这期内容当中小编将会给大家带来有关java利用POI如何实现操作excel文件,文章内容丰富且以专业的角度为大家分析和叙述,阅读完这篇文章希望大家可以有所收获。
一、POI的定义
JAVA中操作Excel的有两种比较主流的工具包: JXL 和 POI 。jxl 只能操作Excel 95, 97, 2000也即以.xls为后缀的excel。而poi可以操作Excel 95及以后的版本,即可操作后缀为 .xls 和 .xlsx两种格式的excel。
POI全称 Poor Obfuscation Implementation,直译为“可怜的模糊实现”,利用POI接口可以通过JAVA操作Microsoft office 套件工具的读写功能。官网:http://poi.apache.org ,POI支持office的所有版本,首先去官网下载如下界面:
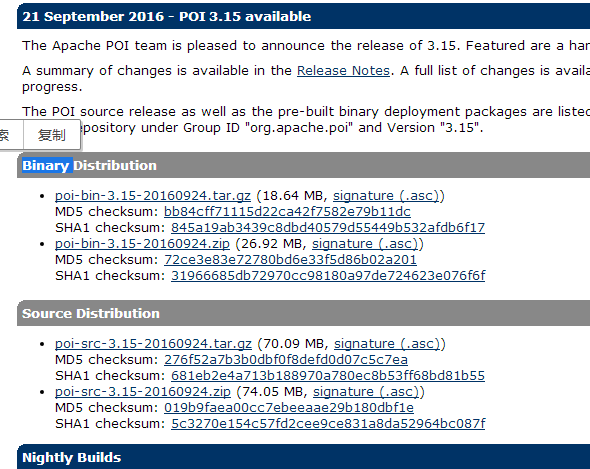
下载完后,打开“poi-bin-3.15-20160924.tar.gz”获取操作excel需要的jar包,并将这些jar包复制到项目中。对于只操作2003 及以前版本的excel,只需要poi-3.15.jar ,如果需要同时对2007及以后版本进行操作则需要复制
poi-ooxml-3.15.jar
poi-ooxml-schemas-3.15.jar
以及复制在ooxml-lib目录下的xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar(但不知为何,我下的jar文件中没有dom4j.jar)这个文件,还是加上dom4j.jar,防止报错.
二、使用junit进行操作Excel测试
首先明确Excel工作簿对象、工作表对象、行对象、以及单元格对象。
具体代码如下注意要分清楚究竟是2007版本以前,还是2007版本以后(包括2007版本):下面这段代码是2007版本以前的:
这段代码只是将数据写入到Excel文件中创建
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
* 注意这只是07版本以前的做法对应的excel文件的后缀名为.xls
* 07版本和07版本以后的做法excel文件的后缀名为.xlsx
*/
//创建新工作簿
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
//新建工作表
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("hello");
//创建行,行号作为参数传递给createRow()方法,第一行从0开始计算
HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(0);
//创建单元格,row已经确定了行号,列号作为参数传递给createCell(),第一列从0开始计算
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(2);
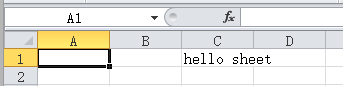
//设置单元格的值,即C1的值(第一行,第三列)
cell.setCellValue("hello sheet");
//输出到磁盘中
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("E:\\root\\sheet\\11.xls"));
workbook.write(fos);
workbook.close();
fos.close();
}结果如下图:
同样也可以对读取Excel文件,得到Excel文件的数据,并将其打印出来,代码如下:
@Test
public void testReadExcel() throws Exception
{
//创建输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("E:\\root\\sheet\\11.xls"));
//通过构造函数传参
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fis);
//获取工作表
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//获取行,行号作为参数传递给getRow方法,第一行从0开始计算
HSSFRow row = sheet.getRow(0);
//获取单元格,row已经确定了行号,列号作为参数传递给getCell,第一列从0开始计算
HSSFCell cell = row.getCell(2);
//设置单元格的值,即C1的值(第一行,第三列)
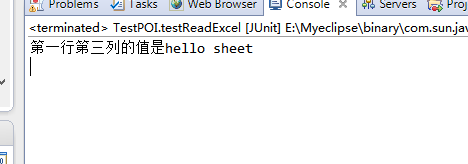
String cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
System.out.println("第一行第三列的值是"+cellValue);
workbook.close();
fis.close();
}结果如下图:
上面操作的都是07版本以前的Excel文件,即后缀名为.xls,07和07版本以后的Excel文件后缀名为.xlsx相应的工作簿的对象名也改为:
//创建工作簿
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();代码如下,创建excel文件并保存数据到excel文件:
@Test
public void write07() throws Exception
{
//创建工作簿
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//新建工作表
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("hello");
//创建行,0表示第一行
XSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(0);
//创建单元格行号由row确定,列号作为参数传递给createCell;第一列从0开始计算
XSSFCell cell = row.createCell(2);
//给单元格赋值
cell.setCellValue("hello sheet");
//创建输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("E:\\root\\sheet\\hello.xlsx"));
workbook.write(fos);
workbook.close();
fos.close();
}与之对应的读取数据,代码如下:
@Test
public void read07() throws Exception
{
//创建输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("E:\\root\\sheet\\hello.xlsx"));
//由输入流得到工作簿
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
//得到工作表
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheet("hello");
//得到行,0表示第一行
XSSFRow row = sheet.getRow(0);
//创建单元格行号由row确定,列号作为参数传递给createCell;第一列从0开始计算
XSSFCell cell = row.getCell(2);
//给单元格赋值
String cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
System.out.println("C1的值是"+cellValue);
int a[][] = new int[10][30];
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
workbook.close();
fis.close();
}问题出现了,也可以解释为需求:当不能确定究竟是读取07以前(例如2003,95,97,2000)还是07版本以后的Excel文件,我们当然希望程序能够自动识别,并创建相应的对象,去操作excel文件,代码如下:
@Test
public void reda03and07() throws Exception
{
//读取03或07的版本
String filePath = "E:\\root\\sheet\\hello.xlsx";
if(filePath.matches("^.+\\.(?i)((xls)|(xlsx))$"))
{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(filePath);
boolean is03Excell = filePath.matches("^.+\\.(?i)(xls)$")?true:false;
Workbook workbook = is03Excell ? new HSSFWorkbook(fis):new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
Cell cell = row.getCell(2);
System.out.println("第一行第一列的数据是:"+cell.getStringCellValue());
}
}学完了上面几个例子,接下来就是应用它了,我们经常需要在一个页面中批量导出和批量导出数据,这里就涉及到对excel文件的操作,当然还有其它的文件格式,我们使用一个lList<User> list 来保存,在这里我们写了一个ExcelUtil这个工具类:代码如下:
package com.ittax.core.util;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFFont;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFHeader;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.util.CellRangeAddress;
import com.ittax.nsfw.user.entity.User;
/**
* excel工具类,支持批量导出
* @author lizewu
*
*/
public class ExcelUtil {
/**
* 将用户的信息导入到excel文件中去
* @param userList 用户列表
* @param out 输出表
*/
public static void exportUserExcel(List<User> userList,ServletOutputStream out)
{
try{
//1.创建工作簿
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
//1.1创建合并单元格对象
CellRangeAddress callRangeAddress = new CellRangeAddress(0,0,0,4);//起始行,结束行,起始列,结束列
//1.2头标题样式
HSSFCellStyle headStyle = createCellStyle(workbook,(short)16);
//1.3列标题样式
HSSFCellStyle colStyle = createCellStyle(workbook,(short)13);
//2.创建工作表
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("用户列表");
//2.1加载合并单元格对象
sheet.addMergedRegion(callRangeAddress);
//设置默认列宽
sheet.setDefaultColumnWidth(25);
//3.创建行
//3.1创建头标题行;并且设置头标题
HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(0);
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(0);
//加载单元格样式
cell.setCellStyle(headStyle);
cell.setCellValue("用户列表");
//3.2创建列标题;并且设置列标题
HSSFRow row2 = sheet.createRow(1);
String[] titles = {"用户名","账号","所属部门","性别","电子邮箱"};
for(int i=0;i<titles.length;i++)
{
HSSFCell cell2 = row2.createCell(i);
//加载单元格样式
cell2.setCellStyle(colStyle);
cell2.setCellValue(titles[i]);
}
//4.操作单元格;将用户列表写入excel
if(userList != null)
{
for(int j=0;j<userList.size();j++)
{
//创建数据行,前面有两行,头标题行和列标题行
HSSFRow row3 = sheet.createRow(j+2);
HSSFCell cell1 = row3.createCell(0);
cell1.setCellValue(userList.get(j).getName());
HSSFCell cell2 = row3.createCell(1);
cell2.setCellValue(userList.get(j).getAccount());
HSSFCell cell3 = row3.createCell(2);
cell3.setCellValue(userList.get(j).getDept());
HSSFCell cell4 = row3.createCell(3);
cell4.setCellValue(userList.get(j).isGender()?"男":"女");
HSSFCell cell5 = row3.createCell(4);
cell5.setCellValue(userList.get(j).getEmail());
}
}
//5.输出
workbook.write(out);
workbook.close();
//out.close();
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
*
* @param workbook
* @param fontsize
* @return 单元格样式
*/
private static HSSFCellStyle createCellStyle(HSSFWorkbook workbook, short fontsize) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
HSSFCellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle();
style.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);//水平居中
style.setVerticalAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.VERTICAL_CENTER);//垂直居中
//创建字体
HSSFFont font = workbook.createFont();
font.setBoldweight(HSSFFont.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD);
font.setFontHeightInPoints(fontsize);
//加载字体
style.setFont(font);
return style;
}
}紧接着就是在UseService中调用方法并写出exportExcel方法:
@Override
public void exportExcel(List<User> userList, ServletOutputStream out) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ExcelUtil.exportUserExcel(userList, out);
}
@Override
public void importExcel(File file, String excelFileName) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//1.创建输入流
try {
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
boolean is03Excel = excelFileName.matches("^.+\\.(?i)(xls)$");
//1.读取工作簿
Workbook workbook = is03Excel?new HSSFWorkbook(inputStream):new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
//2.读取工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//3.读取行
//判断行数大于二,是因为数据从第三行开始插入
if(sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows() > 2)
{
User user = null;
//跳过前两行
for(int k=2;k<sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();k++ )
{
//读取单元格
Row row0 = sheet.getRow(k);
user = new User();
//用户名
Cell cell0 = row0.getCell(0);
user.setName(cell0.getStringCellValue());
//账号
Cell cell1 = row0.getCell(1);
user.setAccount(cell1.getStringCellValue());
//所属部门
Cell cell2 = row0.getCell(2);
user.setDept(cell2.getStringCellValue());
//设置性别
Cell cell3 = row0.getCell(3);
boolean gender = cell3.getStringCellValue() == "男"?true:false;
user.setGender(gender);
//设置手机
String mobile = "";
Cell cell4 = row0.getCell(4);
try {
mobile = cell4.getStringCellValue();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
double dmoblie = cell4.getNumericCellValue();
mobile = BigDecimal.valueOf(dmoblie).toString();
}
user.setMobile(mobile);
//设置电子邮箱
Cell cell5 = row0.getCell(5);
user.setEmail(cell5.getStringCellValue());
//默认用户密码是123456
user.setPassword("123456");
//用户默认状态是有效
user.setState(User.USER_STATE_VALIDE);
//保存用户
save(user);
}
}
workbook.close();
inputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}最后就是在Action中调用service方法:
//导出用户列表
public void exportExcel()
{
try
{
//1.查找用户列表
userList = userService.findObjects();
//2.导出
HttpServletResponse response = ServletActionContext.getResponse();
//这里设置的文件格式是application/x-excel
response.setContentType("application/x-excel");
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + new String("用户列表.xls".getBytes(), "ISO-8859-1"));
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
userService.exportExcel(userList, outputStream);
if(outputStream != null)
outputStream.close();
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String importExcel()
{
if(userExcel!= null)
{
//判断是否是Excel文件
if(userExcelFileName.matches("^.+\\.(?i)((xls)|(xlsx))$"))
{
userService.importExcel(userExcel, userExcelFileName);
}
}
return"list";
}注意的是应该使用ServletOutputStream这个类,最后实现了批量导出和导入数据。
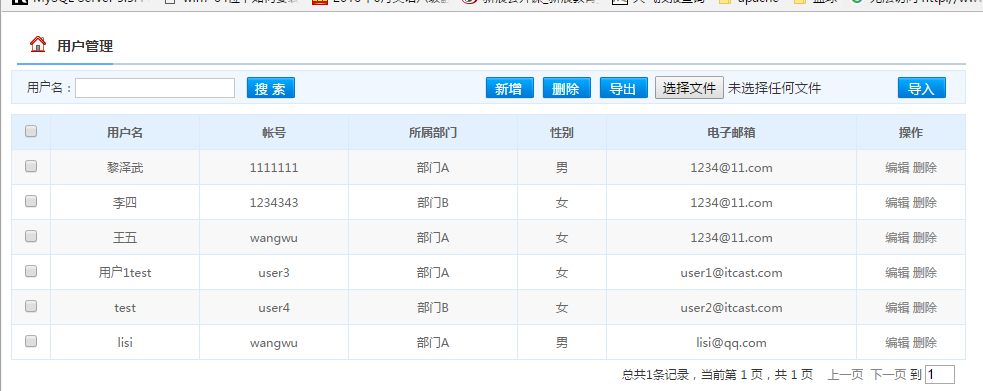
导出用户结果如下图;

导入结果如下图;
导入前:
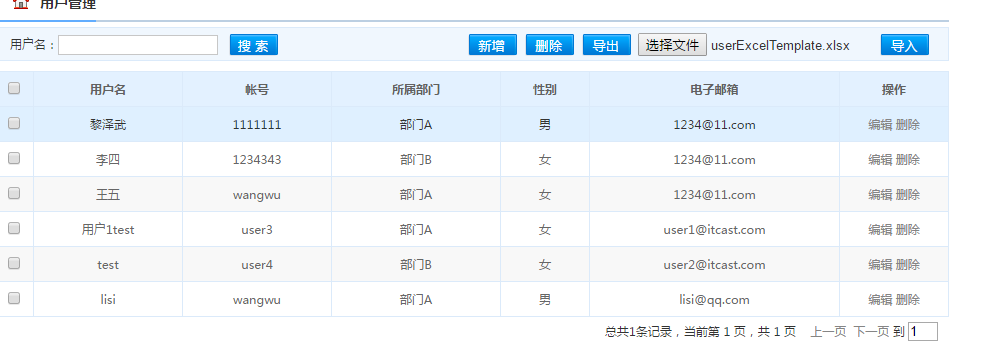
导入后的结果;
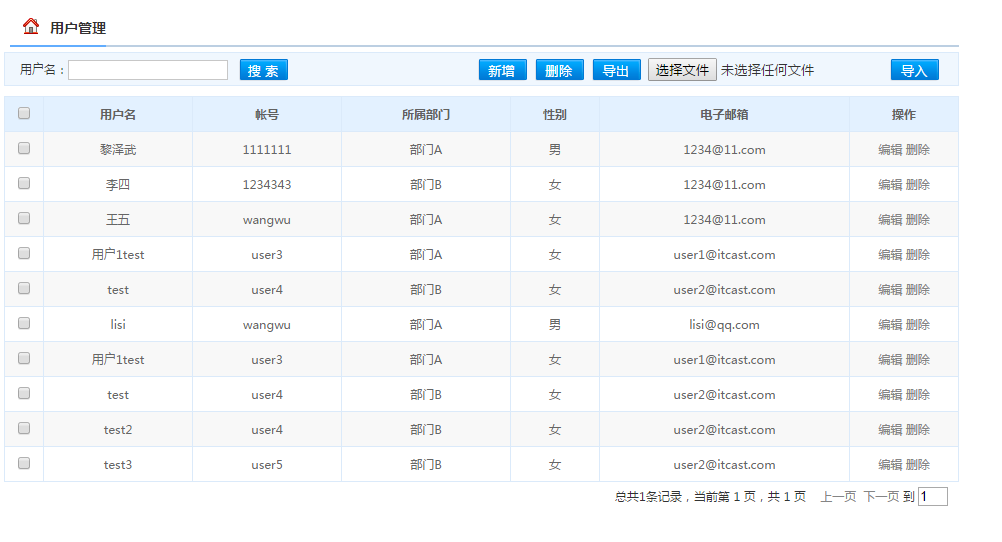
ok,关于POI操作EXCEL文件就暂时到此为止了
上述就是小编为大家分享的java利用POI如何实现操作excel文件了,如果刚好有类似的疑惑,不妨参照上述分析进行理解。如果想知道更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。