小编给大家分享一下eclipse是怎样实现可认证的DH密钥交换协议,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后大所收获,下面让我们一起去探讨方法吧!
可认证的DH密钥交换协议,供大家参考,具体内容如下
一、实验目的
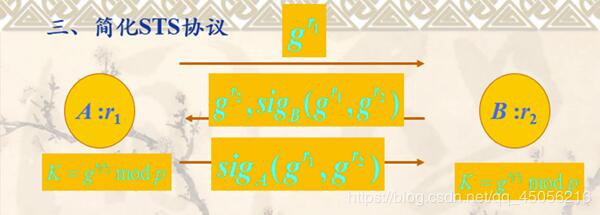
通过使用密码学库实现可认证的DH密钥交换协议(简化STS协议),能够编写简单的实验代码进行正确的协议实现和验证。
二、实验要求
1、熟悉DH密钥交换算法基本原理;
2、理解原始DH密钥交换算法存在的中间人攻击;
3、理解简化STS协议抗中间人攻击的原理。
4、掌握使用java编写实验代码进行正确的简化STS协议实现和验证。
三、 开发环境
JDK 1.7,Java开发环境(本实验采用Windows+eclipse作为实验环境),要求参与实验的同学按照对称加密提供的方法,提前安装好JDK。
四、实验原理
通过使用密码学库实现可认证的DH密钥交换协议(简化STS协议),能够编写简单的实验代码进行正确的协议实现和验证。
代码段:
AuthDHKeyAgree
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Random;
public class AuthDHKeyAgree {
private static final int securityParam = 1023;
public static BigInteger p;
public static BigInteger q;
public static BigInteger g;
//生成安全素数p,p=2q+1,q为一个1023 bits的大素数
public static void safePGen() {
BigInteger one = new BigInteger("1",10);
BigInteger two = new BigInteger("2",10);
do {
p = new BigInteger("0",10);
q = new BigInteger(securityParam, 100, new Random());
p = p.add(q.multiply(two).add(one));
}while( p.isProbablePrime(100) == false );
}
//选取随机生成元g,通过随机选择[2,p-2]之间的数g,然后判断g^q mod p是否等于1,如果不等于1,则g为生成元
public static void generatorGGen() {
BigInteger one = new BigInteger("1",10);
BigInteger two = new BigInteger("2",10);
BigInteger result;
do {
g = new BigInteger(securityParam, new Random());
g = g.mod(p.subtract(one));
result = g.modPow(q, p);
}while( g.compareTo(two) < 0 || result.compareTo(one) == 0 );
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("系统初始化,生成安全素数p,选取随机生成元g...");
safePGen();
System.out.println("p: "+p.toString(16));
System.out.println("q: "+q.toString(16));
generatorGGen();
System.out.println("g: "+g.toString(16));
//Alice选择随机秘密值 0<=r1<=p-1
BigInteger r1 = new BigInteger(securityParam, new Random());
BigInteger A;
r1 = r1.mod(p);
//Alice计算g^r1 mod p
A = g.modPow(r1, p);
//Bob选择随机秘密值0<=r2<=p-1
BigInteger r2 = new BigInteger(securityParam, new Random());
BigInteger B;
//Bob计算g^r2 mod p
B = g.modPow(r2, p);
//Bob初始化一个RSA签名算法对象
RSASignatureAlgorithm BobRSA = new RSASignatureAlgorithm();
BobRSA.initKeys();
byte[] BobM = (A.toString()+B.toString()+"Alice"+"Bob").getBytes();
//Bob生成签名
BigInteger BobSig = BobRSA.signature(BobM);
//Alice验证签名
BobM = (A.toString()+B.toString()+"Alice"+"Bob").getBytes();
boolean result = BobRSA.verify(BobM, BobSig);
if( result == true ) System.out.println("Alice验证签名通过。");
else System.out.println("Alice验证签名不通过。");
//Alice计算会话密钥
BigInteger sessionKey = (A.multiply(B)).mod(p);
System.out.println("Alice计算得到的会话密钥为:"+sessionKey.toString(16));
//Alice初始化一个RSA签名算法对象
RSASignatureAlgorithm AliceRSA = new RSASignatureAlgorithm();
AliceRSA.initKeys();
byte[] AliceM = (A.toString()+B.toString()+"Alice"+"Bob").getBytes();
//Alice生成签名
BigInteger AliceSig = AliceRSA.signature(AliceM);
//Bob验证签名
AliceM = (A.toString()+B.toString()+"Alice"+"Bob").getBytes();
result = AliceRSA.verify(AliceM, AliceSig);
if ( result == true ) System.out.println("Bob验证签名通过。");
else System.out.println("Bob验证签名不通过");
//Bob计算会话密钥
sessionKey = (B.multiply(A)).mod(p);
System.out.println("Bob计算得到的会话密钥为:"+sessionKey.toString(16));
}
}RSASignatureAlgorithm
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Random;
public class RSASignatureAlgorithm {
BigInteger n;
BigInteger e;
BigInteger d;
public BigInteger __hash(byte m[]) {
MessageDigest md;
try {
md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
md.update(m);
byte b[] = new byte[33];
System.arraycopy(md.digest(), 0, b, 1, 32);
return new BigInteger(b);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
System.out.println("this cannot happen.");
}
return null;
}
public void initKeys() {
BigInteger p = new BigInteger(1024, 500, new Random());
BigInteger q = new BigInteger(1024, 500, new Random());
assert(p.compareTo(q) != 0);
n = p.multiply(q);
BigInteger fi_n = p.subtract(BigInteger.ONE)
.multiply(q.subtract(BigInteger.ONE));
e = new BigInteger(512, 100, new Random());
d = e.modInverse(fi_n);
System.out.println("n : " + n.toString(16));
System.out.println("e : " + e.toString(16));
System.out.println("d : " + d.toString(16));
}
public BigInteger signature(byte m[]) {
BigInteger s = __hash(m).modPow(d, n);
System.out.println("s : " + s);
return s;
}
public boolean verify(byte m[], BigInteger s) {
BigInteger left = __hash(m).mod(n);
BigInteger right = s.modPow(e, n);
return left.compareTo(right) == 0;
}
}看完了这篇文章,相信你对eclipse是怎样实现可认证的DH密钥交换协议有了一定的了解,想了解更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢各位的阅读!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。