这期内容当中小编将会给大家带来有关android应用中怎么利用onLayout()实现一个流式布局,文章内容丰富且以专业的角度为大家分析和叙述,阅读完这篇文章希望大家可以有所收获。
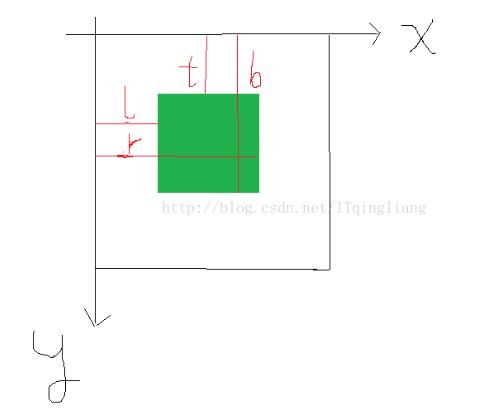
在onLayout方法中有四个参数,我画了一个简单的图来分清楚值哪里。
FlowLayout.Java
package com.example.my_view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
* 自定义布局 流布局
*/
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
/**
*
* @param changed
* @param l 左
* @param t 上
* @param r 右
* @param b 下
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
//获得子控件的数量
int childCount = getChildCount();
//当前子控件的左边坐标
int cl = 0;
//当前子控件的上边坐标
int ct = 0;
//ViewGroup整体宽度
int width = r - l;
//行高
int lineHeight = 0;
//遍历所有子控件
for(int i = 0; i < childCount; i++){
//获取当前控件
View childAt = getChildAt(i);
//获取宽度
int cw = childAt.getMeasuredWidth();
//获取高度
int ch = childAt.getMeasuredHeight();
//当前控件右边
int cr = cl + cw;
//当前控件下边
int cb = ct + ch;
//判断是否换行
if(cr > width){
//如果换行重新计算上下左右地值
cl = 0;
cr = cl + cw;
ct += lineHeight;
cb = ct + ch;
//换行后,第一个控件作为最大行高
lineHeight = ch;
}else{
//如果不换行,需要计算最大高度
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight,ch);
}
childAt.layout(cl,ct,cr,cb);
//横向向后移动一个,前面控件的右边作为后面控件的左边
cl = cr;
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//测量所有子控件
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.example.my_view.FlowLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.my_view.MainActivity">
<!--
<com.example.my_view.Counter
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:number="10"
app:bgColor="#ff002b"
app:textColor="#0fd444"/>-->
<!--<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我在自定义布局的下面"/>-->
<Button
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:text="button2"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="180dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="button3"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="button4"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:text="button5"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="button6"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
android:text="button7"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="button8"/>
</com.example.my_view.FlowLayout>上述就是小编为大家分享的android应用中怎么利用onLayout()实现一个流式布局了,如果刚好有类似的疑惑,不妨参照上述分析进行理解。如果想知道更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。