本篇内容介绍了“基于Java递归算法的封装解决方法是什么”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
递归算法的核心思想是通过将问题重复分解为同类的或其子问题的方式,从而可以使用统一的解决方式。很多编程语言支持方法或函数自我调用,简单的说,就是在函数或方法体内,自身可以再次调用自身的方法结构。
这里通过递归的方式,计算阶乘、求和等相关逻辑。
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result1 = factorial(5);
System.out.println(result1);
int result2 = sum(100) ;
System.out.println(result2);
}
// 递归阶乘
private static int factorial (int n){
if(n <= 1){
return n ;
}else{
return n*factorial(n-1);
}
}
// 递归求和
private static int sum (int f){
if(f <= 1){
return f ;
}else{
return f + sum(f-1);
}
}
}使用方法
使用递归的时候,要明确业务逻辑可以分解为重复相同的问题,且要清楚的知道递归的结束条件,不然很容易出现死循环。
优缺点描述
递归算法的代码比较简洁,可读性较好;但是在实际的业务处理中会出现多次的重复调用,如果处理不好,很容易出现StackOverflowError报错。
树形结构是一层次的嵌套结构。一个树形结构的外层和内层有相似的结构,所以这种结构多可以递归的表示。
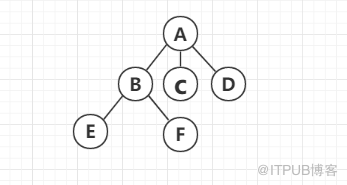
根节点
树的根源,没有父节点的节点,如上图A节点。
兄弟节点
拥有同一父节点的子节点。如图B与C与D节点。
叶子节点
没有子节点的节点。如图E和F等节点。
分支度
指一个节点有几个子节点。 如:A为3、B为2。
节点深度
指从该节点到某一节点的最长路径。如图A为2、B为1。
基于递归算法下,处理很多树形结构的业务数据。常见的业务场景如下:
省市区三级联动查询 ;
系统模块、菜单、按钮的授权 ;
常见的业务数据分类:商品分类等 ;
常见各种行业分类细化 ;
在管理系统中,对系统模块、菜单、按钮授权操作时候可能会出现如下情况。

假如系统管理员的权限如图所示,但是给到运营人员的权限如下,需要把3号菜单和5号菜单设置为同级别,这时候基本的处理手法就是把3号菜单父级ID作为3号菜单和下属功能的权限的根节点,这里把这里当成两颗树进行分别处理,最后合并数据就好。必要时按照配上节点编码,例如NODE01,NODE0101,NODE0102等方式,这里针对这个场景描述,就是希望在处理类似业务时候,思路要开阔,不必拘泥于单个树形结构。业务很多时候都是出人意料甚至是令人生厌,不过这确实就是生活。
这里展示一个树形结构常用的几个封装方法,例如创建树形结构,遍历,判断等。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ThreeUtil {
/**
* 递归创建树形结构
*/
private static List<ThreeNode> getTree(List<ThreeNode> nodeList, Integer parentId) {
List<ThreeNode> threeNodeList = new ArrayList<>() ;
for (ThreeNode entity : nodeList) {
Integer nodeId = entity.getId() ;
Integer nodeParentId = entity.getParentId() ;
if (parentId.intValue() == nodeParentId.intValue()) {
List<ThreeNode> childList = getTree(nodeList,nodeId) ;
if (childList != null && childList.size()>0){
entity.setChildNode(childList);
entity.setChildNodeSize(childList.size());
}
threeNodeList.add(entity) ;
}
}
return threeNodeList ;
}
/**
* 获取指定子节点
*/
private static List<ThreeNode> getChildTree (Integer id,List<ThreeNode> nodeList){
List<ThreeNode> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
for (ThreeNode entity : nodeList) {
if (entity.getParentId().intValue() == id) {
List<ThreeNode> childList = getChildTree(entity.getId(),nodeList) ;
entity.setChildNode(childList);
entity.setChildNodeSize(childList.size());
resultList.add(entity) ;
}
}
return resultList ;
}
/**
* 遍历树形结构
*/
private static transient List<Integer> treeIdList = new ArrayList<>() ;
private static List<Integer> getTreeInfo (List<ThreeNode> treeList){
for (ThreeNode entity : treeList) {
if (entity.getChildNodeSize()!=null && entity.getChildNodeSize()>0){
getTreeInfo(entity.getChildNode());
}
treeIdList.add(entity.getId());
}
return treeIdList ;
}
/**
* 判断节是否是叶子节点
*/
private static boolean hasChildNode (Integer id,List<ThreeNode> nodeList){
for (ThreeNode entity:nodeList){
if (entity.getParentId().intValue() == id){
return true ;
}
}
return false ;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<ThreeNode> threeNodeList = new ArrayList<>() ;
threeNodeList.add(new ThreeNode(1,"节点A",0)) ;
threeNodeList.add(new ThreeNode(2,"节点B",1)) ;
threeNodeList.add(new ThreeNode(3,"节点C",1)) ;
threeNodeList.add(new ThreeNode(4,"节点D",1)) ;
threeNodeList.add(new ThreeNode(5,"节点E",2)) ;
threeNodeList.add(new ThreeNode(6,"节点F",2)) ;
// 测试1
List<ThreeNode> getTree = getTree(threeNodeList,0) ;
System.out.println(getTree);
// 测试2
// List<ThreeNode> getChildTree = getChildTree(2,threeNodeList) ;
// System.out.println(getChildTree);
// 测试3
List<Integer> treeIdList = getTreeInfo(getTree) ;
System.out.println(treeIdList);
// 测试4
System.out.println(hasChildNode(2,threeNodeList)) ;
}
}“基于Java递归算法的封装解决方法是什么”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注亿速云网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。