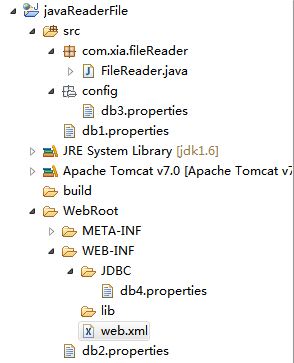
因为是用ServletContext读取文件路径,所以配置文件可以放入在WEB-INF的classes目录中,也可以在应用层级及WEB-INF的目录中。文件存放位置具体在eclipse工程中的表现是:可以放在src下面,也可放在WEB-INF及Web-Root下面等。因为是读取出路径后,用文件流进行读取的,所以可以读取任意的配置文件包括xml和properties。缺点:不能在servlet外面应用读取配置信息。
1.首先创建一个动态的javaweb项目,项目目录如下:
2.创建一个servlet(FileReader.java)
package com.xia.fileReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class FileReader extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
/**
* response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");目的是控制浏览器用UTF-8进行解码;
* 这样就不会出现中文乱码了
*/
response.setHeader("content-type","text/html;charset=UTF-8");
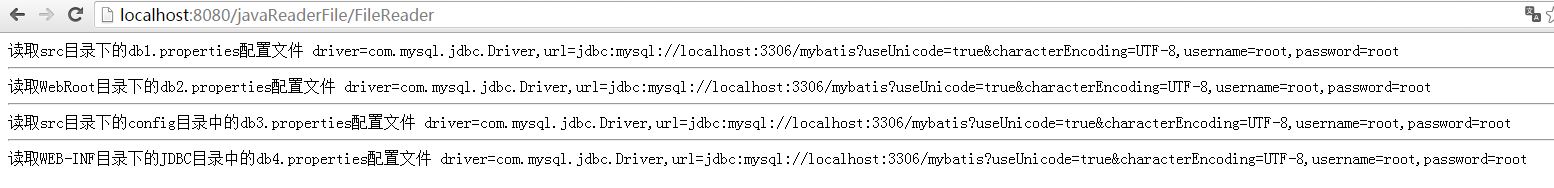
readSrcDirPropCfgFile(response);//读取src目录下的db1.properties配置文件
response.getWriter().println("<hr/>");
readWebRootDirPropCfgFile(response);//读取WebRoot目录下的db2.properties配置文件
response.getWriter().println("<hr/>");
readSrcSourcePackPropCfgFile(response);//读取src目录下的config目录中的db3.properties配置文件
response.getWriter().println("<hr/>");
readWEBINFPropCfgFile(response);//读取WEB-INF目录下的JDBC目录中的db4.properties配置文件
}
public void readSrcDirPropCfgFile(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String path = "/WEB-INF/classes/db1.properties";
InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream(path);
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(in);
String driver = props.getProperty("jdbc.driver");
String url = props.getProperty("jdbc.url");
String username = props.getProperty("jdbc.username");
String password = props.getProperty("jdbc.password");
response.getWriter().println("读取src目录下的db1.properties配置文件");
response.getWriter().println(MessageFormat.format( "driver={0},url={1},username={2},password={3}",
driver,url, username, password));
}
public void readWebRootDirPropCfgFile(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException{
String path = "/db2.properties";
InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream(path);
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(in);
String driver = props.getProperty("jdbc.driver");
String url = props.getProperty("jdbc.url");
String username = props.getProperty("jdbc.username");
String password = props.getProperty("jdbc.password");
response.getWriter().println("读取WebRoot目录下的db2.properties配置文件");
response.getWriter().println(MessageFormat.format( "driver={0},url={1},username={2},password={3}",
driver,url, username, password));
}
public void readSrcSourcePackPropCfgFile(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String path = "/WEB-INF/classes/config/db3.properties";
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath(path);
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(realPath),"UTF-8");
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(reader);
String driver = props.getProperty("jdbc.driver");
String url = props.getProperty("jdbc.url");
String username = props.getProperty("jdbc.username");
String password = props.getProperty("jdbc.password");
response.getWriter().println("读取src目录下的config目录中的db3.properties配置文件");
response.getWriter().println(MessageFormat.format( "driver={0},url={1},username={2},password={3}",
driver,url, username, password));
}
public void readWEBINFPropCfgFile(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String path = "/WEB-INF/JDBC/db4.properties";
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath(path);
System.out.println("realPath:"+realPath);
System.out.println("contextPath:"+this.getServletContext().getContextPath());
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(realPath),"UTF-8");
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(reader);
String driver = props.getProperty("jdbc.driver");
String url = props.getProperty("jdbc.url");
String username = props.getProperty("jdbc.username");
String password = props.getProperty("jdbc.password");
response.getWriter().println("读取WEB-INF目录下的JDBC目录中的db4.properties配置文件");
response.getWriter().println(MessageFormat.format( "driver={0},url={1},username={2},password={3}",
driver,url, username, password));
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
}3.配置servlet(web.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>javaReaderFile</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <servlet> <servlet-name>FileReader</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.xia.fileReader.FileReader</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>FileReader</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/FileReader</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
4.测试
方式二:采用ResourceBundle类读取配置信息
优点是:可以以完全限定类名的方式加载资源后,直接的读取出来,且可以在非Web应用中读取资源文件。
缺点:只能加载类src下面的资源文件且只能读取.properties文件。
/**
* 获取指定配置文件中所有的数据
* @param propertyName
* 调用方式:
* 1.配置文件放在resource源包下,不用加后缀
* PropertiesUtil.getAllMessage("message");
* 2.放在包里面的
* PropertiesUtil.getAllMessage("com.test.message");
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getAllMessage(String propertyName) {
// 获得资源包
ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle(propertyName.trim());
// 通过资源包拿到所有的key
Enumeration<String> allKey = rb.getKeys();
// 遍历key 得到 value
List<String> valList = new ArrayList<String>();
while (allKey.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = allKey.nextElement();
String value = (String) rb.getString(key);
valList.add(value);
}
return valList;
}方式三:采用ClassLoader方式进行读取配置信息
优点是:可以在非Web应用中读取配置资源信息,可以读取任意的资源文件信息
缺点:只能加载类src下面的资源文件,不适合装载大文件,否则会导致jvm内存溢出
package com.xia.fileReader;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Properties;
public class ReadByClassLoader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
readPropFileByClassLoad();
}
public static void readPropFileByClassLoad() throws IOException{
//读取src下面config包内的配置文件db3.properties
InputStream in = ReadByClassLoader.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config/db3.properties");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(br);
for(Object s: props.keySet()){
System.out.println(s+":"+props.getProperty(s.toString()));
}
}
}方式四: PropertiesLoaderUtils工具类
/**
* Spring 提供的 PropertiesLoaderUtils 允许您直接通过基于类路径的文件地址加载属性资源
* 最大的好处就是:实时加载配置文件,修改后立即生效,不必重启
*/
private static void springUtil(){
Properties props = new Properties();
while(true){
try {
props=PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties("message.properties");
for(Object key:props.keySet()){
System.out.print(key+":");
System.out.println(props.get(key));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
}修改Properties
/**
* 传递键值对的Map,更新properties文件
*
* @param fileName
* 文件名(放在resource源包目录下),需要后缀
* @param keyValueMap
* 键值对Map
*/
public static void updateProperties(String fileName,Map<String, String> keyValueMap) {
//getResource方法使用了utf-8对路径信息进行了编码,当路径中存在中文和空格时,他会对这些字符进行转换,这样,
//得到的往往不是我们想要的真实路径,在此,调用了URLDecoder的decode方法进行解码,以便得到原始的中文及空格路径。
String filePath = PropertiesUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResource(fileName).getFile();
Properties props = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
filePath = URLDecoder.decode(filePath,"utf-8");
log.debug("updateProperties propertiesPath:" + filePath);
props = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new ClassPathResource(fileName));
log.debug("updateProperties old:"+props);
// 写入属性文件
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(filePath)));
props.clear();// 清空旧的文件
for (String key : keyValueMap.keySet())
props.setProperty(key, keyValueMap.get(key));
log.debug("updateProperties new:"+props);
props.store(bw, "");
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}感谢各位的阅读!关于“JavaWeb如何读取配置文件”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,让大家可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到吧!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。