本篇内容主要讲解“怎么用VUE + OPENLAYERS实现实时定位功能”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“怎么用VUE + OPENLAYERS实现实时定位功能”吧!
本系列文章介绍一个简单的实时定位示例,示例的组成主要包括:
服务后端,使用 Java 语言编写,模拟生成 GeoJSON 数据。
前端展示,使用 Vue + OpenLayers ,负责定时向后端服务请求 GeoJSON 数据,并在以标签的形式展现定位数据。
实现的效果:
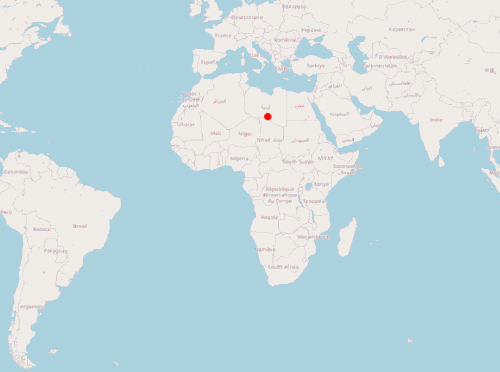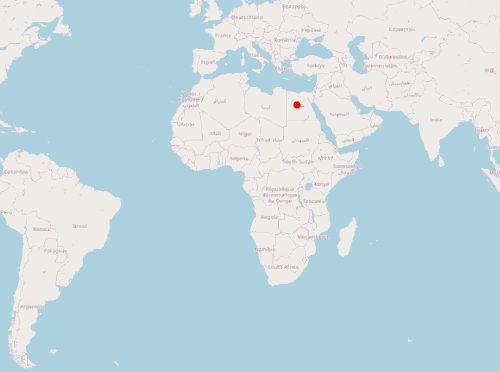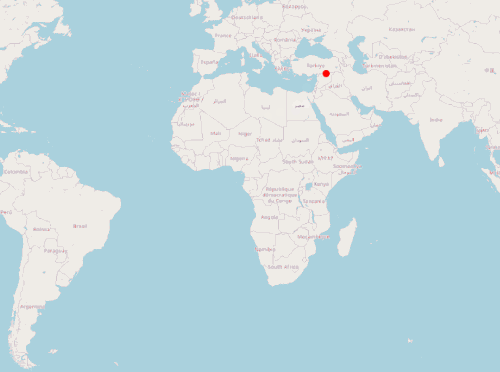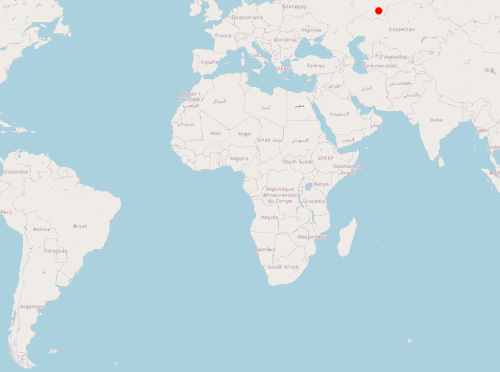
var image = new CircleStyle({
radius: 5,
fill: new Fill({
color: "rgba(255, 0, 0, 1)"
}),
stroke: new Stroke({ color: "red", width: 1 })
});
var styles = {
Point: new Style({
image: image
})
};
var styleFunction = function(feature) {
return styles[feature.getGeometry().getType()];
}; var geojsonObject = {
type: "FeatureCollection",
features: [
{
type: "Feature",
geometry: {
type: "Point",
coordinates: [0, 0]
}
}
//此处可以添加更多 feature
]
}; //读取 GeoJSON, 将其作为 vectorSource 的数据源
var vectorSource = new VectorSource({
features: new GeoJSON().readFeatures(geojsonObject)
});
var vectorLayer = new VectorLayer({
source: vectorSource,
style: styleFunction
}); mounted() {
this.map = new Map({
layers: [
new TileLayer({
source: new OSM()
}),
vectorLayer
],
target: "map",
view: new View({
center: [0, 0],
zoom: 2
})
});
//设置定时任务,调用移动标签方法
setInterval(this.translate, 500);
}, methods: {
translate() {
//遍历标签, 修改坐标位置
vectorSource.forEachFeature(function(f) {
console.log("translate");
//随机产生坐标增量(此处不是坐标绝对值!!!!)
var x = Math.random() * 1000000;
var y = Math.random() * 1000000;
f.getGeometry().translate(x, y);
});
}
}以上是一个简单实时定位前端示例,通过模拟的 GeoJSON 对象展示标签,并通过定时任务模拟标签位置变化。下一篇将使用 Java 服务端提供位置数据,完整模拟一个实时定位系统。
可以在vue项目中直接运行的完整代码:
<template>
<div>
<span>hi, map</span>
<div id="map" class="map"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import "ol/ol.css";
import GeoJSON from "ol/format/GeoJSON";
import Map from "ol/Map";
import View from "ol/View";
import { Circle as CircleStyle, Fill, Stroke, Style } from "ol/style";
import { OSM, Vector as VectorSource } from "ol/source";
import { Tile as TileLayer, Vector as VectorLayer } from "ol/layer";
import Vue from "vue";
var image = new CircleStyle({
radius: 5,
fill: new Fill({
color: "rgba(255, 0, 0, 1)"
}),
stroke: new Stroke({ color: "red", width: 1 })
});
var styles = {
Point: new Style({
image: image
})
};
var styleFunction = function(feature) {
return styles[feature.getGeometry().getType()];
};
var geojsonObject = {
type: "FeatureCollection",
features: [
{
type: "Feature",
geometry: {
type: "Point",
coordinates: [0, 0]
}
}
]
};
var vectorSource = new VectorSource({
features: new GeoJSON().readFeatures(geojsonObject)
});
var vectorLayer = new VectorLayer({
source: vectorSource,
style: styleFunction
});
export default Vue.extend({
data() {
return {
map: {}
};
},
mounted() {
this.map = new Map({
layers: [
new TileLayer({
source: new OSM()
}),
vectorLayer
],
target: "map",
view: new View({
center: [0, 0],
zoom: 2
})
});
setInterval(this.translate, 500);
},
methods: {
translate() {
vectorSource.forEachFeature(function(f) {
console.log("translate");
var x = Math.random() * 1000000;
var y = Math.random() * 1000000;
f.getGeometry().translate(x, y);
});
}
}
});
</script>
<style>
.map {
width: 100%;
height: 600px;
}
</style>到此,相信大家对“怎么用VUE + OPENLAYERS实现实时定位功能”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。