from django.contrib import auth
这个模块中提供了许多方法
user = authenticate(username='someone',password='somepassword')
验证用户名与密码是否正确,一般需要username和password两个关键字参数。
认证通过,返回值是一个User对象。用户名或密码不正确,返回None。
用户名和密码正确
user.is_authenticated=True
user.is_anonymous=false
authenticate()会在User对象上设置一个属性,标识后端认证了该用户,而且该属性在后面的登录过程中也是需要的。
如果我们直接从数据库中使用filter()取出User对象(不使用authenticate()方法获取User对象),是不能使用的。该函数接受一个HttpRequest对象和通过authenticate()验证过的User对象。
该函数使用django的session框架给已经认证的用户加上session id等信息
from django.contrib.auth import authenticate, login
def my_view(request):
username = request.POST['username']
password = request.POST['password']
user = authenticate(username=username, password=password)
if user is not None:
login(request, user)
# Redirect to a success page.
...
else:
# Return an 'invalid login' error message.
...from django.contrib.auth import logout
def logout_view(request):
logout(request)
# Redirect to a success page.
该函数接受一个HttpRequest对象,没有返回值。
当调用该函数时,当前请求的session信息会被全部删除。
该用户即使没有登陆,使用该函数也不会报错。User对象属性:username,password(用hash算法保存到数据库中)检查用户是否suthenticate验证过。
user = auth.authenticate(username=user,password=pwd)
print(user.is_authenticated)
print(user.is_anonymous)
用户名和密码正确,
user.is_authenticated=True,
user.is_anonymous=False要求:
1.用户登录后,才能访问其他页面
2.如果没有登陆,就跳转到登录页面
3.用户在登录页面登录后,自动跳转到之前访问的地址
方法一:
def index(request):
# 没有登陆过,第一次访问index页面,request.user状况如下
print(request.user) # AnonymousUser
print(request.user.is_anonymous) # true
print(request.user.is_authenticated) # false
# 如果用户登录成功,is_authenticated会返回true,request.user.is_anonymous返回false
if request.user.is_authenticated:
return render(request,"index.html")
else:
return redirect('%s?next=%s' % (settings.LOGIN_URL, request.path))
# /login/登录成功后,可以在login中通过return redirect(request.GET.get("next", "/index/"))会重定向到/index/
#request.GET.get("next", "/index/")是如果没有next这个key,设置默认值为/index/
方法二:
# 使用这个装饰器,就不需要像index方法那样,手动判断用户是否登录了。
# 如果用户没有登陆,自动跳转到settings.py中配置的LOGIN_URL路径。此时url为http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/?next=/order/
# /login/登录成功后,可以在login中通过return redirect(request.GET.get("next", "/index/"))会重定向到/order/
@login_required
def order(request):
return HttpResponse("order")
settings.py中配置
LOGIN_URL = "/login/"from django.contrib.auth.models import User
user = User.objects.create_user(username='',password='',email='')当用户修改密码的时候,要让用户输入旧密码,验证输入的旧密码正确,才允许修改密码。
输入的旧密码正确,返回True,否则返回false。user = request.user user.set_password(new_password) user.save
"注册"
def sign_up(request):
state = None
if request.method == 'POST':
password = request.POST.get('password', '')
repeat_password = request.POST.get('repeat_password', '')
email=request.POST.get('email', '')
username = request.POST.get('username', '')
if User.objects.filter(username=username):
state = 'user_exist'
else:
new_user = User.objects.create_user(username=username, password=password,email=email)
return redirect('/book/')
content = {
'state': state,
'user': None,
}
return render(request, 'sign_up.html', content)"修改密码"
@login_required
def set_password(request):
user = request.user
state = None
if request.method == 'POST':
old_password = request.POST.get('old_password', '')
new_password = request.POST.get('new_password', '')
repeat_password = request.POST.get('repeat_password', '')
if user.check_password(old_password):
if not new_password:
state = 'empty'
elif new_password != repeat_password:
state = 'repeat_error'
else:
user.set_password(new_password)
user.save()
return redirect("/log_in/")
else:
state = 'password_error'
content = {
'user': user,
'state': state,
}
return render(request, 'set_password.html', content)views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect
from django.contrib import auth
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import login_required
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
def login(request):
if request.method == "POST":
user = request.POST.get("user")
pwd = request.POST.get("pwd")
# 验证用户名和密码是否正确,如果正确,返回user对象
user = auth.authenticate(username=user,password=pwd)
if user:
auth.login(request, user)
# 用户在登录页面登录后,自动跳转到之前访问的地址
# 如果当前访问/order/,会跳转到login,此时url中为http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/?next=/order/
# 所以可以通过request.GET.get("next", "/index/")获取刚刚访问的路径,
# 如果当前直接访问的是login,则为http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/,访问成功后,跳转到/index/
next_url = request.GET.get("next", "/index/")
return redirect(next_url)
# get请求时,返回login页面
return render(request, "login.html")
def index(request):
# 如果用户登录成功,is_authenticated会返回true,request.user.is_anonymous返回false
if request.user.is_authenticated:
return render(request,"index.html")
else:
return redirect("/login/")
# 使用这个装饰器,就不需要像index方法那样,手动判断用户是否登录了。
# 如果用户没有登陆,自动跳转到settings.py中配置的LOGIN_URL路径。
@login_required
def order(request):
return HttpResponse("order")
def logout(request):
auth.logout(request)
def reg(request):
if request.method == "POST":
user = request.POST.get("user")
pwd = request.POST.get("pwd")
user = User.objects.create_user(username=user, password=pwd)
return redirect("/login/")
return render(request, "reg.html")settings.py
LOGIN_URL = "/login/"login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
用户名 <input type="text" name="user">
密码 <input type="text" name="pwd">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>reg.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/reg/" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
用户名 <input type="text" name="user">
密码 <input type="text" name="pwd">
<input type="submit" value="注册">
</form>
</body>
</html>index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>
</title>
</head>
<body>
{#后端返回request对象,在前段获取用户名#}
<h4>当前用户{{ request.user.username }}</h4>
<a href="/logout/">注销</a>
</body>
</html>"首先注册账户,访问reg"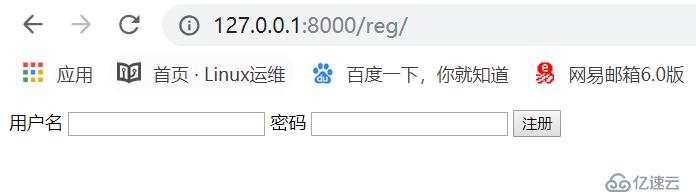
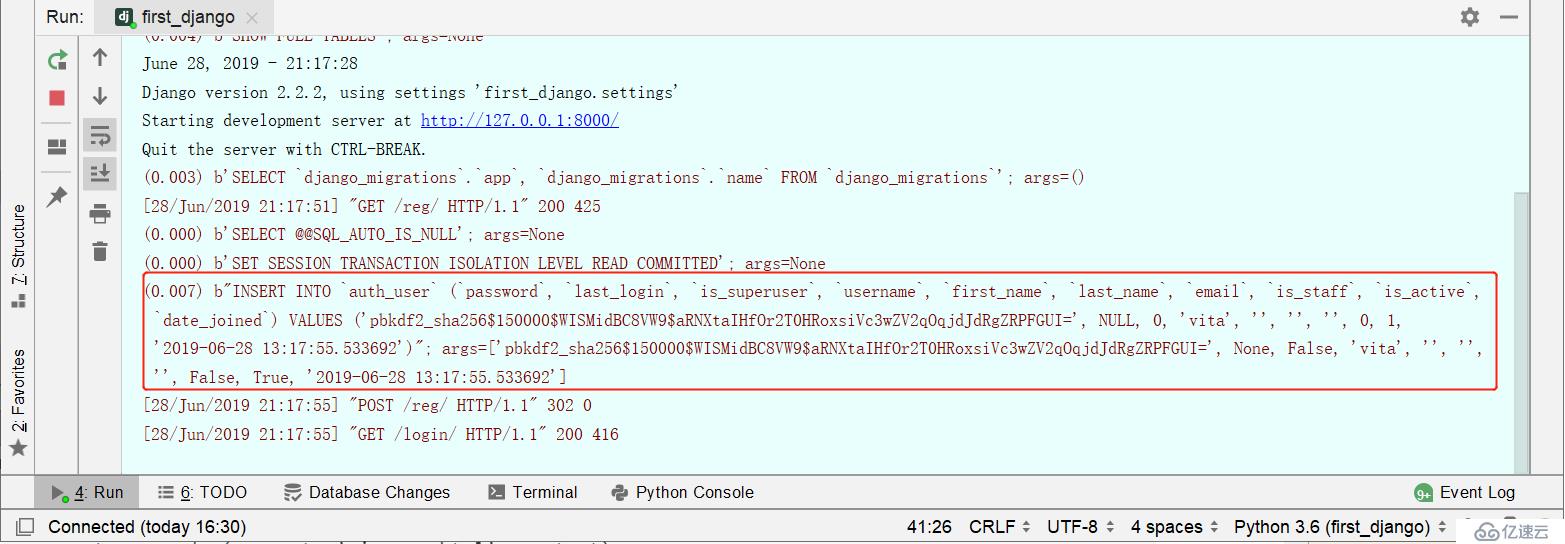
"login"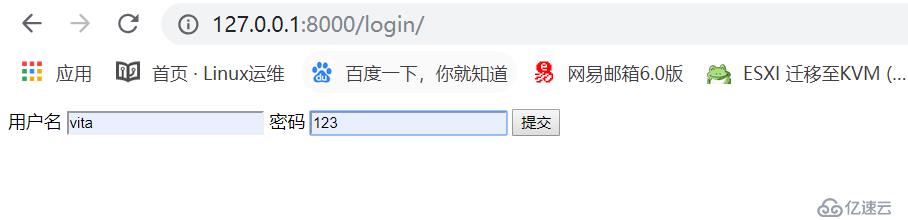
"登录成功"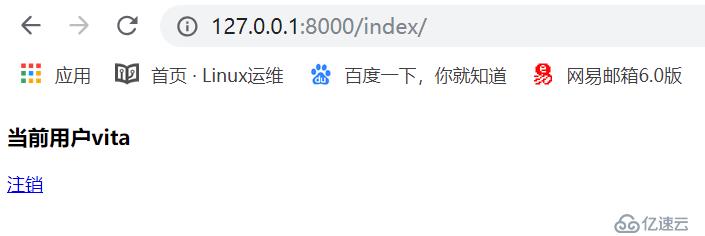
"完整项目查看本人的git哦!!!!!!"亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。