本篇内容主要讲解“怎么移除List中的元素”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“怎么移除List中的元素”吧!
我们先看下这段代码,你有没有写过类似的代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println("开始添加元素 size:" + list.size());
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
list.add(i + 1);
}
System.out.println("元素添加结束 size:" + list.size());
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer next = iterator.next();
if (next % 5 == 0) {
list.remove(next);
}
}
System.out.println("执行结束 size:" + list.size());
}
「毫无疑问,执行这段代码之后,必然报错,我们看下报错信息。」
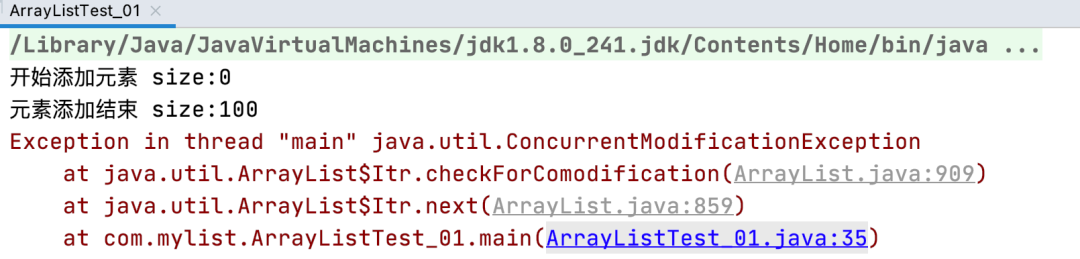
我们可以通过错误信息可以看到,具体的错误是在checkForComodification 这个方法产生的。
首先我们看下ArrayList的iterator这个方法,通过源码可以发现,其实这个返回的是ArrayList内部类的一个实例对象。
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
我们看下Itr类的全部实现。
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
「参数说明:」
cursor : 下一次访问的索引;
lastRet :上一次访问的索引;
expectedModCount :对ArrayList修改次数的期望值,初始值为modCount;
modCount :它是AbstractList的一个成员变量,表示ArrayList的修改次数,通过add和remove方法可以看出;
「几个常用方法:」
hasNext():
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
如果下一个访问元素的下标不等于size,那么就表示还有元素可以访问,如果下一个访问的元素下标等于size,那么表示后面已经没有可供访问的元素。因为最后一个元素的下标是size()-1,所以当访问下标等于size的时候必定没有元素可供访问。
next():
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
注意下,这里面有两个非常重要的地方,cursor初始值是0,获取到元素之后,cursor 加1,那么它就是下次索要访问的下标,最后一行,将i赋值给了lastRet这个其实就是上次访问的下标。
此时,cursor变为了1,lastRet变为了0。
最后我们看下ArrayList的remove()方法做了什么?
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
「重点:」
我们先记住这里,modCount初始值是0,删除一个元素之后,modCount自增1,接下来就是删除元素,最后一行将引用置为null是为了方便垃圾回收器进行回收。
到这里,其实一个完整的判断、获取、删除已经走完了,此时我们回忆下各个变量的值:
cursor : 1(获取了一次元素,默认值0自增了1);
lastRet :0(上一个访问元素的下标值);
expectedModCount :0(初始默认值);
modCount :1(进行了一次remove操作,变成了1);
不知道你还记不记得,next()方法中有两次检查,如果已经忘记的话,建议你往上翻一翻,我们来看下这个判断:
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
当modCount不等于expectedModCount的时候抛出异常,那么现在我们可以通过上面各变量的值发现,两个变量的值到底是多少,并且知道它们是怎么演变过来的。那么现在我们是不是清楚了ConcurrentModificationException异常产生的愿意呢!
「就是因为,list.remove()导致modCount与expectedModCount的值不一致从而引发的问题。」
我们现在知道引发这个问题,是因为两个变量的值不一致所导致的,那么有没有什么办法可以解决这个问题呢!答案肯定是有的,通过源码可以发现,Iterator里面也提供了remove方法。
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
你看它做了什么,它将modCount的值赋值给了expectedModCount,那么在调用next()进行检查判断的时候势必不会出现问题。
那么以后如果需要remove的话,千万不要使用list.remove()了,而是使用iterator.remove(),这样其实就不会出现异常了。
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println("开始添加元素 size:" + list.size());
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
list.add(i + 1);
}
System.out.println("元素添加结束 size:" + list.size());
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer next = iterator.next();
if (next % 5 == 0) {
iterator.remove();
}
}
System.out.println("执行结束 size:" + list.size());
}「建议:」
另外告诉大家,我们在进行测试的时候,如果找不到某个类的实现类,因为有时候一个类有超级多的实现类,但是你不知道它到底调用的是哪个,那么你就通过debug的方式进行查找,是很便捷的方法。
到此,相信大家对“怎么移除List中的元素”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。