这篇文章主要介绍了Springboot基于Redisson如何实现Redis分布式可重入锁源码解析,具有一定借鉴价值,感兴趣的朋友可以参考下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后大有收获,下面让小编带着大家一起了解一下。
我们在实现使用Redis实现分布式锁,最开始一般使用SET resource-name anystring NX EX max-lock-time进行加锁,使用Lua脚本保证原子性进行实现释放锁。这样手动实现比较麻烦,对此Redis官网也明确说Java版使用Redisson来实现。小编也是看了官网慢慢的摸索清楚,特写此记录一下。从官网到整合Springboot到源码解读,以单节点为例。
redis中文官网

Redisson地址
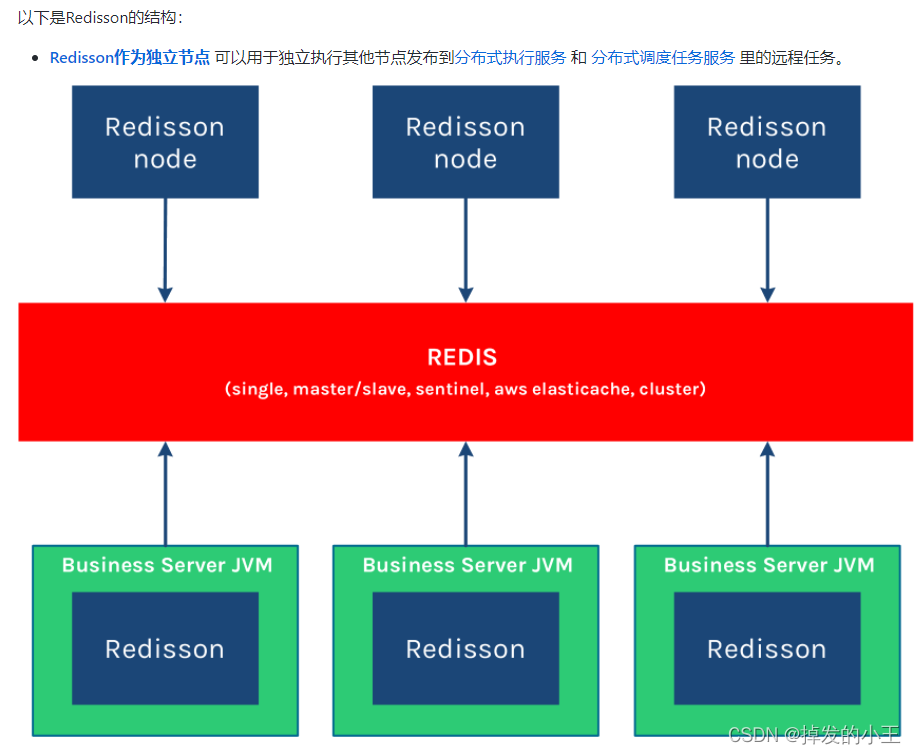
5. Redisson结构
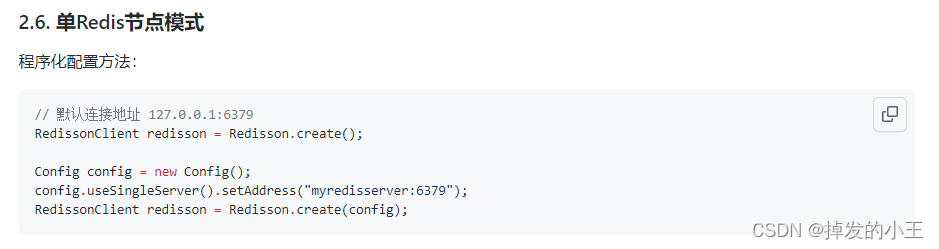
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> </dependency> <!--redis分布式锁--> <dependency> <groupId>org.redisson</groupId> <artifactId>redisson</artifactId> <version>3.12.0</version> </dependency>
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author wangzhenjun
* @date 2022/2/9 9:57
*/
@Configuration
public class MyRedissonConfig {
/**
* 所有对redisson的使用都是通过RedissonClient来操作的
* @return
*/
@Bean(destroyMethod="shutdown")
public RedissonClient redisson(){
// 1. 创建配置
Config config = new Config();
// 一定要加redis://
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.17.130:6379");
// 2. 根据config创建出redissonClient实例
RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create(config);
return redissonClient;
}
}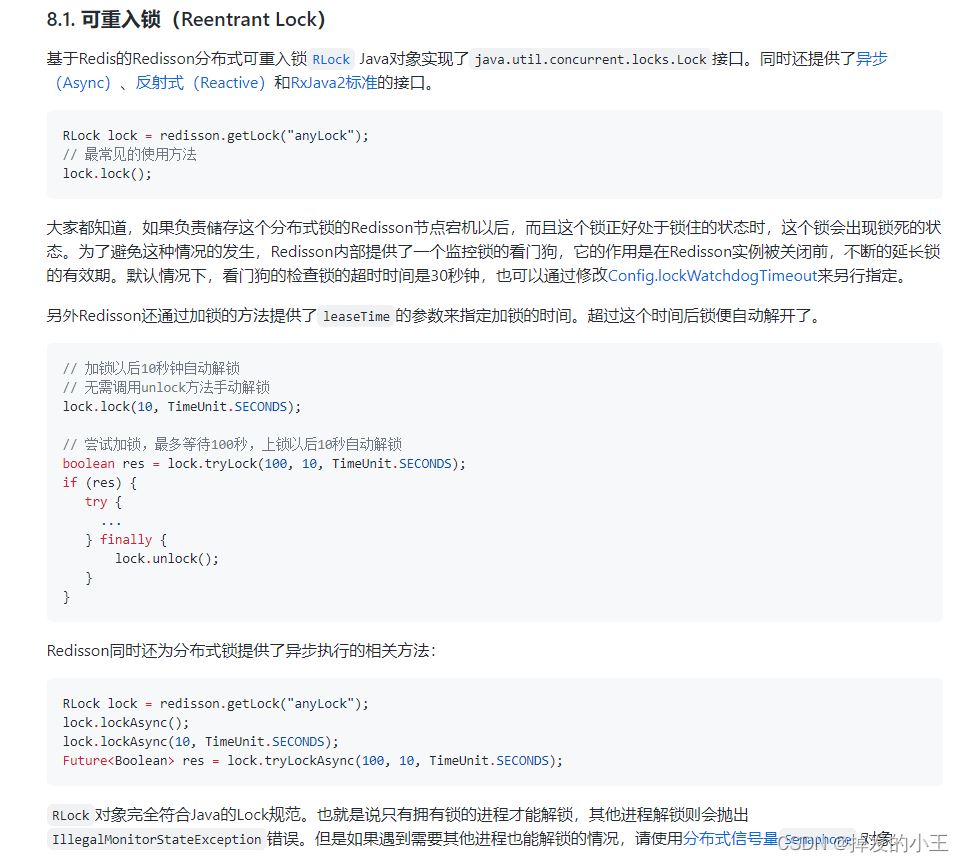
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
// 1.获取一把锁,只要锁名字一样,就是同一把锁
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("my-lock");
// 2. 加锁
lock.lock();// 阻塞试等待 默认加的都是30s
// 带参数情况
// lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);// 10s自动解锁,自动解锁时间一定要大于业务的执行时间。
try {
System.out.println("加锁成功" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 3. 解锁
System.out.println("解锁成功:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
lock.unlock();
}
return "hello";
}
@Override
public void lock() {
try {
// 我们发现不穿过期时间源码默认过期时间为-1
lock(-1, null, false);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
}private void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, boolean interruptibly) throws InterruptedException {
// 获取线程的id,占有锁的时候field的值为UUID:线程号id
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
// 尝试获得锁
Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired 获得锁,返回
if (ttl == null) {
return;
}
// 这里说明获取锁失败,就通过线程id订阅这个锁
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
if (interruptibly) {
commandExecutor.syncSubscriptionInterrupted(future);
} else {
commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
}
try {
// 这里进行自旋,不断尝试获取锁
while (true) {
// 继续尝试获取锁
ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired 获取成功
if (ttl == null) {
// 直接返回,挑出自旋
break;
}
// waiting for message 继续等待获得锁
if (ttl >= 0) {
try {
future.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
if (interruptibly) {
throw e;
}
future.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
} else {
if (interruptibly) {
future.getNow().getLatch().acquire();
} else {
future.getNow().getLatch().acquireUninterruptibly();
}
}
}
} finally {
// 取消订阅
unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
// get(lockAsync(leaseTime, unit));
}
private Long tryAcquire(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// 直接进入异步方法
return get(tryAcquireAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId));
}
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// 这里进行判断如果没有设置参数leaseTime = -1
if (leaseTime != -1) {
return tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
// 此方法进行获得锁,过期时间为看门狗的默认时间
// private long lockWatchdogTimeout = 30 * 1000;看门狗默认过期时间为30s
// 加锁和过期时间要保证原子性,这个方法后面肯定调用执行了Lua脚本,我们下面在看
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
// 开启一个定时任务进行不断刷新过期时间
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
return;
}
// lock acquired 获得锁
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
// 刷新过期时间方法,我们下一步详细说一下
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
// 首先判断锁是否存在
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
// 存在则获取锁
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
// 然后设置过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// hexists查看哈希表的指定字段是否存在,存在锁并且是当前线程持有锁
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
// hincrby自增一
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
// 锁的值大于1,说明是可重入锁,重置过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// 锁已存在,且不是本线程,则返回过期时间ttl
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}一步步往下找源码:scheduleExpirationRenewal --->renewExpiration
根据下面源码,定时任务刷新时间为:internalLockLeaseTime / 3,是看门狗的1/3,即为10s刷新一次
private void renewExpiration() {
ExpirationEntry ee = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ee == null) {
return;
}
Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
ExpirationEntry ent = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ent == null) {
return;
}
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId == null) {
return;
}
RFuture<Boolean> future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
log.error("Can't update lock " + getName() + " expiration", e);
return;
}
if (res) {
// reschedule itself
renewExpiration();
}
});
}
}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
ee.setTimeout(task);
}1. 打开实现类
@Override
public void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) {
try {
// 这里的过期时间为我们输入的10
lock(leaseTime, unit, false);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
}2. 方法lock()实现展示,同三.3源码
3. 直接来到尝试获得锁tryAcquireAsync()方法
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// 这里进行判断如果没有设置参数leaseTime = -1,此时我们为10
if (leaseTime != -1) {
// 来到此方法
return tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
// 此处省略后面内容,前面以详细说明。。。。
}4. 打开tryLockInnerAsync()方法
我们不难发现和没有传过期时间的方法一样,只不过leaseTime的值变了。
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
// 首先判断锁是否存在
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
// 存在则获取锁
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
// 然后设置过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// hexists查看哈希表的指定字段是否存在,存在锁并且是当前线程持有锁
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
// hincrby自增一
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
// 锁的值大于1,说明是可重入锁,重置过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// 锁已存在,且不是本线程,则返回过期时间ttl
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}1. 打开方法实现
@Override
public void unlock() {
try {
// 点击进入释放锁方法
get(unlockAsync(Thread.currentThread().getId()));
} catch (RedisException e) {
if (e.getCause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
throw (IllegalMonitorStateException) e.getCause();
} else {
throw e;
}
}
// Future<Void> future = unlockAsync();
// future.awaitUninterruptibly();
// if (future.isSuccess()) {
// return;
// }
// if (future.cause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
// throw (IllegalMonitorStateException)future.cause();
// }
// throw commandExecutor.convertException(future);
}2. 打开unlockAsync()方法
@Override
public RFuture<Void> unlockAsync(long threadId) {
RPromise<Void> result = new RedissonPromise<Void>();
// 解锁方法,后面展开说
RFuture<Boolean> future = unlockInnerAsync(threadId);
// 完成
future.onComplete((opStatus, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
// 取消到期续订
cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
// 将这个未来标记为失败并通知所有人
result.tryFailure(e);
return;
}
// 状态为空,说明解锁的线程和当前锁不是同一个线程
if (opStatus == null) {
IllegalMonitorStateException cause = new IllegalMonitorStateException("attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: "
+ id + " thread-id: " + threadId);
result.tryFailure(cause);
return;
}
cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
result.trySuccess(null);
});
return result;
}3. 打开unlockInnerAsync()方法
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
// 判断释放锁的线程和已存在锁的线程是不是同一个线程,不是返回空
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
// 释放锁后,加锁次数减一
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
// 判断剩余数量是否大于0
"if (counter > 0) then " +
// 大于0 ,则刷新过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
// 释放锁,删除key并发布锁释放的消息
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; "+
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}感谢你能够认真阅读完这篇文章,希望小编分享的“Springboot基于Redisson如何实现Redis分布式可重入锁源码解析”这篇文章对大家有帮助,同时也希望大家多多支持亿速云,关注亿速云行业资讯频道,更多相关知识等着你来学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。