本篇内容介绍了“redis排序算法有哪些”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
排序算法:
redis的sorted set类型的元素,都会关联一个分数,可以用于排序
适用于:只有点赞、对时间敏感
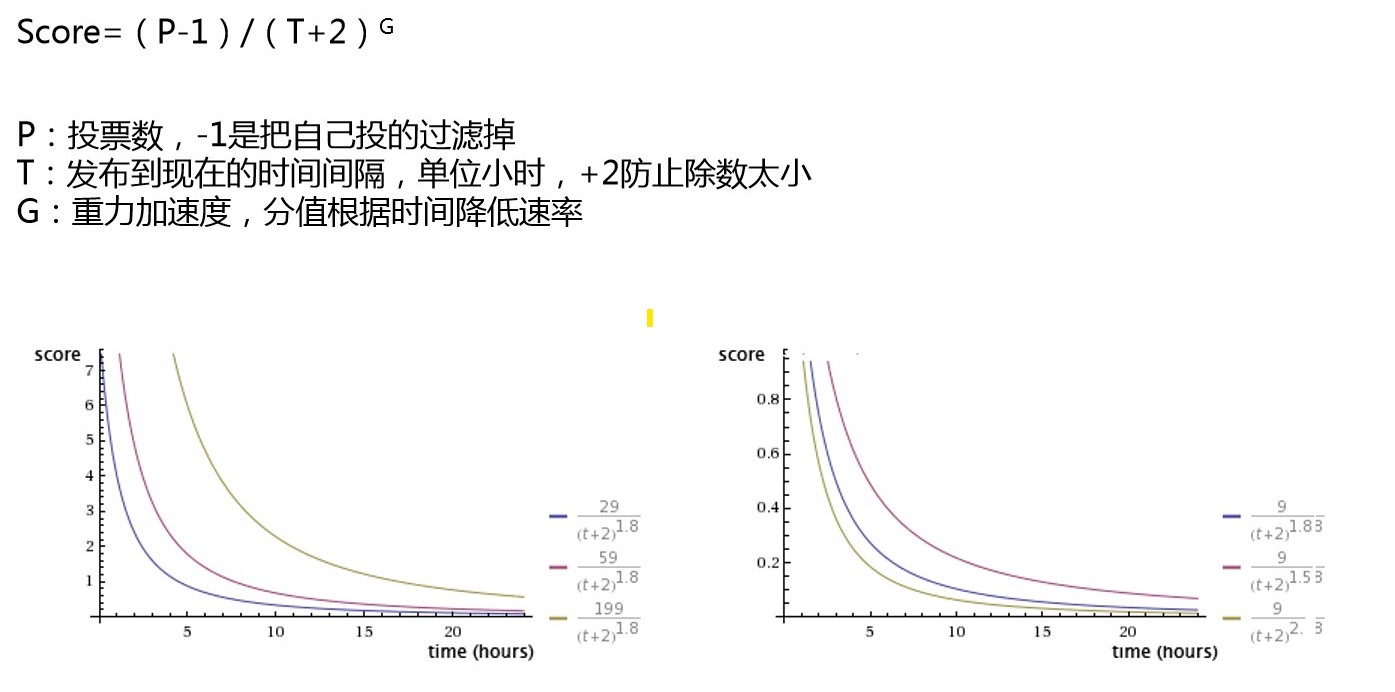
适用于:有点赞点踩、流量较大的

适用于问答网站

适用于:电影评分排序

加在方法上或代码段上:
public class Test1 {
private static Object obj = new Object();
public static void synchronized1() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (obj) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("锁1:" + i + ",t:" + Thread.currentThread());
}
}
}
public static void synchronized2() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (obj) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("锁2:" + i + ",t:" + Thread.currentThread());
}
}
}
public static synchronized void synchronized3() throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("锁1:" + i + ",t:" + Thread.currentThread());
}
}
public static synchronized void synchronized4() throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("锁2:" + i + ",t:" + Thread.currentThread());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
// synchronized1();
// synchronized2();
synchronized3();
synchronized4();//效果一样
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}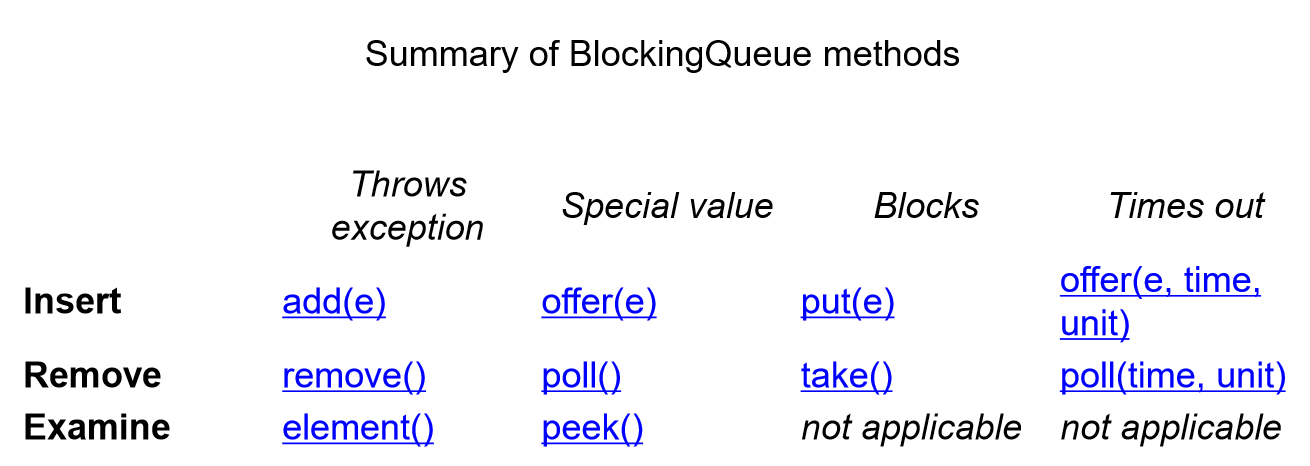
add()方法如果队列满了会报错,put()方法如果队列满了会等待,当队列有空余则进行数据插入,offer()方法如果队列满会返回false,否则插入成功并返回true
examine--检查
使用同步队列可以实现之前的异步模型,但是和redis的List相比,同步队列无法适用于分布式
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Producer.q.put("like");
// Producer.q.put("dislike");
// Producer.q.add("dislike");
Producer.q.offer("dislike");
new Thread(new Consumer(Producer.q), "t1").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(Producer.q), "t2").start();
}
}
class Producer {
public static BlockingQueue<String> q = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(10);
}
class Consumer implements Runnable {
private BlockingQueue<String> q;
Consumer(BlockingQueue<String> q) {
this.q = q;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",消费者数据:" + q.take());
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}public class test3 {
private static int a = 0;
private static AtomicInteger b = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
a++;
b.incrementAndGet();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
Thread.sleep(3000);//等50个线程运行完
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}public class test4 {
public static void testExecutor() throws InterruptedException {
// ExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//所有任务只有一个线程执行
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);// 每个任务都分配一个线程
service.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("Execute1 " + i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
service.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("Execute2 " + i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
service.shutdown();
// 轮询,service是否停止
while (!service.isTerminated()) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("ExecutorService正在运行,Wait for termination.");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
testExecutor();
}
}public class test5 {
public static void testfuture() throws Exception {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future<Integer> future = service.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("开始计算任务。。。");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("开始返回结果。。。");
return 100;
}
});
service.isShutdown();
System.out.println("等待的结果:" + future.get(2000, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
testfuture();
}
}“redis排序算法有哪些”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注亿速云网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/3943244/blog/3082917