这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关SpringBoot 中Security如何使用,文章内容质量较高,因此小编分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后对相关知识有一定的了解。
Security是Spring全家桶中一个安全框架,他的扩展能力非常的强,底层是一条过滤器链。通过简单的配置就可以使用,但通过自己的DIY,可以把每个权限细化到每个链接上去。
shiro没有学,但只推荐学一个安全框架
这里搭建的学习项目都是使用SpringBoot
你可以在maven官网获取最新版本
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId> <version>2.4.2</version> </dependency>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.4.2</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.pipihao</groupId> <artifactId>securitylearn</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>securitylearn</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.21</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.4</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <excludes> <exclude> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </exclude> </excludes> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
server: port: 8001 spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai username: root password: root driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver thymeleaf: cache: false # 因为Thymeleaf很多有默认配置,所以只关了这个缓存,方便刷新
数据库版本为 8.0
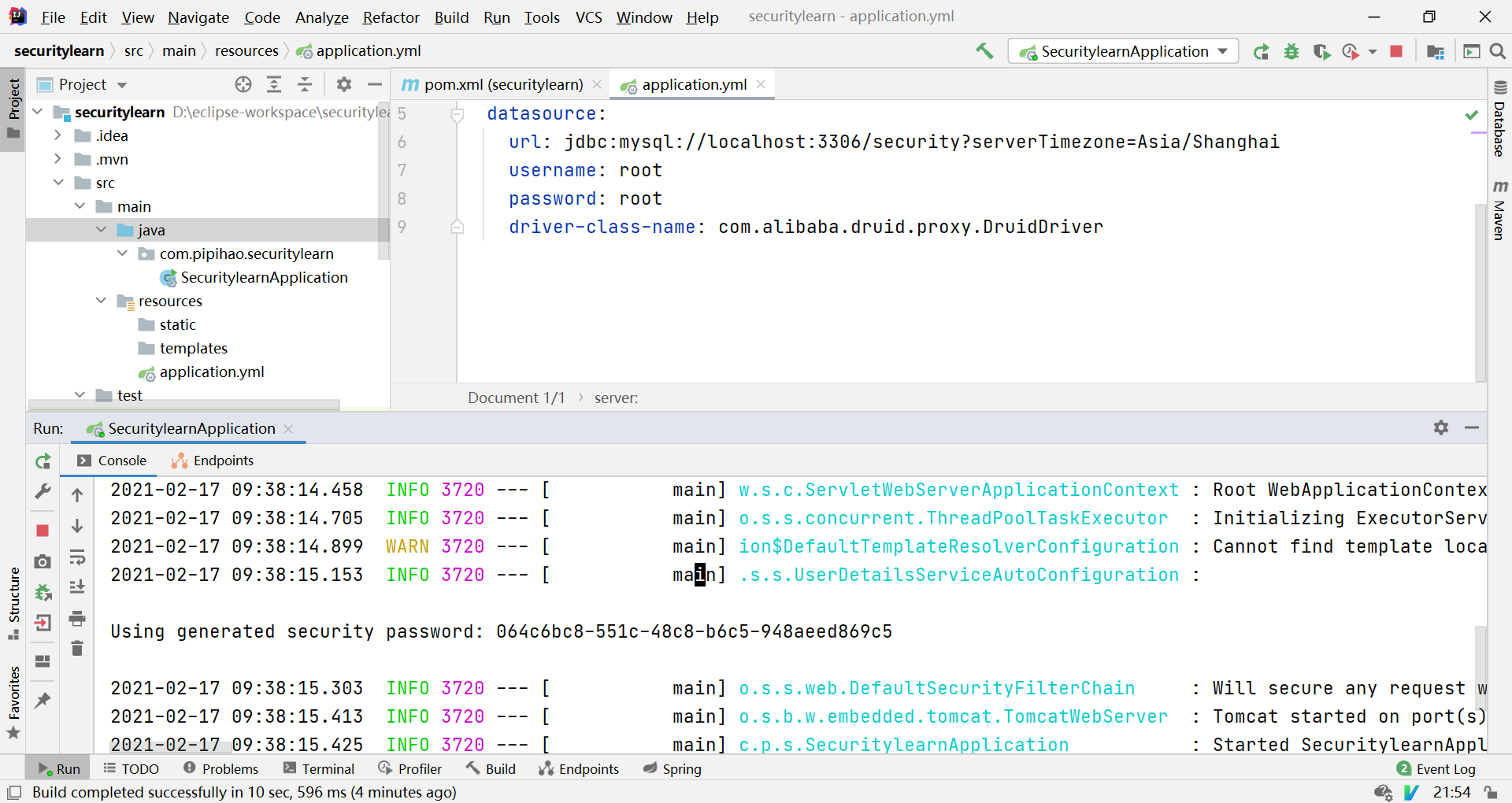
用户名:user
密码:控制台输出的这密码
spring: security: user: name: xx password: xx
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 类是是Security内置提供了一个默认身份验证的抽象类,继承此抽象类实现configure方法则可以对验证操作实现DIY。[于官方文档 6.3 标题可见]
UserDetailsService接口:查询数据库用户名和密码过程
创建类继承UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,重写三个方法
*
创建类实现UserDetailService,编写查询数据过程,返回User对象,这个User对象是安全框架提供对象。
PasswordEncoder: 数据加密接口,用于返回User对象里面的密码加密
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
/*
使用and()方法表示关闭XML标记的Java配置,它允许我们继续配置父标记。如果您阅读代码,它也是有道理的。我想配置授权请求并配置表单登录并配置HTTP基本身份验证。
*/
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/","/no").permitAll() //可以直接访问的路径
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html") //配置登录路径
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/hallo")
.permitAll()
; //设置 登录的网页
http.csrf().disable(); //如果注释了这一行,全部要用_csrf的对象来验证了
}如果是配置访问角色则使用是hasRole与hasAnyRole
这里非常建议点一下看一下hasRole的源码 使用Role的时候,User的权限列表是需要加ROLE_前缀的
这里直接使用的是hasAnyAuthority,还有一个方法是hasAuthority
前者可以配置多个权限,而后者只能配置一个权限
接口只是显示一个字符串
@GetMapping("test") public String sayTest(){ return "Test"; }
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
/*
使用and()方法表示关闭XML标记的Java配置,它允许我们继续配置父标记。如果您阅读代码,它也是有道理的。我想配置授权请求并配置表单登录并配置HTTP基本身份验证。
*/
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/","/no").permitAll() //可以直接访问的路径
.antMatchers("/test").hasAnyAuthority("admin") // 访问权限
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html") //配置登录路径
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/hallo")
.permitAll()
; //设置 登录的网页
http.csrf().disable(); //如果注释了这一行,全部要用_csrf的对象来验证了
}@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(username)){
throw new RuntimeException("用户名不能为空");
}
IUser iUser= userMapper.getUserByUsername(username);
if(iUser == null){
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("无此用户");
}
/*此处查询用户角色*/
List<GrantedAuthority> grantedAuthorityList =
AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList("admin"); // 权限的列表
return new User(iUser.getUsername(),bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode(iUser.getPassword()),grantedAuthorityList);
}// 在此方法内加上一行 protected void configure(HttpSecurity http)
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/unauth.html");判断是否有角色,这里匹配的角色需要加前缀ROLE_
@GetMapping("update")
@Secured({"ROLE_manager"})
public String update(){
return "update";
}使用其功能时需要在application类上开起
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.pipihao.securitylearn.mapper")
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
public class SecuritylearnApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SecuritylearnApplication.class, args);
}
}UserDetailsServiceImpl
List<GrantedAuthority> grantedAuthorityList =
AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList("admin","ROLE_manager");此注解即有权限验证功能,又有角色验证功能
@GetMapping("pre1")
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('ROLE_manager')")
public String prePost1(){
return "prePost1";
}
@GetMapping("pre2")
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('admin')")
public String prePost2(){
return "prePost2";
}@SpringBootApplication
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class SecuritylearnApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SecuritylearnApplication.class, args);
}
}@PostAuthorize 与@PreAuthorize的区别就是,Pre会先拦截后执行,而PostAuthorize是先执行,后拦截
所以我例子中没有过多的讲
Pre是过滤上传的数据,Post过滤返回的数据
@GetMapping("list")
@PostFilter("filterObject.username != 'admin' ")
public List<IUser> list(){
List<IUser> iUsers = new ArrayList<>();
iUsers.add(new IUser(1,"admin","123"));
iUsers.add(new IUser(2,"user","123"));
return iUsers;
}
// Applicationo类上还是要加上下面这个注解,并设置属性值
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)效果图
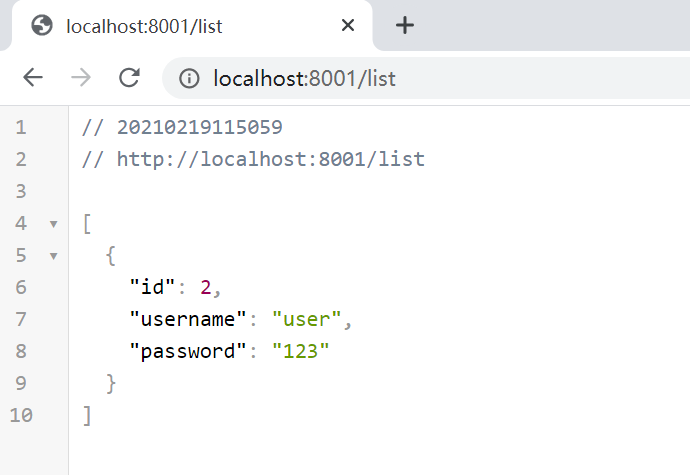
上传则是同理,通过注解写好判断,然后测试即可,注:PreFilter过滤的也只是集合和数组
/*配置退出登录*/
http.logout().logoutUrl("/logout").logoutSuccessUrl("no").permitAll();登录后,直接通过浏览器,访问此路径即可(是的,就是如此)
location.href='/logout';
下面是尚硅谷老师写的原理图和执行流程
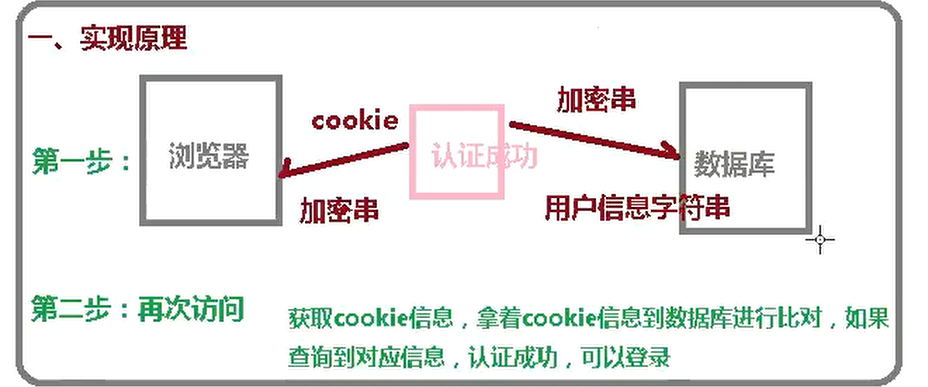
如果是微服务,则把数据库改成redis,把cookie改成jwt生成的token
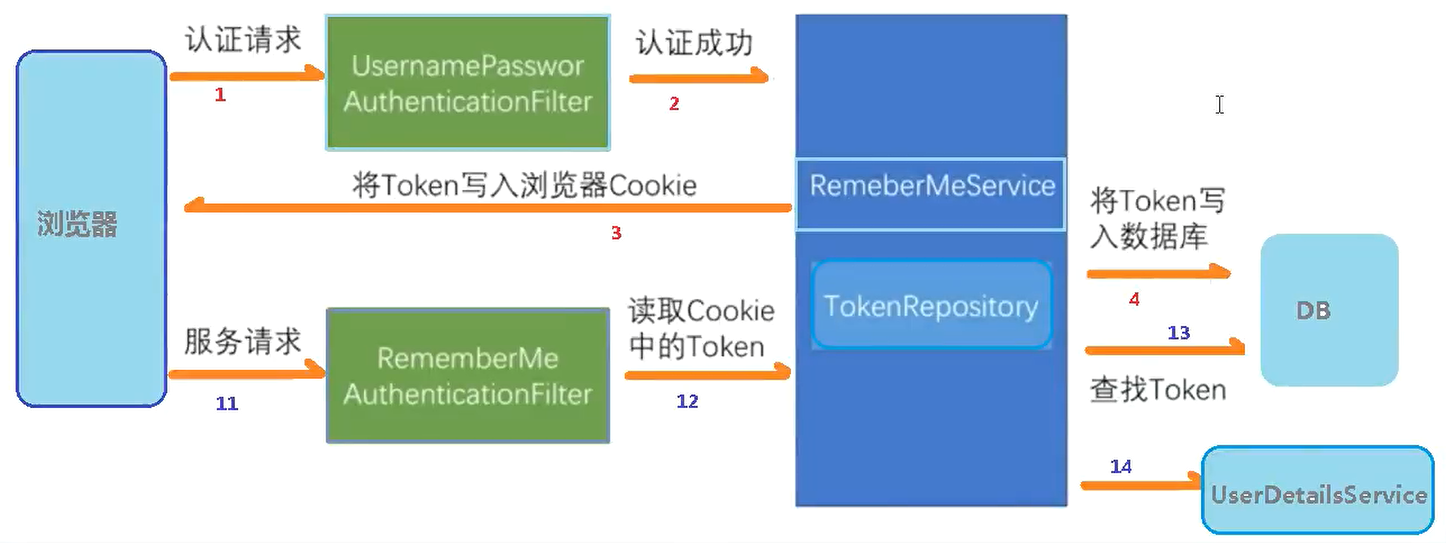
Security 中的一个类内JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl
的常量CREATE_TABLE_SQL
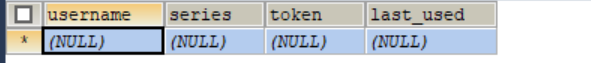
create table persistent_logins (username varchar(64) not null, series varchar(64) primary key, token varchar(64) not null, last_used timestamp not null)
有兴趣的可以看看源码 没兴趣的直接在你使用的数据库内执行上面这行sql创建一个保存登录信息的表
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl 是PersistentTokenRepository实现类
下面这种写那么应该是多态了
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Bean
public PersistentTokenRepository persistentTokenRepository(){
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl jdbcTokenRepository = new JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl();
jdbcTokenRepository.setDataSource(dataSource);
//jdbcTokenRepository.setCreateTableOnStartup(true); 设置启动时创建自动登录表
return jdbcTokenRepository;
}SecurityConfig的方法
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
/*自定义403链接*/
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/unauth.html");
/*配置退出登录*/
http.logout().logoutUrl("/logout").logoutSuccessUrl("/no").permitAll();
/*
使用and()方法表示关闭XML标记的Java配置,它允许我们继续配置父标记。如果您阅读代码,它也是有道理的。我想配置授权请求并配置表单登录并配置HTTP基本身份验证。
*/
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/","/no").permitAll() //可以直接访问的路径
.antMatchers("/test").hasAnyAuthority("admin")
.antMatchers("/unauth").hasAnyAuthority("xxx")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html") //配置登录路径
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/hallo")
.permitAll()
// -------------------就是下面这坨
.and()
.rememberMe().tokenRepository(persistentTokenRepository())
.tokenValiditySeconds(60) // 自动保存的时间,秒为单位
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService)
; //设置 登录的网页
http.csrf().disable(); //如果注释了这一行,全部要用_csrf的对象来验证了
}下面是登录界面
<form action="/doLogin" method="POST"> user:<input type="text" name="username"><br> pswd:<input type="text" name="password"><br> <!--必须name=remember-me不然,是无法接收到是否自动登录的信息的--> 自动登录 <input type="checkbox" name="remember-me"><br> <input type="submit"> </form>
然后在登录的时候打个勾,就可以自动登录了
在DB中会出现如下的信息

第一步 把下面这一行注释了就开启了,也就是说他其实是默认开启的
如果没有关闭,则会NullPointerException
//http.csrf().disable();
Spring Security CSRF 会针对Patch,Post,Put,Delete方法进行防护。(都是一些要更改数据的方法)
系统默认提供了一个csrfToken对象放在HttpSession中,也就是我们所见到了_csrf对象
此对象可以直接使用
开启CSRF后,则登录的时【POST】,也需要验证CSRF,而使用HttpSession则需要使用模板引擎,这里我们使用的是Thymeleaf而非JSP。(大同小异)
注:使用Thymeleaf的时候,类上的Controller注解不能写成RestController,不然无法生效的
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@GetMapping("login")
public String login(){
return "login";
}
}<!doctype html> <html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>登录</title> </head> <body> <!--没加th:则不会有隐藏域自动生成--> <form th:action="'/doLogin'" method="POST"> user:<input type="text" name="username"><br> pswd:<input type="text" name="password"><br> <!--必须name=remember-me不然,是无法接收到是否自动登录的信息的--> 自动登录 <input type="checkbox" name="remember-me"><br> <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>
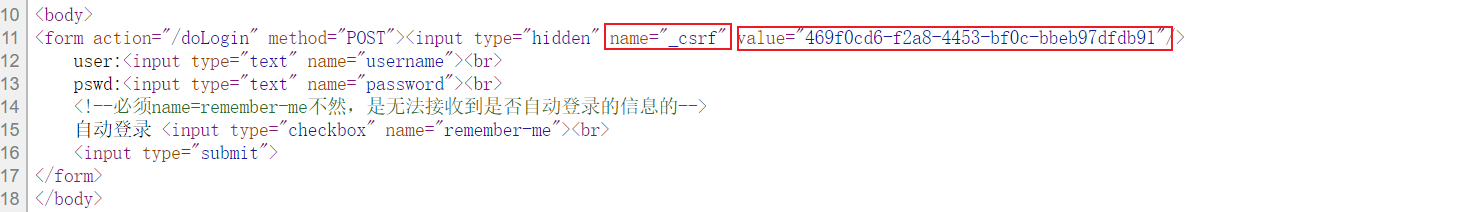
切记,默认开了CSRF,则每个表单中应当手动添加一个隐藏域
当Thymeleaf因为你使用了th,则自动给你生成了。
所以 th:action="'/doLogin'" 这样写可以省事
如下图
关于SpringBoot 中Security如何使用就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。