这期内容当中小编将会给大家带来有关android设备的cpu和内存如何使用Python实现获取,文章内容丰富且以专业的角度为大家分析和叙述,阅读完这篇文章希望大家可以有所收获。
功能:获取android设备中某一个app的cpu和内存
环境:python和adb
使用方法:使用adb连接android设备,打开将要测试的app,执行cpu/内存代码
cpu获取代码如下:(输入参数为脚本执行时间)
# coding:utf-8
'''
获取系统total cpu
'''
import os, csv
import time
import csv
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
cpu_list = []
time_list = []
app_list = []
lines = []
package_name = []
# 读取进程名称(包名)
def get_applist():
global package_name
with open('config/director.txt', encoding='utf-8', mode='r') as f:
lines_all = f.readlines()
for appname in lines_all:
package_name1 = appname
appname_new = appname[0:15]
package_name.append(package_name1)
lines.append(appname_new)
for line in lines:
app_list.append(line.strip())
# 获取cpu数值
def get_cpu():
global filename
with open(filename, encoding="utf-8", mode="r") as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for appname in app_list:
for lis in lines:
# 适配低版本手机
if appname in lis and '%' in lis:
now = time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
time_list.append(now)
cpu_1 = lis.split('%')[0]
cpu_2 = cpu_1.split(' ')
# print(cpu_2)
cpu = cpu_2[len(cpu_2) - 1]
print(cpu, now)
cpu_list.append(cpu)
break
# 适配高版本手机
elif appname in lis:
now = time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
time_list.append(now)
cpu1 = lis.split(' ')
# print(cpu1)
cpu2 = list(set(cpu1))
cpu2.sort(key=cpu1.index)
cpu_h = cpu2[len(cpu2) - 4]
print(cpu_h, now)
cpu_list.append(cpu_h)
break
else:
pass
# csv头部
def write_head():
headers = ['name:']
headers.append(app_list[0])
headers.append('init_cpu')
with open('log_su/cpuinfo.csv', 'w+', newline='') as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=headers)
writer.writeheader()
# 将数值写入csv,用于绘图时读取
def write_report():
# headers = ['name', 'aaa', 'init_cpu']
with open('log_su/cpuinfo.csv', 'a+', newline='') as csvfile:
writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
for key in cpu_list:
writer.writerow([' ', ' ', key])
# 绘制折线图,生成测试报告
def mapping():
filename = 'log_su/cpuinfo.csv'
with open(filename) as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
header_row = next(reader)
highs = []
for row in reader:
high = row[2]
highs.append(high)
# print(highs)
wights = time_list
highs_float = list(map(float, highs))
# print(f"****{highs}")
print(f"CPU值:{highs_float}")
# 输出平均值
total = 0
for value in highs_float:
total += value
average = round(total/len(highs_float), 2)
print(f"CPU平均值:{average}")
#输出最低值和最高值
highs_hl = sorted(highs_float)
print(f"CPU最低值:{highs_hl[0]}")
print(f"CPU最高值:{highs_hl[len(highs_hl)-1]}")
# 根据数据绘制图形
plt.figure(figsize=(11, 4), dpi=600)
# 生成网格
# plt.grid()
plt.grid(axis="y")
# 折线图
if package_name[0] == 'com.oneapp.max.security.pro.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="PPP")
elif package_name[0] == 'com.oneapp.max.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="Opt1.6.1")
elif package_name[0] == 'com.boost.clean.coin.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="Fastclear")
elif package_name[0] == 'com.walk.sports.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="Walk")
elif package_name[0] == 'com.diamond.coin.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="Amber")
elif package_name[0] == 'com.oneapp.max.cleaner.booster.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="Space")
else:
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label=package_name[0])
# 坐标轴范围
# plt.ylim(300, 400)
# plt.xlim(0, 10)
plt.xlabel('time(H:Min:S)', fontsize=16)
plt.ylabel("cpu_realtime(%)", fontsize=16)
plt.title("cpu real time line chart", fontsize=24)
plt.legend()
# 横坐标显示间隔
if len(wights) <= 15:
pass
else:
t = int(len(wights) / 15)
plt.xticks(range(0, len(wights), t))
# 纵坐标显示间隔
# plt.yticks(range(100, 300, 10))
# 旋转日期
plt.gcf().autofmt_xdate()
# 展示每个坐标
# for a, b in zip(wights, highs_float):
# plt.text(a, b, (a, b), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=8)
# plt.show()
time_now = time.strftime("%m%d-%H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
path = "report/" + time_now
plt.savefig(path)
# 自动识别当前需检测的
def name_app():
cmd = 'adb shell dumpsys window | grep mCurrentFocus > log_su/name_info.csv'
os.system(cmd)
with open('log_su/name_info.csv', encoding='utf-8', mode='r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
if 'mCurrentFocus' in line:
name1 = line.split('/')[0].split(' ')
name = name1[len(name1) - 1]
with open('config/director.txt', encoding='utf-8', mode='w') as f_name:
text = name
f_name.write(text)
print(f"将要监测的包名为:{text}")
#控制监测时间
def time_control():
global filename
while True:
end_time = time.time()
if (end_time - start_time)/60 >= tol_time: #分钟
# if end_time - start_time >= tol_time: # 秒
break
time.sleep(1)
adb = "adb shell top -n 1 > log_su/adb_info.csv"
d = os.system(adb)
filename = "log_su/adb_info.csv"
get_cpu()
if __name__ == "__main__":
name_app()
tol_time = int(input("请输入脚本执行时间(分钟):"))
start_time = time.time()
get_applist()
write_head()
time_control()
write_report()
mapping()会在.py文件同级目录下生成3个文件夹,config、log_su、report,其中运行结果在report中
结果以是生成折线图,看起来直观,如下:
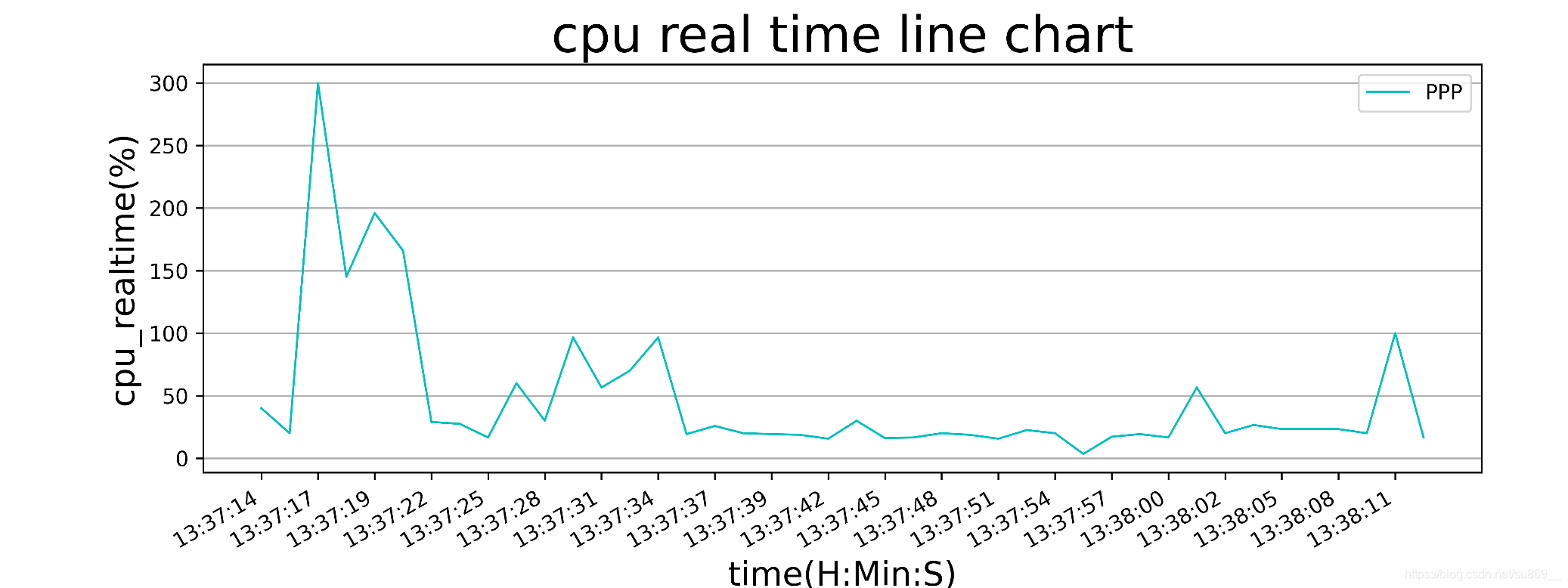
这里我解释下,cpu占比是adb获取的实时占比,但是满值并不一定是100%,比如这张图,用的是一个八核的手机,所以CPU满值是800%
内存获取代码如下:(输入参数为脚本执行时间)
# coding:utf-8
'''
获取系统total memory
'''
import os, csv
import time
import csv
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
mem_dict = {}
time_list = []
app_list = []
package_name = []
t = 0
def get_applist():
global package_name
with open('config/director.txt', encoding='utf-8', mode='r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
package_name1 = line
package_name.append(package_name1)
app_list.append(line.strip())
def get_mem():
global filename
with open(filename, encoding="utf-8", mode="r") as f:
lines = f.readlines()
start_flag = False
for appname in app_list:
for line in lines:
if "Total PSS by OOM adjustment" in line:
break
if appname in line and 'pid' in line and 'kB' in line:
mem_v = line.strip().split(':')[0].replace('kB', '').replace(',', '')
line_name = line.split(':')[1].split('(')[0].strip()
if line_name in appname:
mem_v = round(float(mem_v) / 1024, 2)
mem_dict[appname] = mem_v
now_v = time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
# now_int = int(now_v)
time_list.append(now_v)
print(mem_v, now_v)
break
elif appname in line and 'pid' in line and 'K' in line:
mem_v = line.strip().split(':')[0].replace('K', '').replace(',', '')
line_name = line.split(':')[1].split('(')[0].strip()
if line_name in appname:
mem_v = round(float(mem_v) / 1024, 2)
mem_dict[appname] = mem_v
now_v = time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
# now_int = int(now_v)
time_list.append(now_v)
print(mem_v, now_v)
break
def write_head():
headers = ['name:']
headers.append(app_list[0])
headers.append('init_mem')
with open('log_su/meminfo.csv', 'w+', newline='') as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=headers)
writer.writeheader()
def write_report():
headers = ['name','aaa', 'init_mem']
with open('log_su/meminfo.csv', 'a+', newline='') as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=headers)
for key in mem_dict:
writer.writerow({'init_mem': mem_dict[key]})
def mapping():
filename = 'log_su/meminfo.csv'
with open(filename) as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
header_row = next(reader)
highs = []
for row in reader:
high = row[2]
highs.append(high)
# print(highs)
wights = time_list
highs_float = list(map(float, highs))
print(f"内存值:{highs_float}")
# 输出平均值
total = 0
for value in highs_float:
total += value
average = round(total / len(highs_float), 2)
print(f"内存平均值:{average}")
# 输出最低值和最高值
highs_hl = sorted(highs_float)
print(f"内存最低值:{highs_hl[0]}")
print(f"内存最高值:{highs_hl[len(highs_hl) - 1]}")
# 根据数据绘制图形
plt.figure(figsize=(11, 4), dpi=600)
# 生成网格
# plt.grid()
plt.grid(axis="y")
if package_name[0] == 'com.oneapp.max.security.pro.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="PPP")
elif package_name[0] == 'com.oneapp.max.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="Opt")
elif package_name[0] == 'com.boost.clean.coin.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="fastclear")
elif package_name[0] == 'com.walk.sports.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="Walk")
elif package_name[0] == 'com.diamond.coin.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="Amber")
elif package_name[0] == 'com.oneapp.max.cleaner.booster.cn':
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label="Space")
else:
plt.plot(wights, highs_float, "c-", linewidth=1, label=package_name[0])
# 坐标轴范围
# plt.ylim(300, 400)
# plt.xlim(0, 10)
plt.xlabel('time(H:Min:S)', fontsize=16)
plt.ylabel("Number (Mb)", fontsize=16)
plt.title("meminfo", fontsize=24)
plt.legend()
# 横坐标显示间隔
if len(wights) <= 15:
pass
else:
t = int(len(wights) / 15)
plt.xticks(range(0, len(wights), t))
# 坐标刻度
# my_y_ticks = np.arange(300, 400, 10)
# my_x_ticks = np.arange(1, 10, 1)
# plt.xticks(my_x_ticks)
# plt.yticks(my_y_ticks)
# plt.yticks(range(100, 300, 10))
#旋转日期
plt.gcf().autofmt_xdate()
# 展示每个坐标
# for a, b in zip(wights, highs_float):
# plt.text(a, b, (a, b), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=8)
# plt.show()
time_now = time.strftime("%m%d-%H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
path = "report/" + time_now
plt.savefig(path)
def name_app():
cmd = 'adb shell dumpsys window | grep mCurrentFocus > log_su/name_info.csv'
os.system(cmd)
with open('log_su/name_info.csv', encoding='utf-8', mode='r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
if 'mCurrentFocus' in line:
name1 = line.split('/')[0].split(' ')
name = name1[len(name1) - 1]
with open('config/director.txt', encoding='utf-8', mode='w') as f_name:
text = name
f_name.write(text)
print(f"将要监测的包名为:{text}")
def time_control():
global filename
while True:
end_time = time.time()
if (end_time - start_time)/60 >= tol_time: #分钟
# if end_time - start_time >= tol_time: #秒
break
# time.sleep(2)
# filename = str(input("请输入文件名:"))
adb = "adb shell dumpsys meminfo > log_su/adb_info.csv"
d = os.system(adb)
filename = "log_su/adb_info.csv"
get_mem()
write_report()
if __name__ == "__main__":
name_app()
tol_time = int(input("请输入脚本执行时间(分钟):"))
start_time = time.time()
get_applist()
write_head()
time_control()
mapping()会在.py文件同级目录下生成3个文件夹,config、log_su、report,其中运行结果在report中
生成的内存结果图如下:
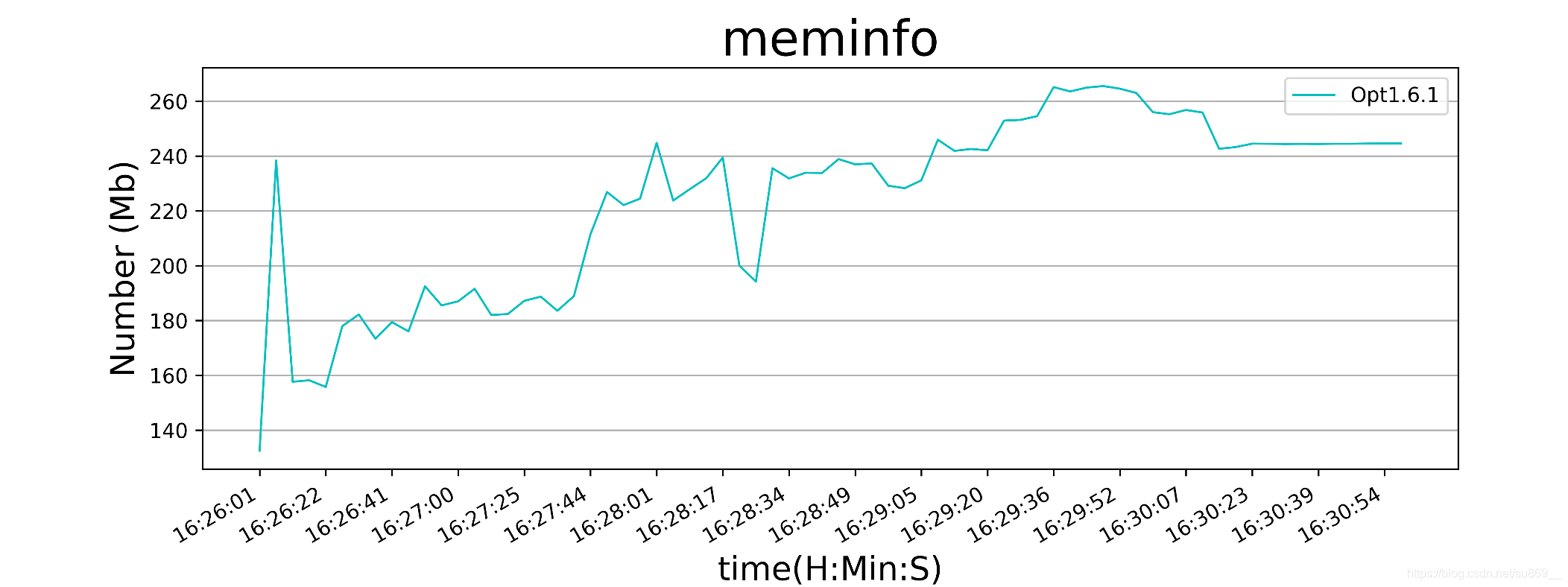
上述就是小编为大家分享的android设备的cpu和内存如何使用Python实现获取了,如果刚好有类似的疑惑,不妨参照上述分析进行理解。如果想知道更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。