这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关Springboot中的jar是怎样的,文章内容质量较高,因此小编分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后对相关知识有一定的了解。
利用IDEA等工具打包会出现springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar,springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar.original,接下来我们就一探究竟,它们之间到底有什么联系。
文件对比:
进入target目录,unzip springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar -d jar命令将springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar解压到jar目录 
进入target目录,unzip springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar.original -d original命令将springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar.original解压到original目录 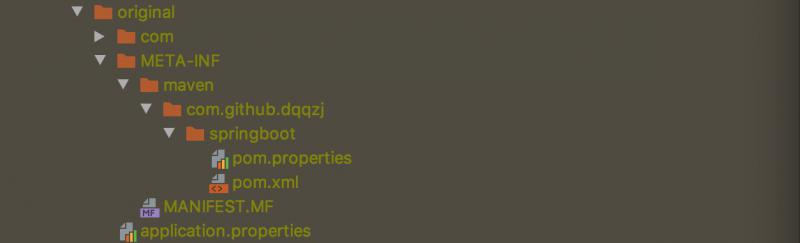
springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar.original不能执行,将它进行repackage后生成springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar就成了我们的可执行fat jar,对比上面文件会发现可执行 fat jar和original jar目录不一样,最关键的地方是多了org.springframework.boot.loader这个包,这个就是我们平时java -jar springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar命令启动的奥妙所在。MANIFEST.MF文件里面的内容包含了很多关键的信息
Manifest-Version: 1.0 Start-Class: com.github.dqqzj.springboot.SpringbootApplication Spring-Boot-Classes: BOOT-INF/classes/ Spring-Boot-Lib: BOOT-INF/lib/ Build-Jdk-Spec: 1.8 Spring-Boot-Version: 2.1.6.RELEASE Created-By: Maven Archiver 3.4.0 Main-Class: org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher
相信不用多说大家都能明白Main-Class: org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher是我们 java -jar命令启动的入口,后续会进行分析,Start-Class: com.github.dqqzj.springboot.SpringbootApplication才是我们程序的入口主函数。
public class JarLauncher extends ExecutableArchiveLauncher {
static final String BOOT_INF_CLASSES = "BOOT-INF/classes/";
static final String BOOT_INF_LIB = "BOOT-INF/lib/";
public JarLauncher() {
}
protected JarLauncher(Archive archive) {
super(archive);
}
/**
* 判断是否归档文件还是文件系统的目录 可以猜想基于文件系统一样是可以启动的
*/
protected boolean isNestedArchive(Entry entry) {
return entry.isDirectory() ? entry.getName().equals("BOOT-INF/classes/") : entry.getName().startsWith("BOOT-INF/lib/");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
* 进入父类初始化构造器ExecutableArchiveLauncher
* launch方法交给Launcher执行
*/
(new JarLauncher()).launch(args);
}
}
public abstract class ExecutableArchiveLauncher extends Launcher {
private final Archive archive;
public ExecutableArchiveLauncher() {
try {
/**
* 使用父类Launcher加载资源,包括BOOT-INF的classes和lib下面的所有归档文件
*/
this.archive = this.createArchive();
} catch (Exception var2) {
throw new IllegalStateException(var2);
}
}
protected ExecutableArchiveLauncher(Archive archive) {
this.archive = archive;
}
protected final Archive getArchive() {
return this.archive;
}
/**
* 从归档文件中获取我们的应用程序主函数
*/
protected String getMainClass() throws Exception {
Manifest manifest = this.archive.getManifest();
String mainClass = null;
if (manifest != null) {
mainClass = manifest.getMainAttributes().getValue("Start-Class");
}
if (mainClass == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No 'Start-Class' manifest entry specified in " + this);
} else {
return mainClass;
}
}
protected List<Archive> getClassPathArchives() throws Exception {
List<Archive> archives = new ArrayList(this.archive.getNestedArchives(this::isNestedArchive));
this.postProcessClassPathArchives(archives);
return archives;
}
protected abstract boolean isNestedArchive(Entry entry);
protected void postProcessClassPathArchives(List<Archive> archives) throws Exception {
}
}
public abstract class Launcher {
public Launcher() {
}
protected void launch(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
*注册协议处理器,由于Springboot是 jar in jar 所以要重写jar协议才能读取归档文件
*/
JarFile.registerUrlProtocolHandler();
ClassLoader classLoader = this.createClassLoader(this.getClassPathArchives());
/**
* this.getMainClass()交给子类ExecutableArchiveLauncher实现
*/
this.launch(args, this.getMainClass(), classLoader);
}
protected ClassLoader createClassLoader(List<Archive> archives) throws Exception {
List<URL> urls = new ArrayList(archives.size());
Iterator var3 = archives.iterator();
while(var3.hasNext()) {
Archive archive = (Archive)var3.next();
urls.add(archive.getUrl());
}
return this.createClassLoader((URL[])urls.toArray(new URL[0]));
}
/**
* 该类加载器是fat jar的关键的一处,因为传统的类加载器无法读取jar in jar模型,所以springboot进行了自己实现
*/
protected ClassLoader createClassLoader(URL[] urls) throws Exception {
return new LaunchedURLClassLoader(urls, this.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
protected void launch(String[] args, String mainClass, ClassLoader classLoader) throws Exception {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader);
this.createMainMethodRunner(mainClass, args, classLoader).run();
}
/**
* 创建应用程序主函数运行器
*/
protected MainMethodRunner createMainMethodRunner(String mainClass, String[] args, ClassLoader classLoader) {
return new MainMethodRunner(mainClass, args);
}
protected abstract String getMainClass() throws Exception;
protected abstract List<Archive> getClassPathArchives() throws Exception;
/**
* 得到我们的启动jar的归档文件
*/
protected final Archive createArchive() throws Exception {
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain = this.getClass().getProtectionDomain();
CodeSource codeSource = protectionDomain.getCodeSource();
URI location = codeSource != null ? codeSource.getLocation().toURI() : null;
String path = location != null ? location.getSchemeSpecificPart() : null;
if (path == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive");
} else {
File root = new File(path);
if (!root.exists()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive from " + root);
} else {
return (Archive)(root.isDirectory() ? new ExplodedArchive(root) : new JarFileArchive(root));
}
}
}
}
public class MainMethodRunner {
private final String mainClassName;
private final String[] args;
public MainMethodRunner(String mainClass, String[] args) {
this.mainClassName = mainClass;
this.args = args != null ? (String[])args.clone() : null;
}
/**
* 最终执行的方法,可以发现是利用的反射调用的我们应用程序的主函数
*/
public void run() throws Exception {
Class<?> mainClass = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass(this.mainClassName);
Method mainMethod = mainClass.getDeclaredMethod("main", String[].class);
mainMethod.invoke((Object)null, this.args);
}
}小结:
内容太多了,未涉及归档文件,协议处理器,打包war同样的可以用命令启动等。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-loader</artifactId> </dependency>
IDEA进行启动类的配置 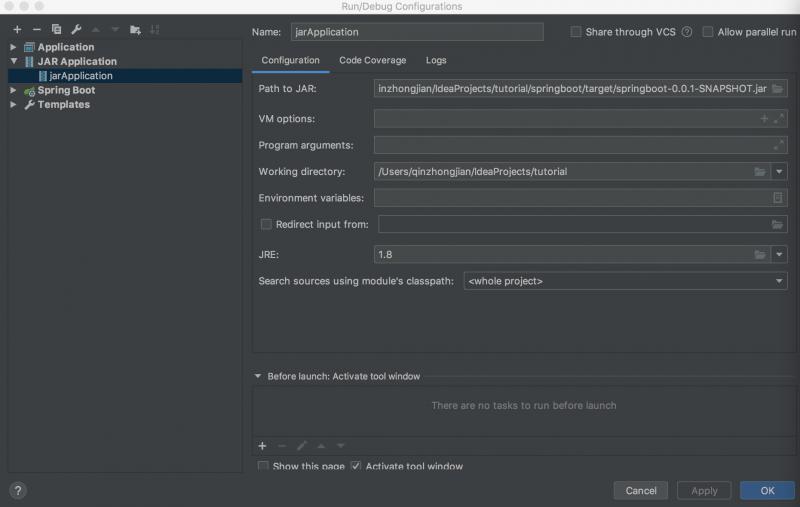
关于Springboot中的jar是怎样的就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。