小编给大家分享一下SpringBoot怎么使用ApplicationContext获取bean对象,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后都有所收获,下面让我们一起去探讨吧!
编写一个ApplicationContextFactory工厂类
public class ApplicationContextFactory{
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext = null;
public static void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext(){
return applicationContext;
}
}在SpringBoot的启动类中设置ApplicationContext
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext app = SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
ApplicationContextFactory.setApplicationContext(app);
}
}通过ApplicationContextFactory获取SpringApplication从而获取bean对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext=ApplicationContextFactory.getApplicationContext(); Clazz clazz = applicationContext.getBean(Clazz.class);
DemoService
@Service
public class DemoService {
public void save(){
System.out.println("DemoService save");
}
}CommonClass
@Component
public class CommonClass {
@Resource
private DemoService demoService;
public void fun(){
System.out.println("fun");
demoService.save();
}
}Controller
@Resource
private CommonClass commonClass;
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/fun")
public void fun(){
commonClass.fun();
}DemoService
@Service
public class DemoService {
public void save(){
System.out.println("DemoService save");
}
}CommonClass
public class CommonClass {
@Resource
private DemoService demoService;
public void fun(){
System.out.println("fun");
demoService.save();
}
}Controller
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/fun")
public void fun(){
CommonClass commonClass = new CommonClass();
commonClass.fun();
}比较两个代码发现后者与前者的区别:因后者的CommonClass 没有使用@Component标注,所以在Controller中不能才用注入方式生成CommonClass对象,而是才用new的方式生成了该对象。
这样一来,CommonClass 对象是手工创建,所以在它内部注入DemoService 对象的代码就错误了。
新建工具类
@Component
public class ApplicationContextUtil implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext act;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
act = applicationContext;
}
/**
* 根据bean的名字获取工厂中对应的bean对象
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
public static Object getBean(String beanName){
return act.getBean(beanName);
}
}注:实际测试发现上面代码中的static不能省略
DemoService
@Service
public class DemoService {
public void save(){
System.out.println("DemoService save");
}
}CommonClass
public class CommonClass {
@Resource
private DemoService demoService;
public void fun(){
DemoService demoService = (DemoService) ApplicationContextUtil.getBean("demoService");
System.out.println("fun");
demoService.save();
}
}此处不再采用注入的方式获取DemoService对象,而是通过工具类的方式
Controller
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/fun")
public void fun(){
CommonClass commonClass = new CommonClass();
commonClass.fun();
}再次运行程序,一切正常
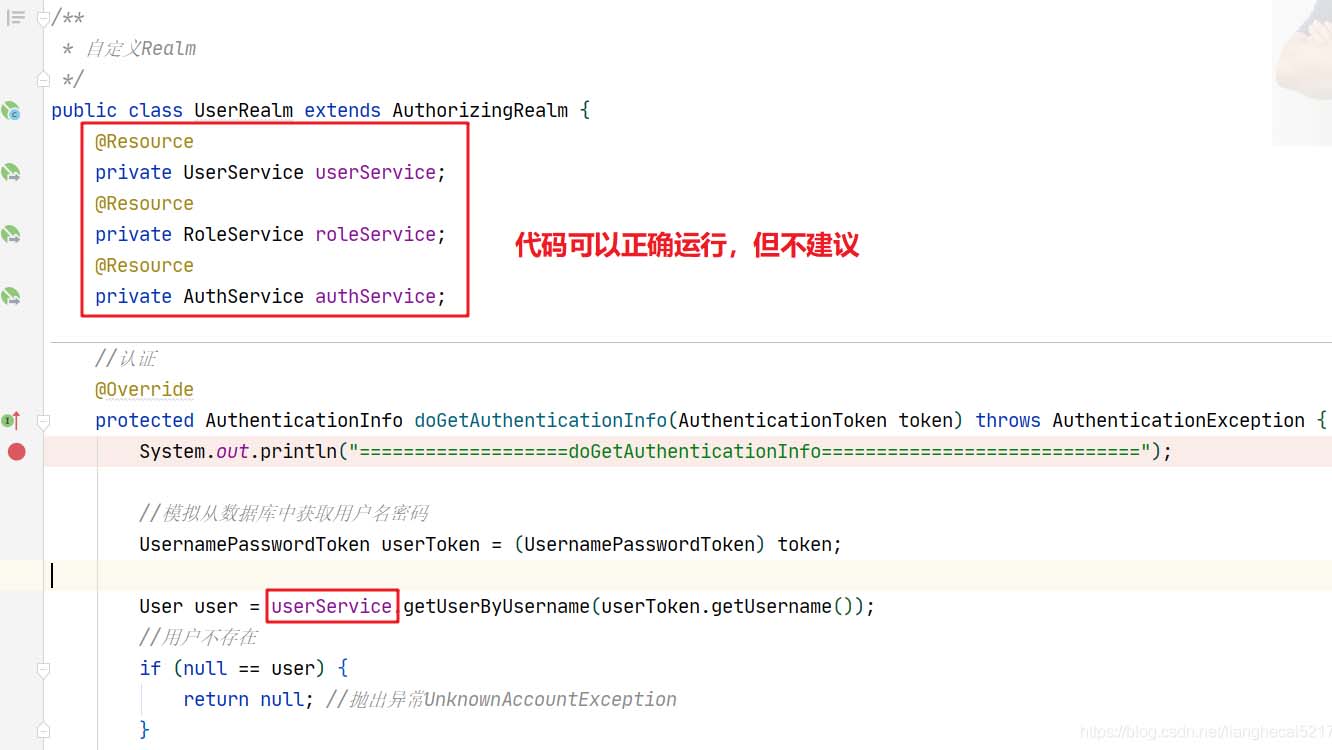
在SpringBoot整合Shiro的案例中,自定义Realm时,需要使用Service的对象。因为自定义的Realm类不能使用@Component之类的注解注释,所以使用本案例介绍的方法是正确的解决方案。尽管在1.6.0的shiro-all中下面代码可以正确运行:
看完了这篇文章,相信你对“SpringBoot怎么使用ApplicationContext获取bean对象”有了一定的了解,如果想了解更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢各位的阅读!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。