这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关python如何实现将天气预报可视化,小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后可以有所收获。
其中:
红线代表当天最高气温,蓝线代表最低气温,最高气温点上的标注为当天的天气情况。
如果使夜晚运行程序,则最高气温和最低气温的点会重合,使由爬取数据产生误差导致的。
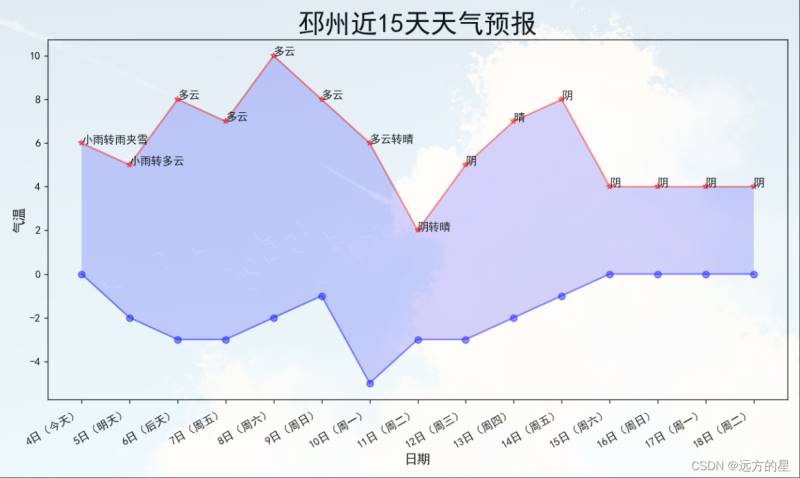
详细请看注释
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
"""
# @Time: 2022/1/4 11:02
# @Author: 远方的星
# @CSDN: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44921056
"""
import chardet
import requests
from lxml import etree
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 随机产生请求头
ua = UserAgent(verify_ssl=False, path='D:/Pycharm/fake_useragent.json')
# 随机切换请求头
def random_ua():
headers = {
"user-agent": ua.random
}
return headers
# 解析页面
def res_text(url):
res = requests.get(url=url, headers=random_ua())
res.encoding = chardet.detect(res.content)['encoding']
response = res.text
html = etree.HTML(response)
return html
# 获得未来七天及八到十五天的页面链接
def get_url(url):
html = res_text(url)
url_7 = 'http://www.weather.com.cn/' + html.xpath('//*[@id="someDayNav"]/li[2]/a/@href')[0]
url_8_15 = 'http://www.weather.com.cn/' + html.xpath('//*[@id="someDayNav"]/li[3]/a/@href')[0]
# print(url_7)
# print(url_8_15)
return url_7, url_8_15
# 获取未来七天的天气情况
def get_data_7(url):
html = res_text(url)
list_s = html.xpath('//*[@id="7d"]/ul/li') # 获取天气数据列表
Date, Weather, Low, High = [], [], [], []
for i in range(len(list_s)):
list_date = list_s[i].xpath('./h2/text()')[0] # 获取日期,如:4日(明天)
# print(list_data)
list_weather = list_s[i].xpath('./p[1]/@title')[0] # 获取天气情况,如:小雨转雨夹雪
# print(list_weather)
tem_low = list_s[i].xpath('./p[2]/i/text()') # 获取最低气温
tem_high = list_s[i].xpath('./p[2]/span/text()') # 获取最高气温
if tem_high == []: # 遇到夜晚情况,筛掉当天的最高气温
tem_high = tem_low # 无最高气温时,使最高气温等于最低气温
tem_low = int(tem_low[0].replace('℃', '')) # 将气温数据处理
tem_high = int(tem_high[0].replace('℃', ''))
# print(type(tem_high))
Date.append(list_date), Weather.append(list_weather), Low.append(tem_low), High.append(tem_high)
excel = pd.DataFrame() # 定义一个二维列表
excel['日期'] = Date
excel['天气'] = Weather
excel['最低气温'] = Low
excel['最高气温'] = High
# print(excel)
return excel
def get_data_8_15(url):
html = res_text(url)
list_s = html.xpath('//*[@id="15d"]/ul/li')
Date, Weather, Low, High = [], [], [], []
for i in range(len(list_s)):
# data_s[0]是日期,如:周二(11日),data_s[1]是天气情况,如:阴转晴,data_s[2]是最低温度,如:/-3℃
data_s = list_s[i].xpath('./span/text()')
# print(data_s)
date = modify_str(data_s[0]) # 获取日期情况
weather = data_s[1]
low = int(data_s[2].replace('/', '').replace('℃', ''))
high = int(list_s[i].xpath('./span/em/text()')[0].replace('℃', ''))
# print(date, weather, low, high)
Date.append(date), Weather.append(weather), Low.append(low), High.append(high)
# print(Date, Weather, Low, High)
excel = pd.DataFrame() # 定义一个二维列表
excel['日期'] = Date
excel['天气'] = Weather
excel['最低气温'] = Low
excel['最高气温'] = High
# print(excel)
return excel
# 将8-15天日期格式改成与未来7天一致
def modify_str(date):
date_1 = date.split('(')
date_2 = date_1[1].replace(')', '')
date_result = date_2 + '(' + date_1[0] + ')'
return date_result
# 实现数据可视化
def get_image(date, weather, high, low):
# 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
# 用来正常显示负号
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 根据数据绘制图形
fig = plt.figure(dpi=128, figsize=(10, 6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
plt.plot(date, high, c='red', alpha=0.5, marker='*')
plt.plot(date, low, c='blue', alpha=0.5, marker='o')
# 给图表中两条折线中间的部分上色
plt.fill_between(date, high, low, facecolor='blue', alpha=0.2)
# 设置图表格式
plt.title('邳州近15天天气预报', fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel('日期', fontsize=12)
# 绘制斜的标签,以免重叠
fig.autofmt_xdate()
plt.ylabel('气温', fontsize=12)
# 参数刻度线设置
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=10)
# 修改刻度
plt.xticks(date[::1])
# 对点进行标注,在最高气温点处标注当天的天气情况
for i in range(15):
ax.annotate(weather[i], xy=(date[i], high[i]))
# 显示图片
plt.show()
def main():
base_url = 'http://www.weather.com.cn/weather1d/101190805.shtml'
url_7, url_8_15 = get_url(base_url)
data_1 = get_data_7(url_7)
data_2 = get_data_8_15(url_8_15)
data = pd.concat([data_1, data_2], axis=0, ignore_index=True) # ignore_index=True实现两张表拼接,不保留原索引
get_image(data['日期'], data['天气'], data['最高气温'], data['最低气温'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()关于“python如何实现将天气预报可视化”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,使各位可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,请把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。