Hadoop MapReduce 是一个分布式计算框架,用于编写批处理应用程序。编写好的程序可以提交到 Hadoop 集群上用于并行处理大规模的数据集。
MapReduce 作业通过将输入的数据集拆分为独立的块,这些块由 map 以并行的方式处理,框架对 map 的输出进行排序,然后输入到 reduce 中。MapReduce 框架专门用于 <key,value> 键值对处理,它将作业的输入视为一组 <key,value> 对,并生成一组 <key,value> 对作为输出。输出和输出的 key 和 value 都必须实现Writable 接口。
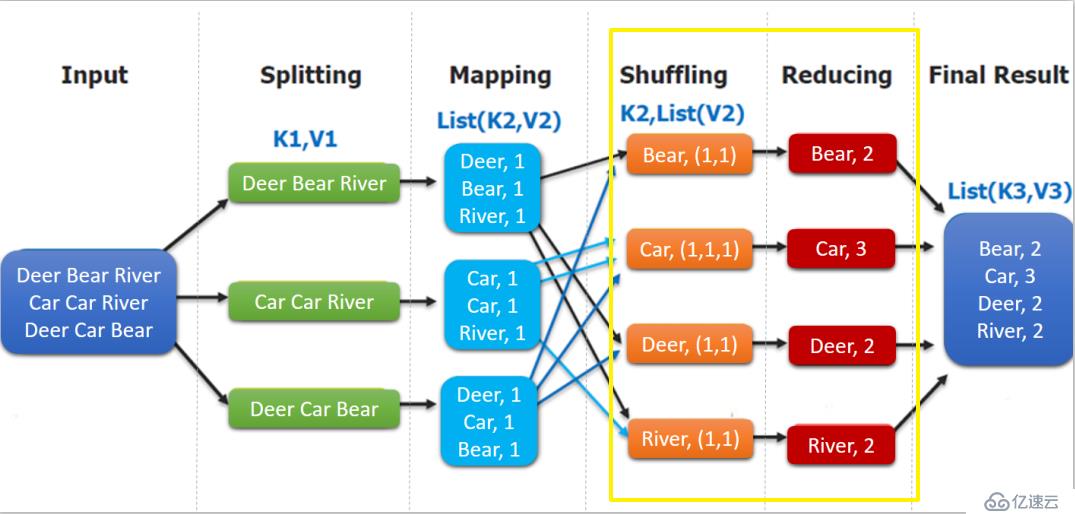
(input) <k1, v1> -> map -> <k2, v2> -> combine -> <k2, v2> -> reduce -> <k3, v3> (output)这里以词频统计为例进行说明,MapReduce 处理的流程如下:

input : 读取文本文件;
splitting : 将文件按照行进行拆分,此时得到的 K1 行数,V1 表示对应行的文本内容;
List(K2,V2),其中 K2 代表每一个单词,由于是做词频统计,所以 V2 的值为 1,代表出现 1 次;Mapping 操作可能是在不同的机器上并行处理的,所以需要通过 shuffling 将相同 key 值的数据分发到同一个节点上去合并,这样才能统计出最终的结果,此时得到 K2 为每一个单词,List(V2) 为可迭代集合,V2 就是 Mapping 中的 V2;Reducing 对 List(V2) 进行归约求和操作,最终输出。MapReduce 编程模型中 splitting 和 shuffing 操作都是由框架实现的,需要我们自己编程实现的只有 mapping 和 reducing,这也就是 MapReduce 这个称呼的来源。
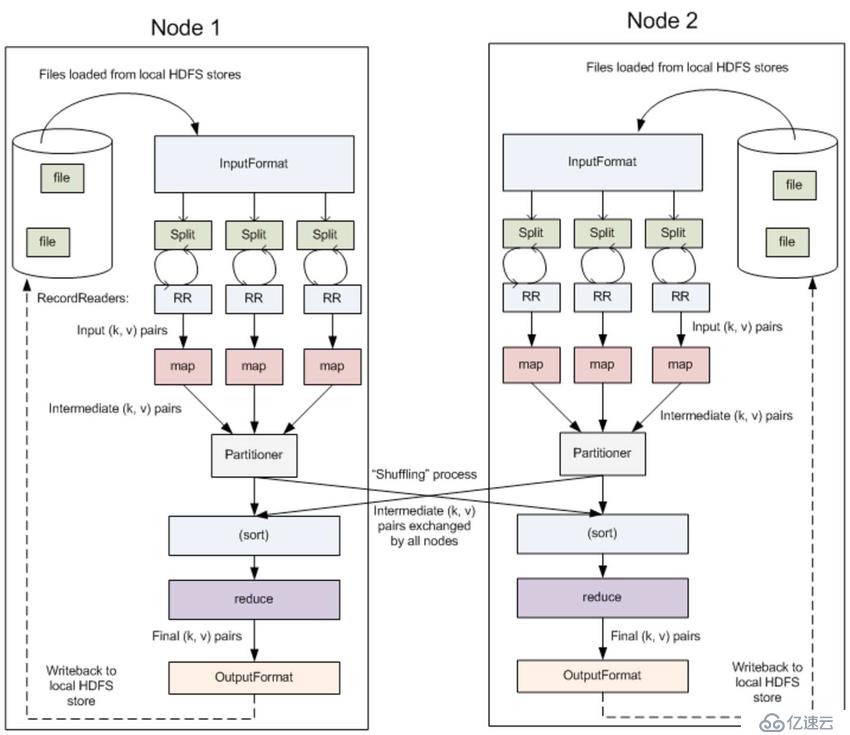
InputFormat 将输出文件拆分为多个 InputSplit,并由 RecordReaders 将 InputSplit 转换为标准的<key,value>键值对,作为 map 的输出。这一步的意义在于只有先进行逻辑拆分并转为标准的键值对格式后,才能为多个 map 提供输入,以便进行并行处理。
combiner 是 map 运算后的可选操作,它实际上是一个本地化的 reduce 操作,它主要是在 map 计算出中间文件后做一个简单的合并重复 key 值的操作。这里以词频统计为例:
map 在遇到一个 hadoop 的单词时就会记录为 1,但是这篇文章里 hadoop 可能会出现 n 多次,那么 map 输出文件冗余就会很多,因此在 reduce 计算前对相同的 key 做一个合并操作,那么需要传输的数据量就会减少,传输效率就可以得到提升。
但并非所有场景都适合使用 combiner,使用它的原则是 combiner 的输出不会影响到 reduce 计算的最终输入,例如:求总数,最大值,最小值时都可以使用 combiner,但是做平均值计算则不能使用 combiner。
不使用 combiner 的情况:
<div align="center"> <img width="600px" src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/heibaiying/BigData-Notes/master/pictures/mapreduce-without-combiners.png"/> </div>
使用 combiner 的情况:
<div align="center"> <img width="600px" src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/heibaiying/BigData-Notes/master/pictures/mapreduce-with-combiners.png"/> </div>
可以看到使用 combiner 的时候,需要传输到 reducer 中的数据由 12keys,降低到 10keys。降低的幅度取决于你 keys 的重复率,下文词频统计案例会演示用 combiner 降低数百倍的传输量。
partitioner 可以理解成分类器,将 map 的输出按照 key 值的不同分别分给对应的 reducer,支持自定义实现,下文案例会给出演示。
这里给出一个经典的词频统计的案例:统计如下样本数据中每个单词出现的次数。
Spark HBase Hive Flink Storm Hadoop HBase Spark Flink HBase Storm HBase Hadoop Hive Flink HBase Flink Hive Storm Hive Flink Hadoop HBase Hive Hadoop Spark HBase Storm HBase Hadoop Hive Flink HBase Flink Hive Storm Hive Flink Hadoop HBase Hive
为方便大家开发,我在项目源码中放置了一个工具类 WordCountDataUtils,用于模拟产生词频统计的样本,生成的文件支持输出到本地或者直接写到 HDFS 上。
项目代码下载地址:hadoop-word-count
想要进行 MapReduce 编程,需要导入 hadoop-client 依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>${hadoop.version}</version>
</dependency>将每行数据按照指定分隔符进行拆分。这里需要注意在 MapReduce 中必须使用 Hadoop 定义的类型,因为 Hadoop 预定义的类型都是可序列化,可比较的,所有类型均实现了 WritableComparable 接口。
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
String[] words = value.toString().split("\t");
for (String word : words) {
context.write(new Text(word), new IntWritable(1));
}
}
}WordCountMapper 对应下图的 Mapping 操作:

WordCountMapper 继承自 Mappe 类,这是一个泛型类,定义如下:
WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>
public class Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> {
......
}mapping 输入 key 的类型,即每行的偏移量 (每行第一个字符在整个文本中的位置),Long 类型,对应 Hadoop 中的 LongWritable 类型;mapping 输入 value 的类型,即每行数据;String 类型,对应 Hadoop 中 Text 类型;mapping 输出的 key 的类型,即每个单词;String 类型,对应 Hadoop 中 Text 类型;mapping 输出 value 的类型,即每个单词出现的次数;这里用 int 类型,对应 IntWritable 类型。在 Reduce 中进行单词出现次数的统计:
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
int count = 0;
for (IntWritable value : values) {
count += value.get();
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(count));
}
}如下图,shuffling 的输出是 reduce 的输入。这里的 key 是每个单词,values 是一个可迭代的数据类型,类似 (1,1,1,...)。
组装 MapReduce 作业,并提交到服务器运行,代码如下:
/**
* 组装作业 并提交到集群运行
*/
public class WordCountApp {
// 这里为了直观显示参数 使用了硬编码,实际开发中可以通过外部传参
private static final String HDFS_URL = "hdfs://192.168.0.107:8020";
private static final String HADOOP_USER_NAME = "root";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 文件输入路径和输出路径由外部传参指定
if (args.length < 2) {
System.out.println("Input and output paths are necessary!");
return;
}
// 需要指明 hadoop 用户名,否则在 HDFS 上创建目录时可能会抛出权限不足的异常
System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", HADOOP_USER_NAME);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
// 指明 HDFS 的地址
configuration.set("fs.defaultFS", HDFS_URL);
// 创建一个 Job
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration);
// 设置运行的主类
job.setJarByClass(WordCountApp.class);
// 设置 Mapper 和 Reducer
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
// 设置 Mapper 输出 key 和 value 的类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 设置 Reducer 输出 key 和 value 的类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 如果输出目录已经存在,则必须先删除,否则重复运行程序时会抛出异常
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI(HDFS_URL), configuration, HADOOP_USER_NAME);
Path outputPath = new Path(args[1]);
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outputPath, true);
}
// 设置作业输入文件和输出文件的路径
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 将作业提交到群集并等待它完成,参数设置为 true 代表打印显示对应的进度
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
// 关闭之前创建的 fileSystem
fileSystem.close();
// 根据作业结果,终止当前运行的 Java 虚拟机,退出程序
System.exit(result ? 0 : -1);
}
}需要注意的是:如果不设置 Mapper 操作的输出类型,则程序默认它和 Reducer 操作输出的类型相同。
在实际开发中,可以在本机配置 hadoop 开发环境,直接在 IDE 中启动进行测试。这里主要介绍一下打包提交到服务器运行。由于本项目没有使用除 Hadoop 外的第三方依赖,直接打包即可:
# mvn clean package使用以下命令提交作业:
hadoop jar /usr/appjar/hadoop-word-count-1.0.jar \ com.heibaiying.WordCountApp \ /wordcount/input.txt /wordcount/output/WordCountApp
作业完成后查看 HDFS 上生成目录:
# 查看目录
hadoop fs -ls /wordcount/output/WordCountApp
# 查看统计结果
hadoop fs -cat /wordcount/output/WordCountApp/part-r-00000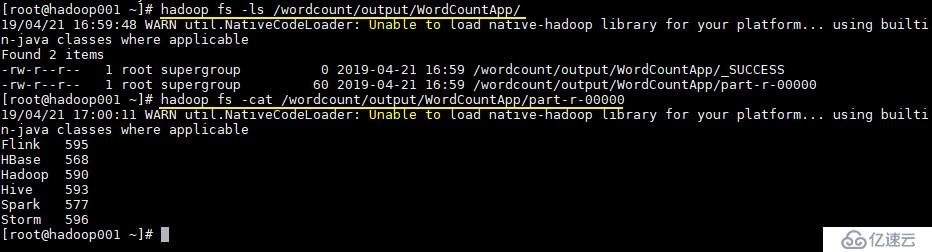
想要使用 combiner 功能只要在组装作业时,添加下面一行代码即可:
// 设置 Combiner
job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReducer.class);加入 combiner 后统计结果是不会有变化的,但是可以从打印的日志看出 combiner 的效果:
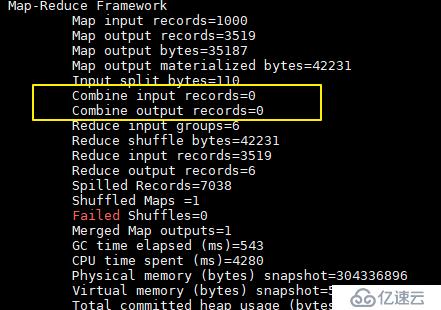
没有加入 combiner 的打印日志:
加入 combiner 后的打印日志如下:
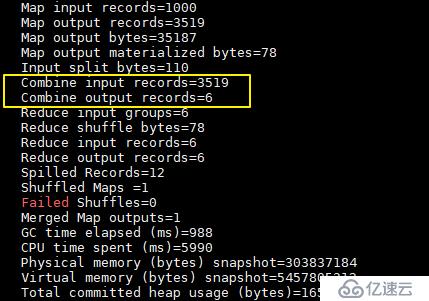
这里我们只有一个输入文件并且小于 128M,所以只有一个 Map 进行处理。可以看到经过 combiner 后,records 由 3519 降低为 6(样本中单词种类就只有 6 种),在这个用例中 combiner 就能极大地降低需要传输的数据量。
这里假设有个需求:将不同单词的统计结果输出到不同文件。这种需求实际上比较常见,比如统计产品的销量时,需要将结果按照产品种类进行拆分。要实现这个功能,就需要用到自定义 Partitioner。
这里先介绍下 MapReduce 默认的分类规则:在构建 job 时候,如果不指定,默认的使用的是 HashPartitioner:对 key 值进行哈希散列并对 numReduceTasks 取余。其实现如下:
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
public int getPartition(K key, V value,
int numReduceTasks) {
return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}这里我们继承 Partitioner 自定义分类规则,这里按照单词进行分类:
public class CustomPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, IntWritable> {
public int getPartition(Text text, IntWritable intWritable, int numPartitions) {
return WordCountDataUtils.WORD_LIST.indexOf(text.toString());
}
}在构建 job 时候指定使用我们自己的分类规则,并设置 reduce 的个数:
// 设置自定义分区规则
job.setPartitionerClass(CustomPartitioner.class);
// 设置 reduce 个数
job.setNumReduceTasks(WordCountDataUtils.WORD_LIST.size());执行结果如下,分别生成 6 个文件,每个文件中为对应单词的统计结果:
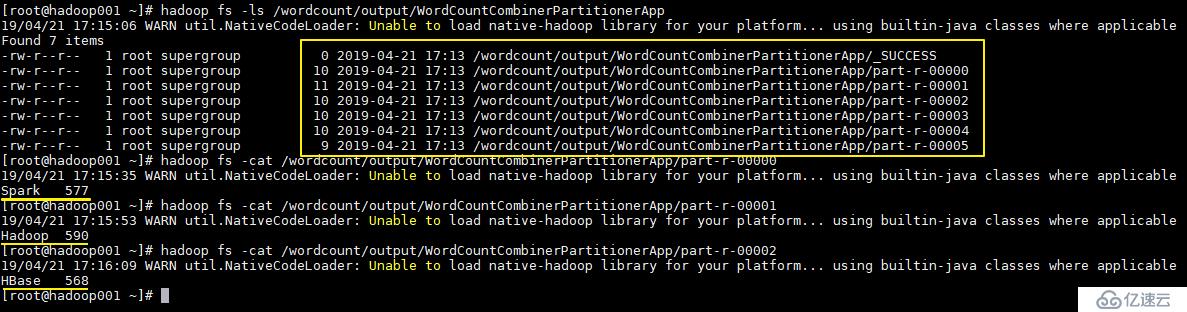
更多大数据系列文章可以参见 GitHub 开源项目: 大数据入门指南
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。