在android developer 的开发文当中是这么描述SparesArray的:
SparseArrays map integers to Objects. Unlike a normal array ofObjects, there can be gaps in the indices. It is intended to be more efficientthan using a HashMap to map Integers to Objects.
大概意思是SparseArrays是映射Integer—> Objects 类型的,就像这样: SparseArrays< Object>而且在指数级别的数量的增长上来说和HashMap相比较的话,性能方面SparseArrays更好。
为什么会突然说SparseArrays呢?因为我在看Activity源码的时候看到了这段代码:
privatestaticclassManagedDialog {
Dialog mDialog;
Bundle mArgs;
}
private SparseArray<ManagedDialog> mManagedDialogs;
我不知道SparseArray是什么,然后点进去继续看这个类的实现,和开始介绍
/**
* SparseArrays map integers to Objects. Unlike a normal array of Objects,
* there can be gaps in the indices. It is intended to be more memory efficient
* than using a HashMap to map Integers toObjects, both because it avoids
* auto-boxing keys and its data structure doesn'trely on an extra entry object
* for each mapping.
**/
前半段和上面api文档上介绍的一样,后半段的意思就是因为数据结构的实体类不依赖外在实体并且避免了自动装箱时候的key,所以效率更高。(效率高的另外一个原因我们等下再说)
我继续回来看代码发现在下面这段代码中用到了SparseArray.
finalint[]ids = b.getIntArray(SAVED_DIALOG_IDS_KEY);
finalintnumDialogs = ids.length;
mManagedDialogs = newSparseArray<ManagedDialog>(numDialogs);
for(inti = 0; i < numDialogs; i++) {
final Integer dialogId = ids[i];
Bundle dialogState = b.getBundle(savedDialogKeyFor(dialogId));
if (dialogState != null) {
// Calling onRestoreInstanceState() below will invoke dispatchOnCreate
// so tell createDialog() not to do it, otherwise we get an exception
final ManagedDialog md = new ManagedDialog();
md.mArgs = b.getBundle(savedDialogArgsKeyFor(dialogId));
md.mDialog = createDialog(dialogId, dialogState, md.mArgs);
if (md.mDialog != null) {
mManagedDialogs.put(dialogId, md);
onPrepareDialog(dialogId,md.mDialog,md.mArgs);
md.mDialog.onRestoreInstanceState(dialogState);
}
}
}
上面这段代码做的事情就是根据对话框id的个数来创建SparesArrays的大小。并且根据ManagedDialog的id存dialogState,也就是存dialog的状态。说白了就是<Integer,Object>格式的HashMap。
我回去继续阅读SparesArrays的源码发现:
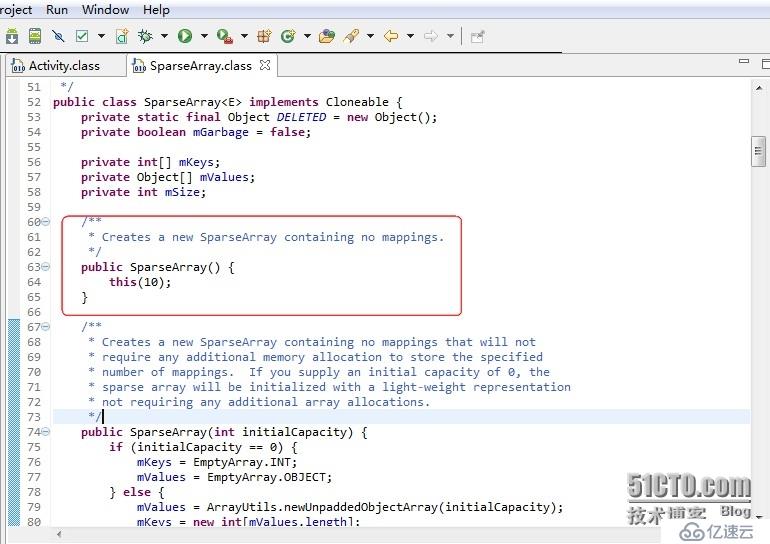
它的构造方法设置了默认大小为10,
和List一样,获取元素的方法有两个如图所示我们可以发现
public E get(int key)方法还是调用的public E get(int key, E valueIfKeyNotFound)。只是在找不到元素的时候设置了默认的返回值为null。
值得注意的是,它查找的时候用的是二分查找(折半查找)算法,所以快。
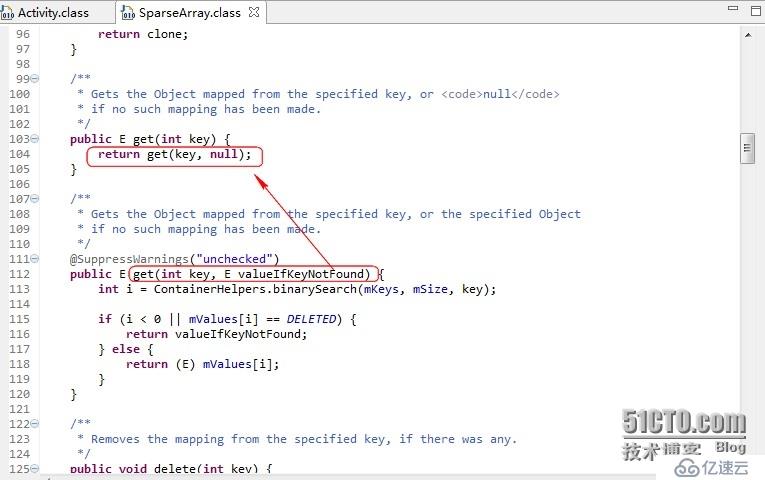
感觉整个SparesArrays的核心就是binarySearch。我们看下它的源代码:
static int binarySearch(int[] array, int size, intvalue) {
int lo =0;
int hi =size - 1;
while(lo <= hi) {
final int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
final int midVal = array[mid];
if(midVal < value) {
lo = mid + 1;
}else if (midVal > value) {
hi = mid - 1;
}else {
return mid; // value found
}
}
return~lo; // value not present
}
static intbinarySearch(long[] array, int size, long value) {
int lo =0;
int hi =size - 1;
while(lo <= hi) {
final int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
final long midVal = array[mid];
if(midVal < value) {
lo = mid + 1;
}else if (midVal > value) {
hi = mid - 1;
}else {
return mid; // value found
}
}
return~lo; // value not present
}
再来看它删除的时候有四种方法;
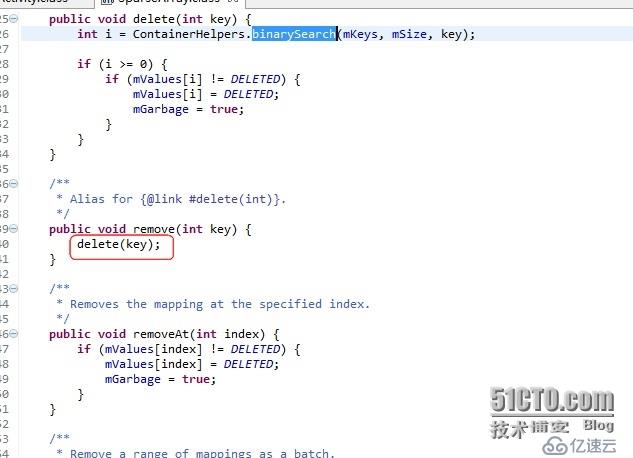
前三种中
public void delete(int key)是根据折半查找删除,
public void remove(int key)调用的是delete(int key)
public void removeAt(int index)根据index删除
public void removeAtRange(int index, int size)这个是调用publicvoid removeAt(int index)(上面截图中没有)
添加数据方法有public voidput(int key, E value)
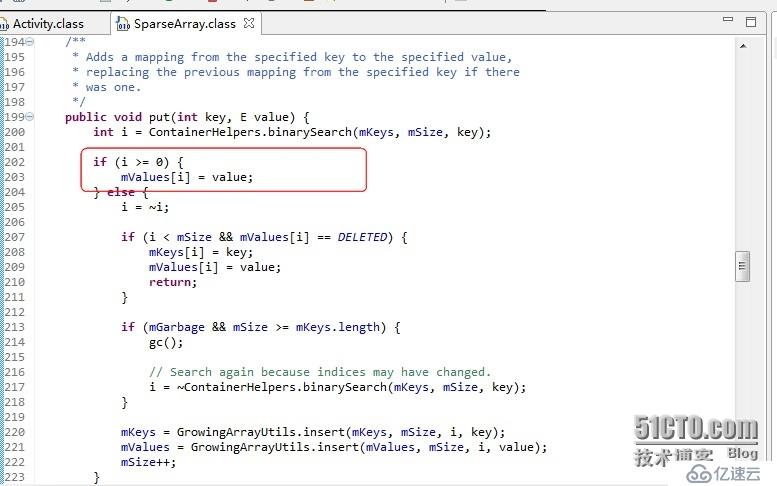
在红框中的代码表示 put的时候会先查案当前的SparesArrays中是否存在此数据,如果存在那么就是修改这个数值,不会添加,如果没有查找到那么久会添加。
还有一个方法是修改数组中的数值的
public void setValueAt(int index, Evalue)
如注释中说的,会给index的位置的value进行修改。
public int keyAt(int index)这个方法是根据index来获取key值。范围是0-size-1.

同样的public E valueAt(int index)就是根据index来获取对应位置的object。如图:

还有public void append(int key,E value)方法,这个方法是在key远远大于数组中所有的key的时候添加数据提高性能的方法,如果key>0 并且key小于等等数组中最后一个的key的情况下还是调用的put方法。

最后一个方法就是toString,也就是打印出整个数组的字符串。这个没多大意思就不贴出代码了。
另外 想要阅读android源码的一种方式可以戳这里:
http://poarry.blog.51cto.com/5970996/1630731
以上纯属个人见解,如有失误,欢迎指正poarryScript@gmail.com
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。