本文小编为大家详细介绍“怎么使用MySQL进行JDBC编程与增删改查”,内容详细,步骤清晰,细节处理妥当,希望这篇“怎么使用MySQL进行JDBC编程与增删改查”文章能帮助大家解决疑惑,下面跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来学习新知识吧。
JDBC是一种用于执行sql语句的Java API,他是java中的数据库连接规范,这个API由一些接口和类组成。它为java开发人员操作数据库提供了一个标准的API,可以为多种关系数据库提供统一访问
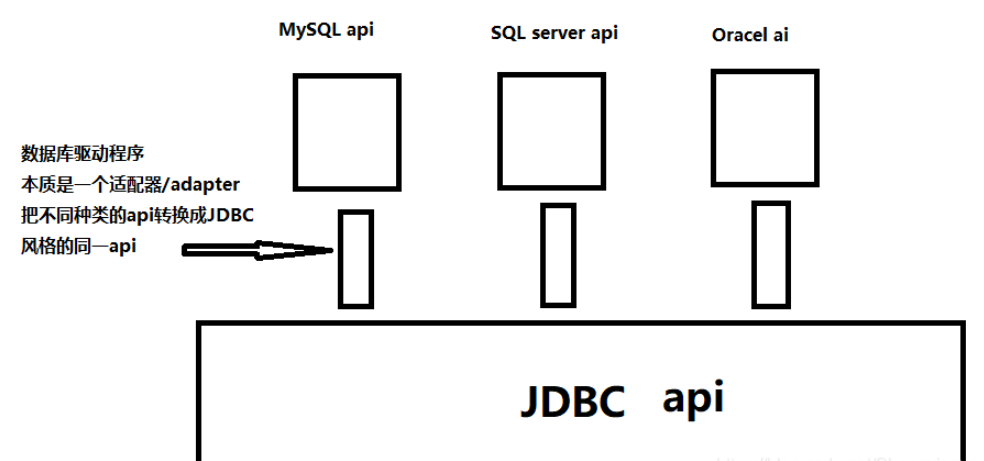
本质是通过代码自己实现一个MySQL客户端,通过网络和服务器进行数据的交互,客户端不能凭空出现,所以数据库提供了一组API方便我们实现
数据库的种类有很多,不同的数据库提供的API不太一样,所以java为了解决这一问题提供了JDBC,java自带的一种数据库操作API,这种API覆盖所有数据库操作的操作方式
本质上是java自身完成了JDBC API和数据库API之间进行转换
创建DataSource对象,这个对象就描述了数据库服务器在哪
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
//设置数据库所在的地址
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/lmp?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
//设置登录数据库的用户名
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
//设置登录数据库的密码
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("woshizhu123");通过Connection连接数据库(输入密码连接成功)
//import java.sql.Connection;
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();拼接sql语句(写入sql语句)
String sql = "insert into student values(1,'张三')";将sql语句包装成对象
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);执行sql语句(按下回车执行sql语句)
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();执行 update delete insert 使用 executeUpdate() 方法
执行 select 使用 executeQuery() 方法
使用 executeQuery() 方法 会返回一个resultSet集合, 包含查找到的数据, 初始情况下resultSet不指向任一行记录, 使用next,让他指向第一条记录, 再使用next指向下一条记录
释放资源
statement.close();
connection.close();public class TestJDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java102?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("woshizhu123");
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println("输入id");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入名字");
String name = scanner.next();
String sql = "insert into student values(?,?)";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,id);
statement.setString(2,name);
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();
if(ret == 1){
System.out.println("插入成功");
}else {
System.out.println("插入失败");
}
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}public class TestJDBCDelete
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java102?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("woshizhu123");
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要删除的id");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
String sql = "delete from student where id = ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1,id);
int ret = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(ret);
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}public class TestJDBCUpdate {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java102?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("woshizhu123");
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要修改的学生id");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入要修改的学生姓名");
String name = scanner.next();
String sql = "update student set name = ? where id = ?";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,name);
statement.setInt(2,id);
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(ret);
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}public static void testJDBCSelect() throws SQLException {
//1创建DataSource对象
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
//2连接数据库
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java_5_31?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("listen");
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
//3拼接sql
String sql = "select * from student";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//4执行sql
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
//5遍历得到的集合
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
int classId = resultSet.getInt("classId");
System.out.println("id " + id + " name " + name + " classId " + classId);
}
//6关闭资源
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}读到这里,这篇“怎么使用MySQL进行JDBC编程与增删改查”文章已经介绍完毕,想要掌握这篇文章的知识点还需要大家自己动手实践使用过才能领会,如果想了解更多相关内容的文章,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云数据库 MySQL」免部署即开即用,比自行安装部署数据库高出1倍以上的性能,双节点冗余防止单节点故障,数据自动定期备份随时恢复。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。