本篇内容介绍了“spring框架入门之怎么使用切面编程AOP”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
特点:字节码随用随创建,随用随加载
作用:在不修改源码的基础上对方法进行增强
分类:
| 基于接口的动态代理 | 基于子类的动态代理 | |
|---|---|---|
| 涉及的类 | Proxy | Enhancer |
| 提供者 | JDK官方 | 第三方库cglib |
| 如何创建代理对象 | 使用Proxy中的 newProxyInstance 方法 | 使用Enhancer类中的create方法 |
| 创建代理对象的要求 | 被代理类至少实现一个接口,没有则不能使用 | 被代理对象不能是最终类 |
newProxyInstance方法的参数:
ClassLoader : 类加载器。用于加载代理对象字节码,和被代理类使用相同的类加载器。
写法: 代理对象.getClass().getClassLoader()
Class[] : 字节码数组。用于让代理对象和被代理对象有相同方法。
写法: 代理对象.getClass().getInterfaces()
InvocationHandler:用于增强的代码。书写对被代理方法增强的代码,一般书写此接口的实现类,通常情况下是匿名内部类,但不是必须的,此接口的实现类一般谁用到谁写。
InvocationHandler参数中的invoke方法,执行被代理对象的任何接口方法都会经过该方法。方法参数及其含义:
proxy :代理对象的引用
method :当前执行的方法
args:当前执行方法所需的参数
返回值:与被代理类有相同的返回值
代码示例:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ProducerImpl producer = new ProducerImpl();
producer.saleProduct(1000f);// 销售产品,拿到钱1000.0
System.out.println("对方法进行增强后。。。。。");
Producer proxyProduct = (Producer) Proxy.newProxyInstance(producer.getClass().getClassLoader(),
producer.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* 执行被代理对象的任何接口方法都会经过该方法
* 方法的参数含义
* @param proxy 代理对象的引用
* @param method 当前执行方法
* @param args 当前执行方法所需的参数
* @return 和被代理对象有相同的返回值
* @throws Throwable
*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 提供增强的代码
Object returnValue = null;
// 1.获取方法的执行参数
Float money = (Float) args[0];
// 2.判断当前方法是不是销售方法
if ("saleProduct".equals(method.getName())){
returnValue = method.invoke(producer, money * 0.8f);
}
return returnValue;
}
});
proxyProduct.saleProduct(1000f);// 销售产品,拿到钱800.0
}
}create方法的参数:
Class:字节码。用于指定被代理对象的字节码。
Callback:用于提供增强的代码,类似于基于接口的动态代理的invoke方法。一般写的是该接口的子接口实现类 MethodInterceptor
create参数中 MethodInterceptor 的方法参数:
o :代理对象的引用
method :当前执行的方法
objects:当前执行方法所需的参数
methodProxy:当前执行方法的代理对象
代码示例:
public class Client {
final Producer producer = new Producer();
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Producer producer = new Producer();
producer.saleProduct(1000f);// 售卖商品,得到钱1000.0
System.out.println("对方法进行增强后。。。。。");
Producer cglibProducer = (Producer) Enhancer.create(producer.getClass(), new MethodInterceptor() {
/**
* 执行任何被处理对象的任何方法都会经过该方法
* @param o 代理对象的引用
* @param method 当前的执行方法
* @param objects 当前执行方法所需的参数
* @param methodProxy 当前执行方法的代理对象
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
// 提供增强的方法
Object returnValue = null;
// 1.获取当前方法的执行参数
Float money = (Float) objects[0];
// 2.判断当前的方法是不是销售动作
if ("saleProduct".equals(method.getName())){
returnValue = method.invoke(producer, money * 0.8f);
}
return returnValue;
}
});
cglibProducer.saleProduct(1000f);// 售卖商品,得到钱800.0
}
}动态代理的一般使用方式:
获取被代理类对象(被代理对象的字节码、被代理类对象的类加载器等信息)
在代理类提供的方法中对被代理类中的方法进行增强
spring中的AOP是通过配置的方式实现动态代理
**Joinpoint(连接点):**指被拦截到的点。在spring中这些点指的是方法,因为spring只支持方法类型的连接点。可以理解为业务层中所有的方法。
**Pointcut(切入点):**指需要对那些Joinpoint进行拦截的定义。可以理解为被增强的方法。
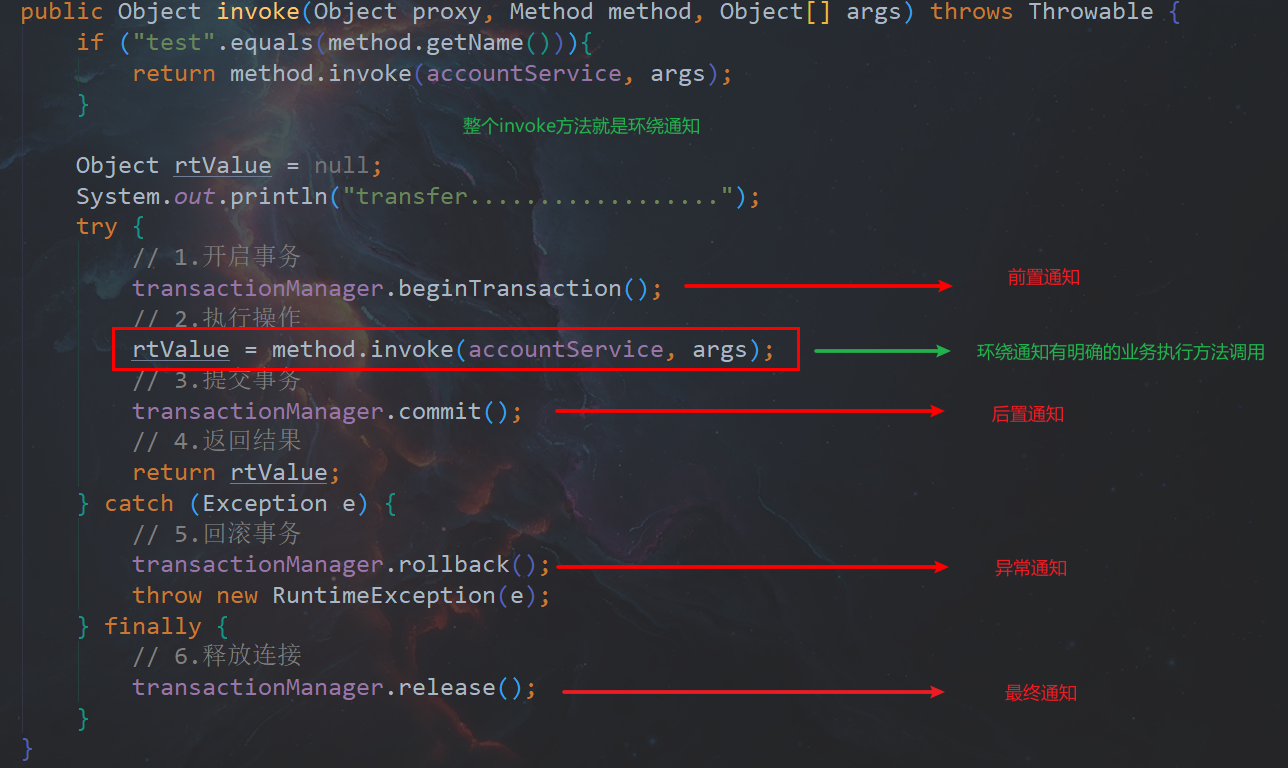
**Advice(通知/增强):**指拦截到Joinpoint后需要做的事情。通知类型:前置通知,后置通知,异常通知,最终通知,环绕通知。
前置通知:在执行业务层方法前的通知;
后置通知:在执行业务层方法后的通知;
异常通知:catch中的通知;
最终通知:在finally中的通知;
环绕通知:整个invoke方法执行就是环绕通知;
**Introduction(引介):**一种特殊的通知在不修改类代码的前提下,Introduction可以在运行期为类动态的添加一些方法或Field。
Target(目标对象):代理的目标对象。
**Weaving(织入):**指把增强应用到目标对象来创建代理对象的过程。spring是动态代理织入的,而AspectJ采用编译期织入和类装载期织入。
**Proxy(代理):**一个类被AOP织入增强后,就产生一个结果代理类。
**Aspect(切面):**是切入点和通知(引介)的结合。
开发阶段:
编写核心业务代码(主线开发,熟悉业务代码即可进行开发)
把公共代码提取出来,制作成通知。(开发最后阶段)
在配置文件中声明切入点与通知之间的关系,即切面。
运行阶段:
spring框架监控切入点的方法执行。一旦监控到切入点方法被运行,使用代理机制,动态创建目标对象的代理对象,通知类别,在代理对象的对应位置,将通知对应的功能织入,完成完整的代码逻辑运行。
spring中的AOP会根据目标是否实现了接口来决定采用哪种动态代理的方式
3.1 将通知类交由IoC容器管理
将通知类注册到spring的IoC容器中
<bean id="" class="">
<property name="" ref=""></property>
</bean>3.2 使用 <aop:config> 标签进行AOP配置
用于声明aop配置
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置的代码写在此处 -->
</aop:config>3.3 使用 <aop:aspect> 配置切面
用于配置切面
属性:
① id属性:是给切面提供一个唯一标识
② ref属性:是指定通知类bean的Id。
<aop:aspect id="" ref="">
<!-- 在这里配置通知类型 -->
</aop:aspect><aop:before>:用于配置前置通知
<aop:after-return>:用于配置后置通知
<aop:after-throwing>:用于配置异常通知
<aop:after>:用于配置最终通知
<aop: around>:用于配置环绕通知
① method属性:用于指定Logger类中哪个方法是前置通知
② pointcut属性:用于指定切入点表达式,该表达式的含义指的是对业务层中哪些方法增强
③ pointcut-ref属性:用于指定切入点表达式的id
3.4 使用 <aop:pointcut> 配置切入点表达式
用于配置切入点表达式,就是指定对那些类进行的那些方法进行增强
属性:
① id属性:用于指定切入点的唯一标识
② expression属性:用于配置切入点表达式
<aop:pointcut id="" expression="execution()"/>代码示例:
<!-- 配置service对象 -->
<bean id="accountService" class="cn.bruce.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="testService" class="cn.bruce.service.impl.TestServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 配置Logger类 -->
<bean id="logger" class="cn.bruce.utils.Logger"></bean>
<!-- 配置AOP -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切面 -->
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="logger">
<!-- 配置通知类型,建立通知方法和切入点方法的关联 -->
<aop:before method="printLog" pointcut="execution(* cn.bruce.service.impl.*.*(..))"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="printLog" pointcut="execution(* cn..impl.Test*.*(cn.bruce.domain.Account))"></aop:after>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>关键字:execution("表达式")
表达式写法:访问修饰符 返回值 包名.***.包名.类名.方法名(参数列表)
标准写法:public void cn.bruce.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount()
访问修饰符可以省略(访问权限不能写 *),表示匹配任意类型的访问权限,但Spring现在只支持public权限;
void cn.bruce.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount()
返回值可以使用通配符,表示任意返回值;
* cn.bruce.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount()
包名可以使用通配符,表示任意包,有几级包就要写几个 *;
* *.*.*.*.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount()
包名可以使用 .. 表示当前包及其子包
* cn..AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount()
类名和方法名都可以使用通配符代替
* *..*.*()
**参数列表:**直接写数据类型
基本数据类型直接写名称,如:int long double boolean
引用数据类型要写全类名,如:cn.bruce.domain.Accout
可以使用通配符 * 表示任意类型,但是必须有参数
可以使用通配符 * 进行占位,如:* *..*.*(*, int)
可以使用 .. 表示有无参数均可,有参数可以是任意类型 * *..*.*(..)
全通配写法:* *..*.*(..)
开发中切入点表达式的通常写法:如:切到业务层实现类下的所有方法 * cn.bruce.service.impl.*.*(..)
前置通知 <aop:before>:在切入点方法执行之前执行
后置通知 <aop:after-returning>:在切入点方法执行之后执行。后置通知和异常通知永远只能执行一个
异常通知 <aop:after-throwing>:在切入点方法执行产生异常后执行。异常通知和后置通知永远只能执行一个
最终通知 <aop:after>:无论切入点方法是否正常执行,它都会在其后面执行
环绕通知 <aop:around>:是spring框架为我们提供的一种可以在代码中手动控制增强方法何时执行的方式。
代码示例:
<!-- 配置AOP -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切入点表达式,id属性是表达式的唯一标识,expression属性用于指定表达式内容
此标签可以写在aop:aspect标签内部只能当前切面使用
写在aop:aspect外面,此时表示所有的切面可用
-->
<aop:pointcut id="loggerPointCut" expression="execution(* cn..impl.Account*.*(..))"/>
<!-- 配置切面 -->
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="logger">
<!-- 前置通知:在切入点方法执行之前执行 -->
<aop:before method="beforePrintLog" pointcut-ref="loggerPointCut"></aop:before>
<!-- 后置通知:在切入点方法执行之后执行。后置通知和异常通知永远只能执行一个 -->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturningPrintLog" pointcut-ref="loggerPointCut"></aop:after-returning>
<!-- 异常通知:在切入点方法执行产生异常后执行。异常通知和后置通知永远只能执行一个 -->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowingPrintLog" pointcut-ref="loggerPointCut"></aop:after-throwing>
<!-- 最终通知:无论切入点方法是否正常执行,它都会在其后面执行 -->
<aop:after method="afterPrintLog" pointcut-ref="loggerPointCut"></aop:after>
<!-- 环绕通知:是spring框架为我们提供的一种可以在代码中手动控制增强方法何时执行的方式。 -->
<aop:around method="aroundPrintLog" pointcut-ref="loggerPointCut"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>配置步骤:
①导入maven坐标
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>② 书写spring配置类,开启包扫描和注解支持
@configuration
@ComponentScan("cn.bruce") // 开启包扫描,配置需要扫描的包
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true) // 开启注解驱动
public class SpringConfiguration {
}③ 将业务层实体类交由IoC容器管理
@Service("testService")
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Override
public void testOfVoid() {
System.out.println("testOfVoid is running......");
}
@Override
public void testOfInt(int i) {
System.out.println("testOfInt is running......number is" + i);
}
@Override
public void testOfInteger(Integer i) {
// i = 1/0;
System.out.println("testOfInteger is running......number is" + i);
}
@Override
public void testOfAccount(Account account) {
int i = 1/0;
System.out.println("testOfInt is running......number is" + account);
}
}④ 书写切面类,声明为切面类并设置切入点和通知类型
@Component("logger")
@Aspect // 表示此类为切面类
public class Logger {
@Pointcut("execution(* cn..impl.*.*(..))") // 指定切入点表达式
private void pointcut(){}
/**
* 前置通知
*/
@Before("execution(* cn..impl.*.*(int))")
public void beforePrintLog(){
System.out.println("前置通知Logger类中的beforePrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。");
}
/**
* 后置通知
*/
@AfterReturning("execution(* cn..impl.*.*(Integer))")
public void afterReturningPrintLog(){
System.out.println("后置通知Logger类中的afterReturningPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。");
}
/**
* 异常通知
*/
@AfterThrowing("pointcut()")
public void afterThrowingPrintLog(){
System.out.println("异常通知Logger类中的afterThrowingPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。");
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
@After("execution(* cn..impl.*.*())")
public void afterPrintLog(){
System.out.println("最终通知Logger类中的afterPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。");
}
/**
* 环绕通知
*/
@Around("execution(* cn..impl.*.*(cn.bruce.domain.Account))")
public Object aroundPringLog(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
Object rtValue = null;
try{
//得到方法执行所需的参数
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPringLog方法开始记录日志了。。。前置");
//明确调用业务层方法(切入点方法)
rtValue = pjp.proceed(args);
System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPringLog方法开始记录日志了。。。后置");
return rtValue;
}catch (Throwable t){
System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPringLog方法开始记录日志了。。。异常");
throw new RuntimeException(t);
}finally {
System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPringLog方法开始记录日志了。。。最终");
}
}
}⑤ 书写测试类进行测试
public class TestAOP {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
TestService testService = (TestService) ac.getBean("testService");
testService.testOfInt(133);
System.out.println("-----------");
testService.testOfInteger(112);
System.out.println("-----------");
testService.testOfVoid();
System.out.println("-----------");
Account account = (Account) ac.getBean("account");
account.setName("Bruce");
account.setAge(112);
testService.testOfAccount(account);
}
}“spring框架入门之怎么使用切面编程AOP”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注亿速云网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/RealBruce/blog/4534644