小编给大家分享一下Vue3模板编译优化的示例分析,相信大部分人都还不怎么了解,因此分享这篇文章给大家参考一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后大有收获,下面让我们一起去了解一下吧!
编译入口
了解过 Vue3 的同学肯定知道 Vue3 引入了新的组合 Api,在组件 mount 阶段会调用 setup 方法,之后会判断 render 方法是否存在,如果不存在会调用 compile 方法将 template 转化为 render。
// packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts const mountComponent = (initialVNode, container) => { const instance = ( initialVNode.component = createComponentInstance( // ...params ) ) // 调用 setup setupComponent(instance) } // packages/runtime-core/src/component.ts let compile export function registerRuntimeCompiler(_compile) { compile = _compile } export function setupComponent(instance) { const Component = instance.type const { setup } = Component if (setup) { // ...调用 setup } if (compile && Component.template && !Component.render) { // 如果没有 render 方法 // 调用 compile 将 template 转为 render 方法 Component.render = compile(Component.template, {...}) } }这部分都是 runtime-core 中的代码,之前的文章有讲过 Vue 分为完整版和 runtime 版本。如果使用 vue-loader 处理 .vue 文件,一般都会将 .vue 文件中的 template 直接处理成 render 方法。
// 需要编译器 Vue.createApp({ template: '<div>{{ hi }}</div>' }) // 不需要 Vue.createApp({ render() { return Vue.h('div', {}, this.hi) } })完整版与 runtime 版的差异就是,完整版会引入 compile 方法,如果是 vue-cli 生成的项目就会抹去这部分代码,将 compile 过程都放到打包的阶段,以此优化性能。runtime-dom 中提供了 registerRuntimeCompiler 方法用于注入 compile 方法。
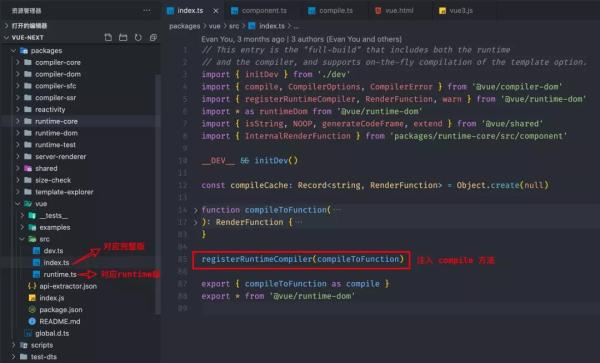
主流程
在完整版的 index.js 中,调用了 registerRuntimeCompiler 将 compile 进行注入,接下来我们看看注入的 compile 方法主要做了什么。
// packages/vue/src/index.ts import { compile } from '@vue/compiler-dom' // 编译缓存 const compileCache = Object.create(null) // 注入 compile 方法 function compileToFunction( // 模板 template: string | HTMLElement, // 编译配置 options?: CompilerOptions ): RenderFunction { if (!isString(template)) { // 如果 template 不是字符串 // 则认为是一个 DOM 节点,获取 innerHTML if (template.nodeType) { template = template.innerHTML } else { return NOOP } } // 如果缓存中存在,直接从缓存中获取 const key = template const cached = compileCache[key] if (cached) { return cached } // 如果是 ID 选择器,这获取 DOM 元素后,取 innerHTML if (template[0] === '#') { const el = document.querySelector(template) template = el ? el.innerHTML : '' } // 调用 compile 获取 render code const { code } = compile( template, options ) // 将 render code 转化为 function const render = new Function(code)(); // 返回 render 方法的同时,将其放入缓存 return (compileCache[key] = render) } // 注入 compile registerRuntimeCompiler(compileToFunction)在讲 Vue2 模板编译的时候已经讲过,compile 方法主要分为三步,Vue3 的逻辑类似:
鸿蒙官方战略合作共建——HarmonyOS技术社区
模板编译,将模板代码转化为 AST;
优化 AST,方便后续虚拟 DOM 更新;
生成代码,将 AST 转化为可执行的代码;
// packages/compiler-dom/src/index.ts import { baseCompile, baseParse } from '@vue/compiler-core' export function compile(template, options) { return baseCompile(template, options) } // packages/compiler-core/src/compile.ts import { baseParse } from './parse' import { transform } from './transform' import { transformIf } from './transforms/vIf' import { transformFor } from './transforms/vFor' import { transformText } from './transforms/transformText' import { transformElement } from './transforms/transformElement' import { transformOn } from './transforms/vOn' import { transformBind } from './transforms/vBind' import { transformModel } from './transforms/vModel' export function baseCompile(template, options) { // 解析 html,转化为 ast const ast = baseParse(template, options) // 优化 ast,标记静态节点 transform(ast, { ...options, nodeTransforms: [ transformIf, transformFor, transformText, transformElement, // ... 省略了部分 transform ], directiveTransforms: { on: transformOn, bind: transformBind, model: transformModel } }) // 将 ast 转化为可执行代码 return generate(ast, options) }计算 PatchFlag
这里大致的逻辑与之前的并没有多大的差异,主要是 optimize 方法变成了 transform 方法,而且默认会对一些模板语法进行 transform。这些 transform 就是后续虚拟 DOM 优化的关键,我们先看看 transform 的代码 。
// packages/compiler-core/src/transform.ts export function transform(root, options) { const context = createTransformContext(root, options) traverseNode(root, context) } export function traverseNode(node, context) { context.currentNode = node const { nodeTransforms } = context const exitFns = [] for (let i = 0; i < nodeTransforms.length; i++) { // Transform 会返回一个退出函数,在处理完所有的子节点后再执行 const onExit = nodeTransforms[i](node, context) if (onExit) { if (isArray(onExit)) { exitFns.push(...onExit) } else { exitFns.push(onExit) } } } traverseChildren(node, context) context.currentNode = node // 执行所以 Transform 的退出函数 let i = exitFns.length while (i--) { exitFns[i]() } }我们重点看一下 transformElement 的逻辑:
// packages/compiler-core/src/transforms/transformElement.ts export const transformElement: NodeTransform = (node, context) => { // transformElement 没有执行任何逻辑,而是直接返回了一个退出函数 // 说明 transformElement 需要等所有的子节点处理完后才执行 return function postTransformElement() { const { tag, props } = node let vnodeProps let vnodePatchFlag const vnodeTag = node.tagType === ElementTypes.COMPONENT ? resolveComponentType(node, context) : `"${tag}"` let patchFlag = 0 // 检测节点属性 if (props.length > 0) { // 检测节点属性的动态部分 const propsBuildResult = buildProps(node, context) vnodeProps = propsBuildResult.props patchFlag = propsBuildResult.patchFlag } // 检测子节点 if (node.children.length > 0) { if (node.children.length === 1) { const child = node.children[0] // 检测子节点是否为动态文本 if (!getStaticType(child)) { patchFlag |= PatchFlags.TEXT } } } // 格式化 patchFlag if (patchFlag !== 0) { vnodePatchFlag = String(patchFlag) } node.codegenNode = createVNodeCall( context, vnodeTag, vnodeProps, vnodeChildren, vnodePatchFlag ) } }buildProps 会对节点的属性进行一次遍历,由于内部源码涉及很多其他的细节,这里的代码是经过简化之后的,只保留了 patchFlag 相关的逻辑。
export function buildProps( node: ElementNode, context: TransformContext, props: ElementNode['props'] = node.props ) { let patchFlag = 0 for (let i = 0; i < props.length; i++) { const prop = props[i] const [key, name] = prop.name.split(':') if (key === 'v-bind' || key === '') { if (name === 'class') { // 如果包含 :class 属性,patchFlag | CLASS patchFlag |= PatchFlags.CLASS } else if (name === 'style') { // 如果包含 :style 属性,patchFlag | STYLE patchFlag |= PatchFlags.STYLE } } } return { patchFlag } }上面的代码只展示了三种 patchFlag 的类型:
节点只有一个文本子节点,且该文本包含动态的数据(TEXT = 1)
<p>name: {{name}}</p>节点包含可变的 class 属性(CLASS = 1 << 1)
<div :class="{ active: isActive }"></div>节点包含可变的 style 属性(STYLE = 1 << 2)
<div :style="{ color: color }"></div>可以看到 PatchFlags 都是数字 1 经过 左移操作符 计算得到的。
export const enum PatchFlags { TEXT = 1, // 1, 二进制 0000 0001 CLASS = 1 << 1, // 2, 二进制 0000 0010 STYLE = 1 << 2, // 4, 二进制 0000 0100 PROPS = 1 << 3, // 8, 二进制 0000 1000 ... }从上面的代码能看出来,patchFlag 的初始值为 0,每次对 patchFlag 都是执行 | (或)操作。如果当前节点是一个只有动态文本子节点且同时具有动态 style 属性,最后得到的 patchFlag 为 5(二进制:0000 0101)。
<p :style="{ color: color }">name: {{name}}</p>
我们将上面的代码放到 Vue3 中运行:
const app = Vue.createApp({ data() { return { color: 'red', name: 'shenfq' } }, template: `<div> <p :style="{ color: color }">name: {{name}}</p> </div>` }) app.mount('#app')最后生成的 render 方法如下,和我们之前的描述基本一致。
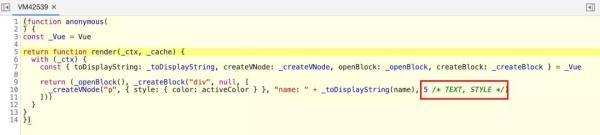
function render() {}
render 优化
Vue3 在虚拟 DOM Diff 时,会取出 patchFlag 和需要进行的 diff 类型进行 &(与)操作,如果结果为 true 才进入对应的 diff。
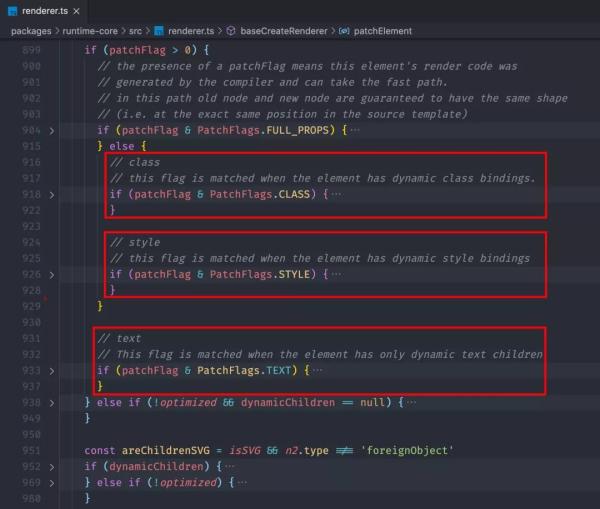
patchFlag 判断
还是拿之前的模板举例:
<p :style="{ color: color }">name: {{name}}</p>如果此时的 name 发生了修改,p 节点进入了 diff 阶段,此时会将判断 patchFlag & PatchFlags.TEXT ,这个时候结果为真,表明 p 节点存在文本修改的情况。

patchFlag
patchFlag = 5 patchFlag & PatchFlags.TEXT // 或运算:只有对应的两个二进位都为1时,结果位才为1。 // 0000 0101 // 0000 0001 // ------------ // 0000 0001 => 十进制 1
if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.TEXT) { if (oldNode.children !== newNode.children) { // 修改文本 hostSetElementText(el, newNode.children) } }但是进行 patchFlag & PatchFlags.CLASS 判断时,由于节点并没有动态 Class,返回值为 0,所以就不会对该节点的 class 属性进行 diff,以此来优化性能。

patchFlag
patchFlag = 5 patchFlag & PatchFlags.CLASS // 或运算:只有对应的两个二进位都为1时,结果位才为1。 // 0000 0101 // 0000 0010 // ------------ // 0000 0000 => 十进制 0
以上是“Vue3模板编译优化的示例分析”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。