这篇文章主要讲解了“Linux内存怎么初始化”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“Linux内存怎么初始化”吧!
void __init paging_init(void){ phys_addr_t pgd_phys = early_pgtable_alloc();//分配一页大小的物理内存放进pgd pgd_t *pgd = pgd_set_fixmap(pgd_phys); map_kernel(pgd);//将内核的各个段进行映射 .text .init .data .bss map_mem(pgd);//将memblock子系统添加的物理内存进行映射(将物理地址映射到线性区域) /* * We want to reuse the original swapper_pg_dir so we don't have to * communicate the new address to non-coherent secondaries in * secondary_entry, and so cpu_switch_mm can generate the address with * adrp+add rather than a load from some global variable. * * To do this we need to go via a temporary pgd. */ cpu_replace_ttbr1(__va(pgd_phys));//切换页表 memcpy(swapper_pg_dir, pgd, PGD_SIZE);//将新建立的页表内容替换swapper_pg_dir页表内容 cpu_replace_ttbr1(lm_alias(swapper_pg_dir)); pgd_clear_fixmap(); memblock_free(pgd_phys, PAGE_SIZE); /* * We only reuse the PGD from the swapper_pg_dir, not the pud + pmd * allocated with it. */ memblock_free(__pa_symbol(swapper_pg_dir) + PAGE_SIZE, SWAPPER_DIR_SIZE - PAGE_SIZE);}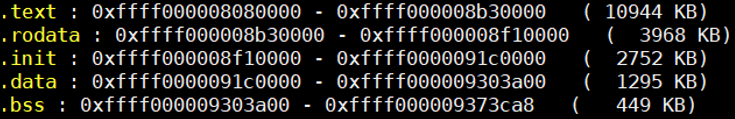
主要是完成通过memblock_add添加到系统中的物理内存映射,注意如果memblock设置了MEMBLOCK_NOMAP标志的话则不对其地址映射。
void __init bootmem_init(void){ unsigned long min, max; min = PFN_UP(memblock_start_of_DRAM()); max = PFN_DOWN(memblock_end_of_DRAM()); early_memtest(min << PAGE_SHIFT, max << PAGE_SHIFT); max_pfn = max_low_pfn = max; arm64_numa_init(); /* * Sparsemem tries to allocate bootmem in memory_present(), so must be * done after the fixed reservations. */ arm64_memory_present(); sparse_init(); zone_sizes_init(min, max); memblock_dump_all();}这个函数基本上完成了linux对物理内存“划分”的初始化,包括node, zone, page frame,以及对应的数据结构。在讲这个函数之前,我们需要了解下物理内存组织。
「Linux是如何组织物理内存的?」
「node」:
目前计算机系统有两种体系结构:
「zone」:
ZONE的意思是把整个物理内存划分为几个区域,每个区域有特殊的含义
enum zone_type {#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA /* * ZONE_DMA is used when there are devices that are not able * to do DMA to all of addressable memory (ZONE_NORMAL). Then we * carve out the portion of memory that is needed for these devices. * The range is arch specific. * * Some examples * * Architecture Limit * --------------------------- * parisc, ia64, sparc <4G * s390 <2G * arm Various * alpha Unlimited or 0-16MB. * * i386, x86_64 and multiple other arches * <16M. */ ZONE_DMA,#endif#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA32 /* * x86_64 needs two ZONE_DMAs because it supports devices that are * only able to do DMA to the lower 16M but also 32 bit devices that * can only do DMA areas below 4G. */ ZONE_DMA32,#endif /* * Normal addressable memory is in ZONE_NORMAL. DMA operations can be * performed on pages in ZONE_NORMAL if the DMA devices support * transfers to all addressable memory. */ ZONE_NORMAL,#ifdef CONFIG_HIGHMEM /* * A memory area that is only addressable by the kernel through * mapping portions into its own address space. This is for example * used by i386 to allow the kernel to address the memory beyond * 900MB. The kernel will set up special mappings (page * table entries on i386) for each page that the kernel needs to * access. */ ZONE_HIGHMEM,#endif ZONE_MOVABLE,#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DEVICE ZONE_DEVICE,#endif __MAX_NR_ZONES};「page」:
代表一个物理页,在内核中一个物理页用一个struct page表示。
「page frame」:
为了描述一个物理page,内核使用struct page结构来表示一个物理页。假设一个page的大小是4K的,内核会将整个物理内存分割成一个一个4K大小的物理页,而4K大小物理页的区域我们称为page frame
「page frame num(pfn)」 :
pfn是对每个page frame的编号。故物理地址和pfn的关系是:
物理地址>>PAGE_SHIFT = pfn
「pfn和page的关系」:
内核中支持了好几个内存模型:CONFIG_FLATMEM(平坦内存模型)CONFIG_DISCONTIGMEM(不连续内存模型)CONFIG_SPARSEMEM_VMEMMAP(稀疏的内存模型)目前ARM64使用的稀疏的类型模式
/* memmap is virtually contiguous. */#define __pfn_to_page(pfn) (vmemmap + (pfn))#define __page_to_pfn(page) (unsigned long)((page) - vmemmap)系统启动的时候,内核会将整个struct page映射到内核虚拟地址空间vmemmap的区域,所以我们可以简单的认为struct page的基地址是vmemmap,则:
vmemmap+pfn的地址就是此struct page对应的地址。
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“Linux内存怎么初始化”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对Linux内存怎么初始化这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是亿速云,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/4585157/blog/4395705