本篇文章为大家展示了spring boot如何实现对RabbitMQ整合,内容简明扼要并且容易理解,绝对能使你眼前一亮,通过这篇文章的详细介绍希望你能有所收获。
1.Fanout Exchange介绍
Fanout Exchange 消息广播的模式,不管路由键或者是路由模式,会把消息发给绑定给它的全部队列,如果配置了routing_key会被忽略。
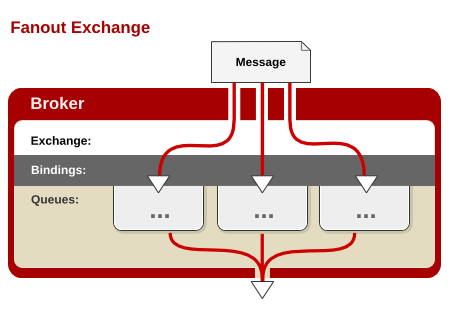
如上图所示,即当使用fanout交换器时,他会将消息广播到与该交换器绑定的所有队列上,这有利于你对单条消息做不同的反应。
例如存在以下场景:一个web服务要在用户完善信息时,获得积分奖励,这样你就可以创建两个对列,一个用来处理用户信息的请求,另一个对列获取这条消息是来完成积分奖励的任务。
2.代码示例
1).Queue配置类
FanoutRabbitConfig.java类:
package com.example.rabbitmqfanout;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FanoutRabbitConfig {
//创建队列
@Bean
public Queue AMessage() {
return new Queue("fanout.A");
}
//创建队列
@Bean
public Queue BMessage() {
return new Queue("fanout.B");
}
//创建队列
@Bean
public Queue CMessage() {
return new Queue("fanout.C");
}
//创建Fanout交换器
@Bean
FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange("fanoutExchange");
}
//将对列绑定到Fanout交换器
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeA(Queue AMessage,FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(AMessage).to(fanoutExchange);
}
//将对列绑定到Fanout交换器
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeB(Queue BMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(BMessage).to(fanoutExchange);
}
//将对列绑定到Fanout交换器
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeC(Queue CMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(CMessage).to(fanoutExchange);
}
}2).消息生产者
FanoutSender.java类:
package com.example.rabbitmqfanout.rabbitmq;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class FanoutSender {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send() {
String context = "hi, fanout msg ";
System.out.println("Sender : " + context);
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange","", context);
}
}3).消息消费者
FanoutReceiverA.java类:
package com.example.rabbitmqfanout.rabbitmq;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.A")
public class FanoutReceiverA {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message) {
System.out.println("fanout Receiver A : " + message);
}
}FanoutReceiverB.java类:
package com.example.rabbitmqfanout.rabbitmq;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.B")
public class FanoutReceiverB {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message) {
System.out.println("fanout Receiver B: " + message);
}
}FanoutReceiverC.java类:
package com.example.rabbitmqfanout.rabbitmq;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.C")
public class FanoutReceiverC {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message) {
System.out.println("fanout Receiver C: " + message);
}
}4).测试
FanoutTest.java类:
package com.example.rabbitmqfanout.rabbitmq;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class FanoutTest {
@Autowired
private FanoutSender sender;
@Test
public void fanoutSender() throws Exception {
sender.send();
}
}上述内容就是spring boot如何实现对RabbitMQ整合,你们学到知识或技能了吗?如果还想学到更多技能或者丰富自己的知识储备,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。