这篇文章给大家分享的是有关C/C++中CJSON怎么用的内容。小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,一起跟随小编过来看看吧。
cJSON 是一个超轻巧,携带方便,单文件,可以作为 ANSI-C 标准的 JSON 解析器,是一个用C语言编写的简单好用的JSON解析器;它只包含一个C文件和一个头文件,可以非常容易集成到自己工程项目中。
并且cJSON是用ANSI C(C89)编写的,可以兼容所有支持C语言的平台和编译器。
cJSON下载地址: https://sourceforge.net/projects/cjson/
cJSON的GitHub仓库地址:https://github.com/DaveGamble/cJSON
JSON是JavaScript Object Notation(JavaScript对象表示法),是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。
JSON主要是用来存储和交换文本信息,类似XML格式;但是JSON比XML更小、更快,更易解析。
JSON是基于ECMAScript (欧洲计算机协会制定的js规范)的一个子集,采用完全独立于编程语言的文本格式来存储和表示数据。
简洁和清晰的层次结构使得 JSON 成为理想的数据交换语言。 易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成,并有效地提升网络传输效率。 比如: Web服务器接口基本都是采用JSON反馈数据,采用JSON格式字符串来描述符信息。 JSON文件的后缀一般是.json,这个只是为了方便辨识。
简单的说,JSON就是按照指定格式序列化的字符串,就算不使用任何现成的解析库,自己也可以按照正常解析字符串的思路去解析;有现成的标准JSON解析库,那就大大减轻了我们的工作量。
JSON格式的数据示例: 这是表示当前时间的JSON字符串
{
"success": "1",
"result": {
"timestamp": "1631849514",
"datetime_1": "2021-09-17 20:31:54",
"datetime_2": "2021年09月17日 20时31分54秒",
"week_1": "5",
"week_2": "星期五",
"week_3": "周五",
"week_4": "Friday"
}
}JSON格式的数据示例: 这是表示未来几天天气预报的json字符串
{
"success": "1",
"result": [
{
"weaid": "1",
"days": "2021-09-17",
"week": "星期五",
"cityno": "beijing",
"citynm": "北京",
"cityid": "101010100",
"temperature": "26℃/17℃",
"humidity": "0%/0%",
"weather": "晴",
"weather_icon": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/d/0.gif",
"weather_icon1": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/n/0.gif",
"wind": "北风转西南风",
"winp": "小于3级",
"temp_high": "26",
"temp_low": "17",
"humi_high": "0",
"humi_low": "0",
"weatid": "1",
"weatid1": "1",
"windid": "8",
"winpid": "0",
"weather_iconid": "0",
"weather_iconid1": "0"
},
{
"weaid": "1",
"days": "2021-09-18",
"week": "星期六",
"cityno": "beijing",
"citynm": "北京",
"cityid": "101010100",
"temperature": "25℃/17℃",
"humidity": "0%/0%",
"weather": "多云",
"weather_icon": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/d/1.gif",
"weather_icon1": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/n/1.gif",
"wind": "西南风",
"winp": "小于3级",
"temp_high": "25",
"temp_low": "17",
"humi_high": "0",
"humi_low": "0",
"weatid": "2",
"weatid1": "2",
"windid": "5",
"winpid": "0",
"weather_iconid": "1",
"weather_iconid1": "1"
},
{
"weaid": "1",
"days": "2021-09-19",
"week": "星期日",
"cityno": "beijing",
"citynm": "北京",
"cityid": "101010100",
"temperature": "19℃/15℃",
"humidity": "0%/0%",
"weather": "小雨转中雨",
"weather_icon": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/d/7.gif",
"weather_icon1": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/n/8.gif",
"wind": "西南风转北风",
"winp": "小于3级转小于3级",
"temp_high": "19",
"temp_low": "15",
"humi_high": "0",
"humi_low": "0",
"weatid": "8",
"weatid1": "9",
"windid": "5",
"winpid": "0",
"weather_iconid": "7",
"weather_iconid1": "8"
},
{
"weaid": "1",
"days": "2021-09-20",
"week": "星期一",
"cityno": "beijing",
"citynm": "北京",
"cityid": "101010100",
"temperature": "26℃/16℃",
"humidity": "0%/0%",
"weather": "多云转晴",
"weather_icon": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/d/1.gif",
"weather_icon1": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/n/0.gif",
"wind": "北风",
"winp": "3-4级转3-4级",
"temp_high": "26",
"temp_low": "16",
"humi_high": "0",
"humi_low": "0",
"weatid": "2",
"weatid1": "1",
"windid": "8",
"winpid": "1",
"weather_iconid": "1",
"weather_iconid1": "0"
},
{
"weaid": "1",
"days": "2021-09-21",
"week": "星期二",
"cityno": "beijing",
"citynm": "北京",
"cityid": "101010100",
"temperature": "27℃/16℃",
"humidity": "0%/0%",
"weather": "晴",
"weather_icon": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/d/0.gif",
"weather_icon1": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/n/0.gif",
"wind": "西北风转北风",
"winp": "小于3级",
"temp_high": "27",
"temp_low": "16",
"humi_high": "0",
"humi_low": "0",
"weatid": "1",
"weatid1": "1",
"windid": "7",
"winpid": "0",
"weather_iconid": "0",
"weather_iconid1": "0"
},
{
"weaid": "1",
"days": "2021-09-22",
"week": "星期三",
"cityno": "beijing",
"citynm": "北京",
"cityid": "101010100",
"temperature": "26℃/18℃",
"humidity": "0%/0%",
"weather": "多云",
"weather_icon": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/d/1.gif",
"weather_icon1": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/n/1.gif",
"wind": "北风转东北风",
"winp": "小于3级",
"temp_high": "26",
"temp_low": "18",
"humi_high": "0",
"humi_low": "0",
"weatid": "2",
"weatid1": "2",
"windid": "8",
"winpid": "0",
"weather_iconid": "1",
"weather_iconid1": "1"
},
{
"weaid": "1",
"days": "2021-09-23",
"week": "星期四",
"cityno": "beijing",
"citynm": "北京",
"cityid": "101010100",
"temperature": "24℃/16℃",
"humidity": "0%/0%",
"weather": "多云",
"weather_icon": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/d/1.gif",
"weather_icon1": "http://api.k780.com/upload/weather/n/1.gif",
"wind": "东北风",
"winp": "小于3级",
"temp_high": "24",
"temp_low": "16",
"humi_high": "0",
"humi_low": "0",
"weatid": "2",
"weatid1": "2",
"windid": "1",
"winpid": "0",
"weather_iconid": "1",
"weather_iconid1": "1"
}
]
}JSON里就分为两种结构: 对象和数组,通过这两种结构可以表示各种复杂的结构。
JSON语法规则
1. 大括号 { } 用来保存对象
2. 中括号 [ ] 用来保存数组,数组里也可以包含多个对象,对象里又可以包含数组,可以嵌套
3. JSON的值表示语法: key : value --> "width": 1280
4. 多个数据由逗号分隔: {"width": 1920,"height": 1080}
JSON值可以是以下几种类型:
1. 数字(整数或浮点数)
2. 字符串(在双引号中)
3. 逻辑值(true 或 false)
4. 数组(在中括号中)
5. 对象(在大括号中)
6. null (空值)
这是下载下来的cJSON源文件,将它加到自己工程中即可。
我这里使用VS2017建立工程,演示实例。
建好工程之后,将文件添加到工程里:
在VS2017里使用C语言的字符串处理函数会报错,提示不安全;
1>d:\linux-share-dir\vs2017\console_cjsontest\console_cjsontest\cjson.c(155): error C4996: 'strcpy': This function or variable may be unsafe. Consider using strcpy_s instead. To disable deprecation, use _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS. See online help for details.
解决办法是:找到【项目属性】,点击【C++】里的【预处理器】,对【预处理器】进行编辑,在里面加入一段代码:_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS。
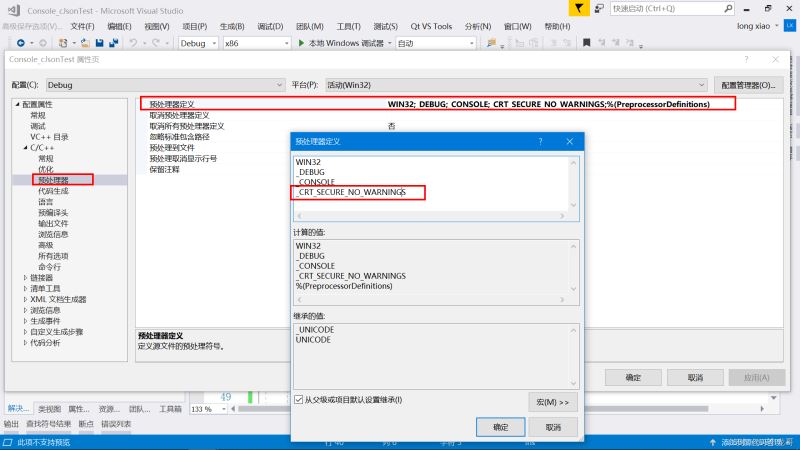
接下来目标是使用cJSON创建出下面这样一个JSON格式数据:
{
"text": "我是一个字符串数据",
"number": 666,
"state1": false,
"state2": true,
"state3": null
}示例代码如下:
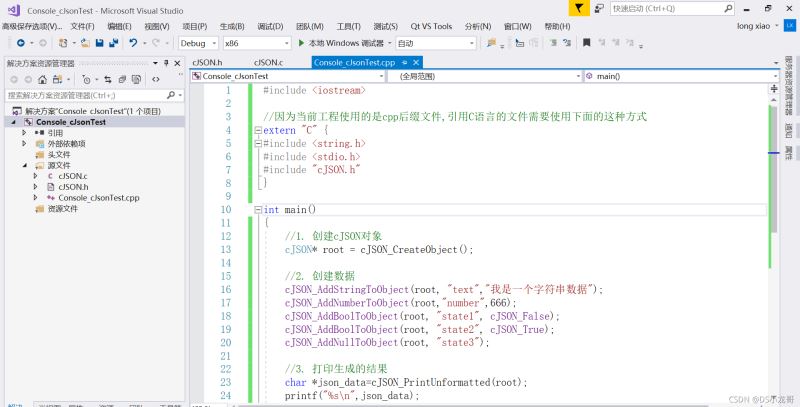
#include <iostream>
//因为当前工程使用的是cpp后缀文件,引用C语言的文件需要使用下面的这种方式
extern "C" {
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "cJSON.h"
}
int main()
{
//1. 创建cJSON对象
cJSON* root = cJSON_CreateObject();
//2. 创建数据
cJSON_AddStringToObject(root, "text","我是一个字符串数据");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(root,"number",666);
cJSON_AddBoolToObject(root, "state1", cJSON_False);
cJSON_AddBoolToObject(root, "state2", cJSON_True);
cJSON_AddNullToObject(root, "state3");
//3. 打印生成的结果
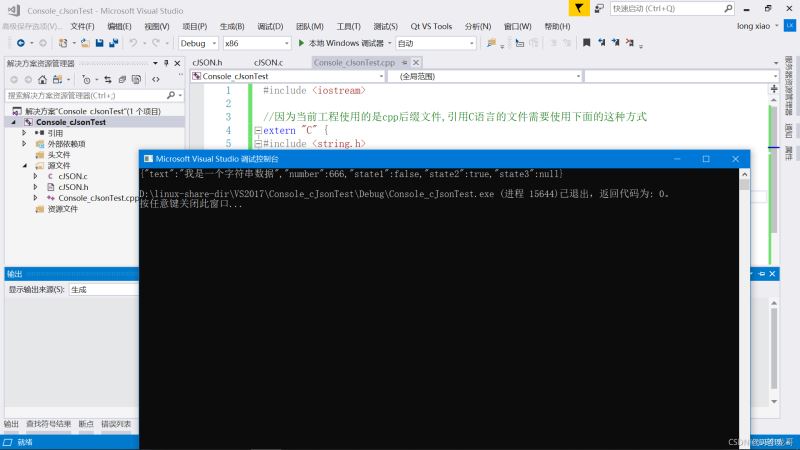
char *json_data=cJSON_PrintUnformatted(root);
printf("%s\n",json_data);
//4. 释放空间
cJSON_Delete(root);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
//因为当前工程使用的是cpp后缀文件,引用C语言的文件需要使用下面的这种方式
extern "C" {
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "cJSON.h"
}
//将要解析的JSON数据.
char data[] =
"{"
"\"text\": \"我是一个字符串数据\","
"\"number\" : 666,"
"\"state1\" : false,"
"\"state2\" : true,"
"\"state3\" : null"
"}";
int main()
{
//1. 载入JSON数据
cJSON* root = cJSON_Parse(data);
if (root == NULL)return 0;
//2. 解析字段
cJSON* item;
item=cJSON_GetObjectItem(root,"text");
if (item)
{
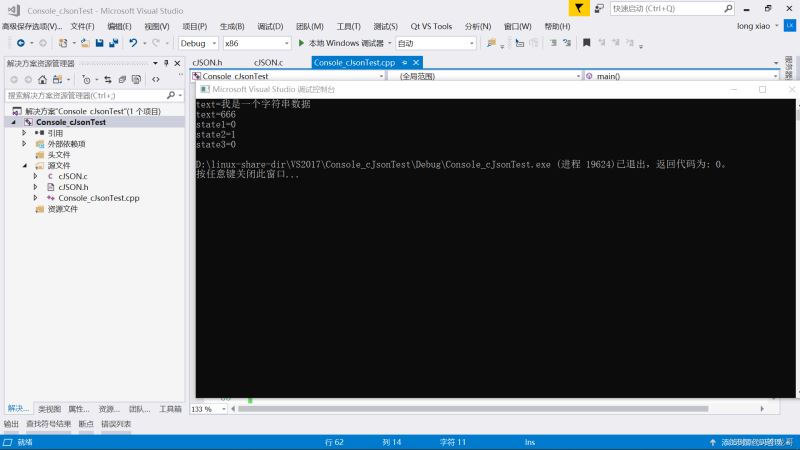
printf("text=%s\n",item->valuestring);
}
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "number");
if (item)
{
printf("text=%d\n", item->valueint);
}
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "state1");
if (item)
{
printf("state1=%d\n", item->valueint);
}
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "state2");
if (item)
{
printf("state2=%d\n", item->valueint);
}
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "state3");
if (item)
{
printf("state3=%d\n", item->valueint);
}
//3. 释放空间
cJSON_Delete(root);
return 0;
}
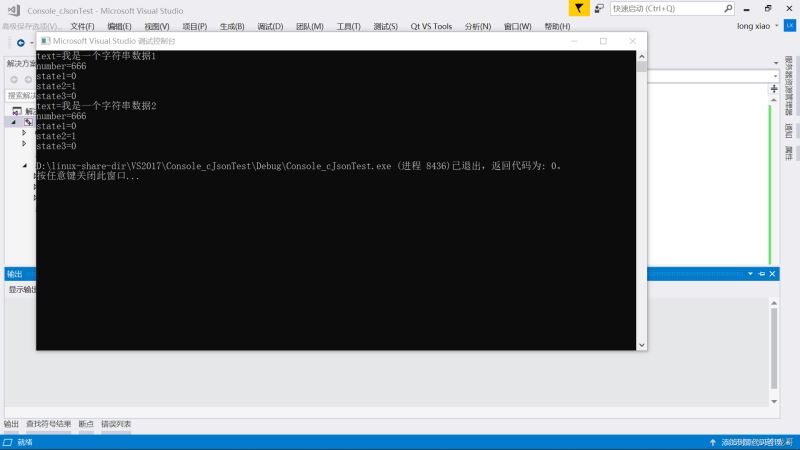
目标: 使用cJSON创建出下面这样一个JSON格式数据
{
"data1": {
"text": "我是一个字符串数据1",
"number": 666,
"state1": false,
"state2": true,
"state3": null
},
"data2": {
"text": "我是一个字符串数据2",
"number": 666,
"state1": false,
"state2": true,
"state3": null
}
}#include <iostream>
//因为当前工程使用的是cpp后缀文件,引用C语言的文件需要使用下面的这种方式
extern "C" {
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "cJSON.h"
}
int main()
{
//1. 创建cJSON对象
cJSON* root = cJSON_CreateObject();
//2. 创建对象数据1
cJSON* item1 = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddStringToObject(item1, "text","我是一个字符串数据1");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(item1,"number",666);
cJSON_AddBoolToObject(item1, "state1", cJSON_False);
cJSON_AddBoolToObject(item1, "state2", cJSON_True);
cJSON_AddNullToObject(item1, "state3");
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "data1", item1);
//3. 创建对象数据2
cJSON* item2 = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddStringToObject(item2, "text", "我是一个字符串数据2");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(item2, "number", 666);
cJSON_AddBoolToObject(item2, "state1", cJSON_False);
cJSON_AddBoolToObject(item2, "state2", cJSON_True);
cJSON_AddNullToObject(item2, "state3");
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "data2", item2);
//3. 打印生成的结果
char *json_data=cJSON_PrintUnformatted(root);
printf("%s\n",json_data);
//4. 释放空间
cJSON_Delete(root);
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
//因为当前工程使用的是cpp后缀文件,引用C语言的文件需要使用下面的这种方式
extern "C" {
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "cJSON.h"
}
//将要解析的JSON数据.
char data[] =
"{"
"\"data1\": {"
"\"text\": \"我是一个字符串数据1\","
"\"number\" : 666,"
"\"state1\" : false,"
"\"state2\" : true,"
"\"state3\" : null"
"},"
"\"data2\": {"
"\"text\":\"我是一个字符串数据2\","
"\"number\" : 666,"
"\"state1\" : false,"
"\"state2\" : true,"
"\"state3\" : null"
"}"
"}";
int main()
{
//1. 载入JSON数据
cJSON* root = cJSON_Parse(data);
if (root == NULL)return 0;
//2. 解析字段
cJSON* item;
item=cJSON_GetObjectItem(root,"data1");
if (item)
{
cJSON *obj;
obj=cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "text");
if (obj)
{
printf("text=%s\n", obj->valuestring);
}
obj=cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "number");
if (obj)
{
printf("number=%d\n", obj->valueint);
}
obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "state1");
if (obj)
{
printf("state1=%d\n", obj->valueint);
}
obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "state2");
if (obj)
{
printf("state2=%d\n", obj->valueint);
}
obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "state3");
if (obj)
{
printf("state3=%d\n", obj->valueint);
}
}
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "data2");
if (item)
{
cJSON *obj;
obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "text");
if (obj)
{
printf("text=%s\n", obj->valuestring);
}
obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "number");
if (obj)
{
printf("number=%d\n", obj->valueint);
}
obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "state1");
if (obj)
{
printf("state1=%d\n", obj->valueint);
}
obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "state2");
if (obj)
{
printf("state2=%d\n", obj->valueint);
}
obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "state3");
if (obj)
{
printf("state3=%d\n", obj->valueint);
}
}
//3. 释放空间
cJSON_Delete(root);
return 0;
}
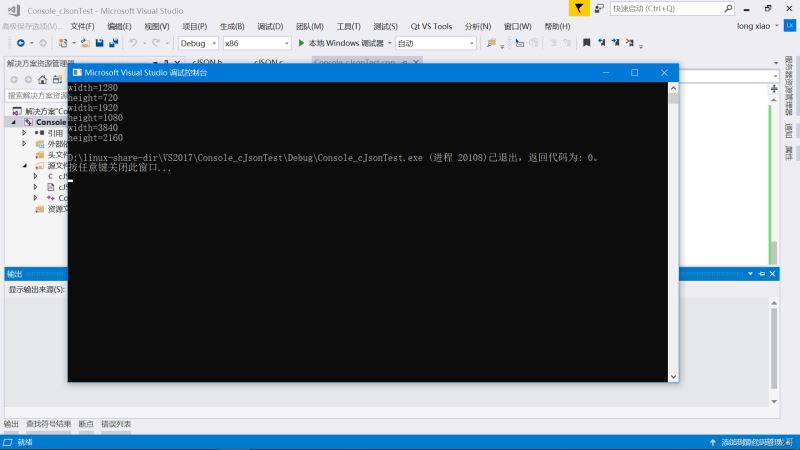
目标: 使用cJSON创建出下面这样一个JSON格式数据
{
"text": [
{
"width": 1280,
"height": 720
},
{
"width": 1920,
"height": 1080
},
{
"width": 3840,
"height": 2160
}
]
}#include <iostream>
//因为当前工程使用的是cpp后缀文件,引用C语言的文件需要使用下面的这种方式
extern "C" {
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "cJSON.h"
}
int main()
{
cJSON *width = NULL;
cJSON *height = NULL;
int i;
const unsigned int resolution_numbers[3][2] = {
{1280, 720},
{1920, 1080},
{3840, 2160}
};
//1. 创建cJSON对象
cJSON* root = cJSON_CreateObject();
//2. 创建数组对象
cJSON *array = cJSON_CreateArray();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "text", array);
for (i = 0; i < (sizeof(resolution_numbers) / (2 * sizeof(int))); ++i)
{
cJSON *obj = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToArray(array, obj);
width = cJSON_CreateNumber(resolution_numbers[i][0]);
cJSON_AddItemToObject(obj, "width", width);
height = cJSON_CreateNumber(resolution_numbers[i][1]);
cJSON_AddItemToObject(obj, "height", height);
}
//3. 打印生成的结果
char *json_data=cJSON_PrintUnformatted(root);
printf("%s\n",json_data);
//4. 释放空间
cJSON_Delete(root);
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
//因为当前工程使用的是cpp后缀文件,引用C语言的文件需要使用下面的这种方式
extern "C" {
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "cJSON.h"
}
//将要解析的JSON数据.
char data[] =
"{"
"\"text\": ["
"{"
"\"width\": 1280,"
"\"height\" : 720"
"},"
"{"
"\"width\": 1920,"
"\"height\" : 1080"
"},"
"{"
"\"width\": 3840,"
"\"height\" : 2160"
"}"
"]"
"}";
int main()
{
//1. 载入JSON数据
cJSON* root = cJSON_Parse(data);
if (root == NULL)return 0;
//2. 解析字段
cJSON* item;
int i;
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "text");
if (item)
{
//获取数组的大小
int ArraySize = cJSON_GetArraySize(item);
//解析数组的里的每个成员
for (i = 0; i < ArraySize; i++)
{
//取出数组下标对象
cJSON *array_item = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, i);
if (array_item == NULL)continue;
//解析数据
cJSON *obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(array_item, "width");
if (obj)
{
printf("width=%d\n",obj->valueint);
}
obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(array_item, "height");
if (obj)
{
printf("height=%d\n", obj->valueint);
}
}
}
//3. 释放空间
cJSON_Delete(root);
return 0;
}
感谢各位的阅读!关于“C/C++中CJSON怎么用”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,让大家可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到吧!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。