这篇“怎么利用Python实现自定义连点器”文章的知识点大部分人都不太理解,所以小编给大家总结了以下内容,内容详细,步骤清晰,具有一定的借鉴价值,希望大家阅读完这篇文章能有所收获,下面我们一起来看看这篇“怎么利用Python实现自定义连点器”文章吧。
前些天留意到我妈一直在预约四价疫苗都约不上,就想着写个程序来模拟人的操作去点击,判断疫苗是否被抢完,无限循环去刷新这个页面,一旦疫苗可预约就立马抢下来选择时间接种人。当预约成功后就语音循环播报:已经抢到,赶紧过来看一下。
基于以上的想法和需求,我花了半小时编辑了以下代码,并在一小时内成功预约。
import pyautogui
from ctypes import * # 获取屏幕上某个坐标的颜色
from time import sleep
import time
start = time.time()
def get_color(x, y):
gdi32 = windll.gdi32
user32 = windll.user32
hdc = user32.GetDC(None) # 获取颜色值
pixel = gdi32.GetPixel(hdc, x, y) # 提取RGB值
r = pixel & 0x0000ff
g = (pixel & 0x00ff00) >> 8
b = pixel >> 16
return [r, g, b]
print(get_color(297,454))
while True:
if get_color(240 , 255) == [60,211,180] or get_color(247,255) == [60,211,180] or get_color(253,255) == [60,211,180] or get_color(260,255) == [60,211,180] or get_color(270,255) == [60,211,180] or get_color(280,255) == [60,211,180] or get_color(290 ,255) == [60,211,180] or get_color(300 ,255) == [60,211,180] or get_color(310,255) == [60,211,180] or get_color(320, 255) == [60,211,180]:
pyautogui.click(310,255)#点进去抢
sleep(0.5)
pyautogui.click(467,262)#选择预约时间
while True:
if get_color(297,454) == [0,142,255]:
break
else:
sleep(0.3)
sleep(0.5)
pyautogui.click(498,454)#点击下午
sleep(0.5)
pyautogui.click(467,520)#选择时间
sleep(0.5)
pyautogui.click(470,899)#点选好了
sleep(0.5)
pyautogui.click(470, 899)#点立即预约
#sleep()
break
else:
pyautogui.click(123,60)
sleep(0.8)#刷新
print('总耗时:'.format(time.time()-start))
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime()))
while 1:
import pyttsx3
engine = pyttsx3.init()
engine.say('我抢到了!快来看一下')
engine.runAndWait()
sleep(1)实现思路大致流程图:
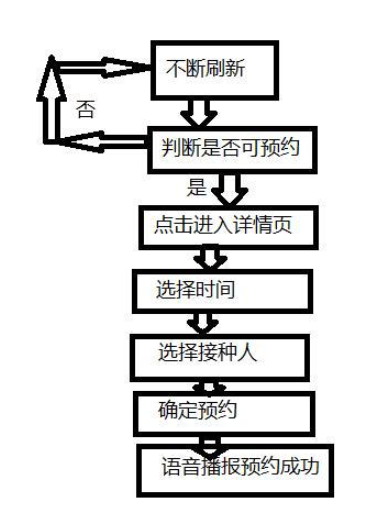
可以看到逻辑非常简单即可实现我想要的功能,不过即使是这样,我也花了差不多半小时的时间来编写代码。于是我就在想,要是以后我要开发抢票、技能连招啊、信息轰炸朋友啊等等的功能,是不是也要这么多时间呢,那我能不能自己造轮子来快速帮助我开发我想要的脚本呢。
一般需要的功能有:点击、延时、连点、拖拽。一般这四个功能就能完成绝大多数的简单的辅助脚本开发了,但我想做得稍微高级一点,功能多一点,就想另外开发:循环、判断、模拟按键、文本输入、存储操作、读取操作的功能。
那么我们就要朝着我们想要实现的九大功能来开发:循环、点击、延时、连点、拖拽、判断、模拟按键、文本输入、存储操作、读取操作。
首先就是希望我的每一步操作都会被程序记录下来并执行,我们可以定义一个列表来存储每一个操作,列表中的每一个元素就是每一步的操作,然后遍历这个列表来读取并执行每一个操作就可以将一整个操作全部执行。
当我的每一步操作都输入完毕后,我都希望程序能自动帮我把程序存储下来方便我下一次使用,这样下次使用就不用再编译多一次了。
每一个列表的第0项就是需要操作的功能,第0项之后都是各种参数。
要想电脑帮我们点击,首先要告诉电脑我要点击的位置在哪里。想要获取鼠标位置就需要用到pyautogui库,这个库下有个position()方法可以返回鼠标位置的X坐标,Y坐标。
定义获取位置函数
import pyautogui
def get_xy():
x, y = pyautogui.position()
return [x,y]用面向对象思想来简化程序,提高代码复用率,使程序可读性更高,是python开发的重要思想之一哦
pyautogui库还有非常多常见功能,感兴趣的可以翻看我之前写的博客:Python速成篇之像selenium一样操作电脑详解
点击功能代码如下
step=[]
while True:
choose = input('请输入你需要使用的功能:')
if choose == '点击':
click = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
click.append('点击')
click.append(click_weizhi)
step.append(click)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')执行时的逻辑
for i in step1:
if i[0] == '点击':
x = int(i[1][0])
y = int(i[1][1])
print(f'{x},{y}')
pyautogui.click(x,y)记录点击需要记录点击功能、位置参数生成一个列表,然后将列表append到step总列表中去
使用到了python内置库中的time模块,可以使程序强制停止相应时间。将参数生成列表append到step总列表中去
if choose =='延时':
while 1:
timerr = []
try:
timex = int(input('请输入延时时间:'))
timerr.append('延时')
timerr.append(timex)
step.append(timerr)
break
except:
print('延时失败/n请输入正确的延时时间')
continue执行时的逻辑
def timer(timex):
time.sleep(timex)
if i[0] == '延时':
t = int(i[1])
timer(t)有些简单的页面可以通过连点来实现抢票等功能,这个功能必不可少
记录这个动作的必要参数有连点功能记录、点击频率参数、通过连点次数完成动作还是通过连点时长完成动作。
同样是调用了获取鼠标位置的函数,
if choose == '连点':
click_liandian = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
click_liandian.append('连点')
click_liandian.append(click_weizhi)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
click_pinlv = float(input('请输入连点频率:'))
while 1:
click_stop_choose = input('“连点次数”or“连点时长”')
if click_stop_choose =='连点次数':
click_cishu = int(input('请输入连点次数:'))
click_liandian.append('连点次数')
click_liandian.append(click_cishu)
click_liandian.append(click_pinlv)
step.append(click_liandian)
print(click_liandian)
print(step)
break
if click_stop_choose == '连点时长':
click_shichang = int(input('请输入连点时长(秒):'))
click_liandian.append('连点时长')
click_liandian.append(click_shichang)
step.append(click_liandian)
click_liandian.append(click_pinlv)
print(click_liandian)
print(step)
break
else:
continue执行时的逻辑
if choose == '连点':
click_liandian = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
click_liandian.append('连点')
click_liandian.append(click_weizhi)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
click_pinlv = float(input('请输入连点频率:'))
while 1:
click_stop_choose = input('“连点次数”or“连点时长”')
if click_stop_choose =='连点次数':
click_cishu = int(input('请输入连点次数:'))
click_liandian.append('连点次数')
click_liandian.append(click_cishu)
click_liandian.append(click_pinlv)
step.append(click_liandian)
print(click_liandian)
print(step)
break
if click_stop_choose == '连点时长':
click_shichang = int(input('请输入连点时长(秒):'))
click_liandian.append('连点时长')
click_liandian.append(click_shichang)
step.append(click_liandian)
click_liandian.append(click_pinlv)
print(click_liandian)
print(step)
break
else:
continue当我们记录完所有操作后我们希望将操作保存下来方便下次使用,不需要从头录入。
这将生成一个与py脚本同级的txt文件,txt文件中保存了所有的步骤,可直接读取使用
if choose =='存储':
if len(step) == 0:
print('还未记录你任何操作,请添加操作再使用存储功能')
else:
do_name = input('请为以上操作命名吧:')
path = r"{}.txt".format(do_name)
with open(path, "w",encoding = 'utf8') as f:
f.write(str(step))这一步呢就稍微麻烦一点,因为txt没办法记录list类型的数据,只能以str类型写出去并且只能以str类型读取进来。我自己定义了一些函数来转化为list类型,比较复杂,就不再说明函数是怎么实现的,日后有机会再跟各位分享。
def writeList2txt(file,data):
'''
将list写入txt
:param data:
:return:
'''
file.write(str(data))
def readListFromStr(str):
'''
str -> List
除去冗余的方法调用
:param str:
:return:
'''
res,pos = help(str,1)
res1=[]
a ='1'
for ii in res:
iii=[]
for i in ii:
if type(i)==type(a):
i = i.replace("'", "")
iii.append(i)
else:
iii.append(i)
res1.append(iii)
return res1
def help(str,startIndex):
'''
单行字符串的读取,形成list
:param str:
:return:
'''
str = str.replace(" ","") # 将所有空格删去
res = []
i = startIndex
pre = startIndex
while i <len(str):
if str[i] == '[':
# 将pre-i-2的字符都切片,切split
if i-2>=pre:
slice = str[pre:i-1].split(',')
for element in slice:
res.append(element)
# 递归调用 加入子list
child,pos = help(str,i+1)
res.append(child)
i = pos # i移动到pos位置,也就是递归的最后一个右括号
pre = pos + 2 # 右括号之后是, [ 有三个字符,所以要+2至少
elif str[i] == ']':
# 将前面的全部放入列表
if i-1>=pre:
slice = str[pre:i].split(',')
for element in slice:
res.append(element)
return res,i
i = i + 1
return res,i
def get_caozuo(caozuopath):
with open(caozuopath , 'r' , encoding='utf8') as f:
data = f.read()
return data
def get_caozuo_name():
files1 = []
file_dir = r"C:\Users\ge\Desktop\test1\我的作品\自定义连点器"
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(file_dir, topdown=False):
files = files[:-1]
for i in files:
files1.append(i[:-4])
return files1
print(get_caozuo_name())
if choose == '循环执行':
caozuojiyi = get_caozuo_name()
while True:
xunhuan_choose = input('已存储的操作有:{}\n请输入循环操作的操作名:'.format(caozuojiyi))
if xunhuan_choose in caozuojiyi:
break
else:
print('存储库中并无你想要的操作,请重新输入:')上面的功能只能把二维的列表导入成list类型的数据类型,不利于后面的导入。一旦存储或导入的列表达到三维或以上就不适用了。后来我在网上搜了半天,终于发现json库里面有方法支持以list的形式导出txt并且可以以list的方式读取。以下是我实现存储导入的逻辑代码:
导入(功能实现)
def txttolist(path):
import json
b = open(path, "r", encoding='UTF-8')
out = b.read()
out = json.loads(out)
return out导入(逻辑代码)
如果程序内存里已有操作了将提示保存
if choose == '导入':
if len(step) == 0:
step = daoru()[0]
else:
baocun_choose = input('此次操作若未保存请先,导入别的操作会覆盖原来的操作,你确定要导入吗?\n请输入“yes”or“no”:\n')
while 1:
if baocun_choose == 'no':
break
if baocun_choose == 'yes':
print('你已取消保存')
step = daoru()[0]
break
else:
yorn = input("请输入'yes'or'no':\n")存储(功能实现)
def cunchu():
yorn = input("执行完毕,是否保存?\n输入'yes'or'no'\n")
while 1:
if yorn == 'yes':
if len(step) == 0:
print('还未记录你任何操作,请添加操作再使用存储功能')
else:
do_name = input('请为以上操作命名吧:')
path = r"{}.txt".format(do_name)
listtotxt(list=step, path=path)
break
if yorn == 'no':
print('你已取消存储')
break
else:
yorn = input("请输入'yes'or'no':\n")
def listtotxt(list, path):
import json
c_list = list
c_list = json.dumps(c_list)
'''将c_list存入文件
'''
a = open(path, "w", encoding='UTF-8')
a.write(c_list)
a.close()
print('已存入txt')存储(逻辑代码)
要是程序内存里还没有操作将提醒
if choose == '存储':
if len(step) == 0:
print('还未记录你任何操作,请添加操作再使用存储功能')
else:
do_name = input('请为以上操作命名吧:')
path = r"{}.txt".format(do_name)
listtotxt(list=step, path=path)这个功能也是基于pyautogui库来使用的,主要用到了pyautogui.dragTo()方法
功能实现
pyautogui.moveTo(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
pyautogui.dragTo(int(i[2][0]), int(i[2][1]), 1, button='left')
print(f'已执行拖拽动作,拖拽起始位置是X:{int(i[1][0])},Y:{int(i[1][1])},拖拽后的位置是X:{int(i[2][0])},Y:{int(i[2][1])}')逻辑代码:
先创建列表tuozhuai,向列表添加三个参数:“拖拽”、第一个位置参数、第二个位置参数
if choose == '拖拽':
tuozhuai = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成移动前的位置输入,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
tuozhuai.append('拖拽')
tuozhuai.append(click_weizhi)
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成移动后的位置输入,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
tuozhuai.append(click_weizhi)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
step.append(tuozhuai)也是用到了pyauogui库,主要使用pyautogui库的pytewrite函数,但是这个函数对中文不友好,于是我另辟蹊径使用pyperclip库的copy函数将要输入的文本内容拷贝打粘贴板,通过控制按键control+v来输入至目标位置。
功能实现
if choose == '输入':
shuru = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到你要输入的位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
txt_in = input('请输入你要在该位置输入的文字:\n')
shuru.append('输入')
shuru.append(click_weizhi)
shuru.append(txt_in)
step.append(shuru)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')逻辑代码
if i[0] == '输入':
pyautogui.click(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
pyperclip.copy(i[2])
time.sleep(0.1)
pyautogui.hotkey('ctrl', 'v')原理相同,将不再赘述
功能实现
if i[0] == '双击':
pyautogui.click(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
pyautogui.click(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
print(f'已执行完点击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{int(i[1][0])},Y:{int(i[1][1])} ')
if i[0] == '右击':
x = int(i[1][0])
y = int(i[1][1])
pyautogui.rightClick(x, y)
print(f'已执行完右击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{x},Y:{y} ')
if i[0] == '中击':
x = int(i[1][0])
y = int(i[1][1])
pyautogui.middleClick(x, y)
print(f'已执行完中击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{x},Y:{y} ')逻辑代码
if choose == '右击':
click_r = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
click_r.append('右击')
click_r.append(click_weizhi)
step.append(click_r)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
if choose == '中击':
click_m = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
click_m.append('中击')
click_m.append(click_weizhi)
step.append(click_m)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
click_double = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
click_double.append('双击')
click_double.append(click_weizhi)
step.append(click_double)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')功能实现
if i[0] == '按键':
pyautogui.hotkey(*i[1])逻辑代码
if choose == '按键':
while 1:
anjian = input('这是模拟操作键盘的操作(例如复制,输入'ctrl‘ + 'c‘):\n')
if anjian != 'q':
anjian = anjian.split('+')
anjians = []
a = []
for an in anjian:
an = an.replace("‘", "").replace("'", "").strip()
if an in pyautogui.KEYBOARD_KEYS:
anjians.append(an)
nihaofan = 0
else:
print('你的输入不合法')
nihaofan = 1
break
if nihaofan == 0:
a.append('按键')
a.append(anjians)
step.append(a)
print('录入成功')
break
if anjian == 'q':
break功能实现
if i[0] == '滚动':
import pywinauto.mouse
x, y = pyautogui.position()
pywinauto.mouse.scroll((x, y), i[1]) # (1100,300)是初始坐标,1000是滑动距离(可负)逻辑代码
if choose == '滚动':
while 1:
gundong = []
try:
gundong1 = int(input('这里是模拟鼠标滚动,请输入你要滚动距离(正数为向上移动,负数为向下移动):\n'))
gundong.append('滚动')
gundong.append(gundong1)
step.append(gundong)
break
except:
print('你的输入有误,请重新输入')def chakan():
if len(step) == 0:
print('暂未录入操作,请先录入操作再查看')
zizeng = 1
for i in step:
if i[0] == '点击':
x = int(i[1][0])
y = int(i[1][1])
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行点击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{x},Y:{y} ')
if i[0] == '延时':
t = int(i[1])
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行延时动作,延时时长:{t}秒')
if i[0] == '连点':
if i[2] == '连点次数':
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行连点操作,你选择的是{i[2]},连点次数是{i[4]}')
if i[2] == '连点时长':
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行连点操作,你选择的是{i[2]},连点时长是{i[4]}秒')
if i[0] == '拖拽':
print(
f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行拖拽动作,拖拽起始位置是X:{int(i[1][0])},Y:{int(i[1][1])},拖拽后的位置是X:{int(i[2][0])},Y:{int(i[2][1])}')
if i[0] == '双击':
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行点击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{int(i[1][0])},Y:{int(i[1][1])} ')
if i[0] == '按键':
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行按键动作,将同时按下”{i[1]}“键')
zizeng += 1执行后将询问是否保存
def zhixing(step):
for i in step:
if i[0] == '点击':
x = int(i[1][0])
y = int(i[1][1])
pyautogui.click(x, y)
print(f'已执行完点击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{x},Y:{y} ')
if i[0] == '延时':
t = int(i[1])
timer(t)
print(f'已执行完延时动作,延时时长:{t}秒')
if i[0] == '连点':
if i[2] == '连点次数':
clicker_cishu(int(i[3]), int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]), int(i[4]))
print(f'已执行完连点操作,你选择的是{i[2]},连点次数是{i[4]}')
if i[2] == '连点时长':
clicker_time(int(i[3]), int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]), int(i[4]))
print(f'已执行完连点操作,你选择的是{i[2]},连点时长是{i[4]}秒')
if i[0] == '拖拽':
pyautogui.moveTo(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
pyautogui.dragTo(int(i[2][0]), int(i[2][1]), 1, button='left')
print(f'已执行拖拽动作,拖拽起始位置是X:{int(i[1][0])},Y:{int(i[1][1])},拖拽后的位置是X:{int(i[2][0])},Y:{int(i[2][1])}')
if i[0] == '双击':
pyautogui.click(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
pyautogui.click(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
print(f'已执行完点击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{int(i[1][0])},Y:{int(i[1][1])} ')
if i[0] == '输入':
pyautogui.click(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
pyperclip.copy(i[2])
time.sleep(0.1)
pyautogui.hotkey('ctrl', 'v')
if i[0] == '按键':
pyautogui.hotkey(*i[1])
if i[0] == '右击':
x = int(i[1][0])
y = int(i[1][1])
pyautogui.rightClick(x, y)
print(f'已执行完右击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{x},Y:{y} ')
if i[0] == '中击':
x = int(i[1][0])
y = int(i[1][1])
pyautogui.middleClick(x, y)
print(f'已执行完中击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{x},Y:{y} ')
if i[0] == '滚动':
import pywinauto.mouse
x, y = pyautogui.position()
pywinauto.mouse.scroll((x, y), i[1]) # (1100,300)是初始坐标,1000是滑动距离(可负) if choose == '执行':
if len(step) == 0:
print('你还未记录任何操作,请至少记录了一个操作再执行')
else:
zhixing(step)
cunchu()到了最难最虐脑的逻辑判断功能了,逻辑判断板块这几个功能困扰了我一整天,敲到我脑壳疼
实现这一功能主要是基于颜色的RBG值来判断程序所要要执行的步骤块。
选择目标点,开启线程去时刻监管这个目标点的颜色变化,一旦目标颜色变为期待值,立即执行之前存储的步骤块,可以选择是否循环这个步骤块的操作。选择完毕后开启第二个线程去执行这个步骤块,此时主程序将继续遍历panduans的操作。设置一个while循环来阻塞主程序的运行及监控state变量值的变化,state初始值为“未触发”,一旦监管线程发现目标值变化为期待值,立即修改state值为“触发”,同时关闭执行步骤块的线程,同时关闭自身的监管线程,此时主程序检测到state值为“触发”后立刻将新的步骤块的线程开启并将state值修改为“未触发”。就此开启新一轮的循环。
之间呢,遇到了多个线程修改同一个值的情况导致报错;遇到了多种停止线程的方法都不适用的情况;遇到了没设置守护进程又要找到这个进程去关闭的情况;尝试了老版的_thread进程库、尝试了主流的threading进程库、尝试了线程池的方法,终于找到一条适合我的方法。不容易呀
if choose == '判断':
if len(panduans) == 0:
tuichu = 0
panduan = input('此功能的实现是基于颜色的RBG值来判断程序所要要执行的步骤块。\n现在,请选择你的‘先执行步骤块等待条件触发'或是‘直接等待条件触发'的操作:(输入"步骤块"或"等待")\n')
if panduan == '如果':
panduan_if = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上吸取颜色,输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
xy = get_xy()
click_color = GetColor(xy)
panduan_yn = input(f'这个位置的RGB为:{click_color},是否确定为下一步骤块的判断根据?(输入"yes"or"no")\n')
while 1:
if panduan_yn == 'yes':
get_caozuo_name()
print(f'请选择满足当颜色为{click_color}时要执行的步骤包:')
steps, steps_name = daoru()
xunhuan_yn = input('这个步骤块是否循环执行至下一条件触发?(输入"yes"or"no")\n')
while 1:
if xunhuan_yn == 'yes':
panduan_if.append('如果')
panduan_if.append(xy)
panduan_if.append(click_color)
panduan_if.append(steps_name)
panduan_if.append('循环')
panduan_if.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_if)
print('添加成功,该步骤包将会循环')
break
elif xunhuan_yn == 'no':
panduan_if.append('如果')
panduan_if.append(xy)
panduan_if.append(click_color)
panduan_if.append(steps_name)
panduan_if.append('不循环')
panduan_if.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_if)
print('添加成功,该步骤包将只执行一次')
break
else:
xunhuan_yn = input('你的输入有误,请输入"yes"or"no":')
tuichu = 1
break
if panduan_yn == 'no':
print('请重新选择')
break
else:
panduan_yn = input('你的输入有误,请输入"yes"or"no"')
if tuichu == 1:
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”)')
if panduan == '步骤块':
panduan_step = []
steps, steps_name = daoru()
xunhuan_yn = input('这个步骤块是否循环执行直至条件触发?(输入"yes"or"no")\n')
while 1:
if xunhuan_yn == 'yes':
panduan_step.append('步骤块')
panduan_step.append('循环')
panduan_step.append(steps_name)
panduan_step.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_step)
break
elif xunhuan_yn == 'no':
panduan_step.append('步骤块')
panduan_step.append('不循环')
panduan_step.append(steps_name)
panduan_step.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_step)
break
else:
xunhuan_yn = input('你的输入有误,请输入"yes"or"no":')
if panduan == '等待':
panduan_if = []
print('你选择了等待,程序将时刻检测目标位置的颜色以执行接下来的步骤块')
panduan_if.append('等待')
panduans.append(panduan_if)
if panduan != '步骤块' and panduan != '如果' and panduan != '等待':
print('你的输入有误')
if len(panduans) > 0:
print('你一录入了至少一个逻辑判断,请选择继续选择目标位置的颜色来触发接下来你选择的步骤块')
panduan_if = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上吸取颜色,输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
xy = get_xy()
click_color = GetColor(xy)
panduan_yn = input(f'这个位置的RGB为:{click_color},是否确定为下一步骤块的判断根据?(输入"yes"or"no")\n')
while 1:
if panduan_yn == 'yes':
get_caozuo_name()
print(f'请选择满足当颜色为{click_color}时要执行的步骤包:')
steps, steps_name = daoru()
xunhuan_yn = input('这个步骤块是否循环执行直至条件触发?(输入"yes"or"no")\n')
while 1:
if xunhuan_yn == 'yes':
panduan_if.append('如果')
panduan_if.append(xy)
panduan_if.append(click_color)
panduan_if.append(steps_name)
panduan_if.append('循环')
panduan_if.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_if)
print('添加成功,该步骤包将会循环')
break
elif xunhuan_yn == 'no':
panduan_if.append('如果')
panduan_if.append(xy)
panduan_if.append(click_color)
panduan_if.append(steps_name)
panduan_if.append('不循环')
panduan_if.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_if)
print('添加成功,该步骤包将只执行一次')
break
else:
xunhuan_yn = input('你的输入有误,请输入"yes"or"no":')
tuichu = 1
break
if panduan_yn == 'no':
print('请重新选择')
break
else:
panduan_yn = input('你的输入有误,请输入"yes"or"no"')
if tuichu == 1:
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”)') if choose == '逻辑执行':
print('这里是逻辑执行库,所有的逻辑判断都会存储到这里')
print(panduans)
xiancheng = threading.Thread(target=zhixingbuzhoukuai, args=('等待', '1', '循环'))
xiancheng.setDaemon(True)
xiancheng.start()
for pan in panduans:
state = '未触发'
if pan[0] == '如果':
print(pan[5])
print(len(pan[5]))
bu = str(pan[5])
print(bu)
bu = readListFromStr(bu)
zhixing(bu)
print(bu)
if state == '未触发':
if pan[4] == '循环':
rgb = pan[2]
rgb_xy = pan[1]
_thread.start_new_thread(jianshi, ())
while 1:
if state == '触发':
xiancheng = threading.Thread(target=zhixingbuzhoukuai, args=(pan[3], pan[5], '循环'))
xiancheng.start()
state = '未触发'
break
if pan[4] == '不循环':
rgb = pan[2]
rgb_xy = pan[1]
_thread.start_new_thread(jianshi, ())
while 1:
if state == '触发':
xiancheng = threading.Thread(target=zhixingbuzhoukuai, args=(pan[3], pan[5], '不循环'))
xiancheng.start()
state = '未触发'
break
if pan[0] == '步骤块':
stop_thread(xiancheng)
if pan[1] == '循环':
xiancheng = threading.Thread(target=zhixingbuzhoukuai, args=(pan[2], pan[3], '循环'))
xiancheng.start()
if pan[1] == '不循环':
xiancheng = threading.Thread(target=zhixingbuzhoukuai, args=(pan[2], pan[3], '不循环'))
xiancheng.start()
if pan[0] == '等待':
print('程序正在监测目标位置RGB值')
print('逻辑执行已全部执行完毕')
break逻辑块存储功能的实现
def listtotxt(list, path):
import json
c_list = list
c_list = json.dumps(c_list)
'''将c_list存入文件
'''
a = open(path, "w", encoding='UTF-8')
a.write(c_list)
a.close()
print('已存入txt')逻辑块存储逻辑代码
if choose == '逻辑块存储':
yorn = input("确定保存?\n输入'yes'or'no'\n")
while 1:
if yorn == 'yes':
if len(panduans) == 0:
print('还未记录你任何操作,请添加操作再使用逻辑块存储功能')
else:
do_name = input('请为以上操作命名吧:')
if '逻辑块存储' in do_name:
do_name = input('抱歉,你的命名里不允许包含”逻辑块存储“,请重新命名')
else:
path = r"{}逻辑块存储.txt".format(do_name)
listtotxt(list=panduans, path=path)
break
if yorn == 'no':
print('你已取消存储')
break
else:
yorn = input("请输入'yes'or'no':\n")逻辑块导入功能的实现
def txttolist(path):
import json
b = open(path, "r", encoding='UTF-8')
out = b.read()
out = json.loads(out)
return out逻辑块导入逻辑代码
if choose == '逻辑块导入':
caozuojiyi = get_caozuokuai_name()
while True:
xunhuan_choose = input('已存储的操作有:{}\n请输入导入操作的操作名:'.format(caozuojiyi))
if xunhuan_choose in caozuojiyi:
break
else:
print('逻辑块存储库中并无你想要的操作,请重新输入:')
caozuopath = r"{}逻辑块存储.txt".format(xunhuan_choose)
panduans = txttolist(path=caozuopath)import threading
import pyautogui
from ctypes import *
import time
import os, sys
import pyperclip
import inspect
import ctypes
import _thread
def _async_raise(tid, exctype):
"""raises the exception, performs cleanup if needed"""
tid = ctypes.c_long(tid)
if not inspect.isclass(exctype):
exctype = type(exctype)
res = ctypes.pythonapi.PyThreadState_SetAsyncExc(tid, ctypes.py_object(exctype))
if res == 0:
raise ValueError("invalid thread id")
elif res != 1:
# """if it returns a number greater than one, you're in trouble,
# and you should call it again with exc=NULL to revert the effect"""
ctypes.pythonapi.PyThreadState_SetAsyncExc(tid, None)
raise SystemError("PyThreadState_SetAsyncExc failed")
def stop_thread(threa):
_async_raise(threa.ident, SystemExit)
def get_caozuo_name():
dirname, filename = os.path.split(os.path.abspath(sys.argv[0]))
files1 = []
file_dir = r"{}".format(os.path.realpath(sys.argv[0])[:-13])
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(file_dir, topdown=False):
files = files[:-1]
for i in files:
if '.txt' in i:
files1.append(i[:-4])
return files1
def get_caozuokuai_name():
dirname, filename = os.path.split(os.path.abspath(sys.argv[0]))
files1 = []
file_dir = r"{}".format(os.path.realpath(sys.argv[0])[:-13])
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(file_dir, topdown=False):
files = files[:-1]
for i in files:
if '逻辑块存储.txt' in i:
files1.append(i[:-9])
return files1
def writeList2txt(file, data):
'''
将list写入txt
:param data:
:return:
'''
file.write(str(data), encoding='uft8')
def readListFromStr(str):
'''
str -> List
除去冗余的方法调用
:param str:
:return:
'''
res, pos = help(str, 1)
res1 = []
a = '1'
for ii in res:
iii = []
for i in ii:
if type(i) == type(a):
i = i.replace("'", "")
iii.append(i)
else:
iii.append(i)
res1.append(iii)
return res1
def help(str, startIndex):
'''
单行字符串的读取,形成list
:param str:
:return:
'''
str = str.replace(" ", "") # 将所有空格删去
res = []
i = startIndex
pre = startIndex
while i < len(str):
if str[i] == '[':
# 将pre-i-2的字符都切片,切split
if i - 2 >= pre:
slice = str[pre:i - 1].split(',')
for element in slice:
res.append(element)
# 递归调用 加入子list
child, pos = help(str, i + 1)
res.append(child)
i = pos # i移动到pos位置,也就是递归的最后一个右括号
pre = pos + 2 # 右括号之后是, [ 有三个字符,所以要+2至少
elif str[i] == ']':
# 将前面的全部放入列表
if i - 1 >= pre:
slice = str[pre:i].split(',')
for element in slice:
res.append(element)
return res, i
i = i + 1
return res, i
def get_caozuo(caozuopath):
with open(caozuopath, 'r', encoding='utf8') as f:
data = f.read()
return data
def get_xy():
x, y = pyautogui.position()
return [x, y]
def GetColor(xy):
x = xy[0]
y = xy[1]
r = 0
g = 0
b = 0
try:
gdi32 = windll.gdi32
user32 = windll.user32
hdc = user32.GetDC(None) # 获取颜色值
pixel = gdi32.GetPixel(hdc, x, y) # 提取RGB值
r = pixel & 0x0000ff
g = (pixel & 0x00ff00) >> 8
b = pixel >> 16
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('\n')
return [r, g, b]
def timer(timex):
time.sleep(timex)
def clicker_cishu(cishu, x, y, pinlv):
for a in range(cishu):
pyautogui.click(x, y)
time.sleep(pinlv)
def clicker_time(shijian, x, y, pinlv):
start = time.time()
while True:
pyautogui.click(x, y)
time.sleep(pinlv)
end = time.time()
shijian1 = end - start
if shijian1 >= shijian:
break
def zhixing(step):
for i in step:
if i[0] == '点击':
x = int(i[1][0])
y = int(i[1][1])
pyautogui.click(x, y)
print(f'已执行完点击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{x},Y:{y} ')
if i[0] == '延时':
t = int(i[1])
timer(t)
print(f'已执行完延时动作,延时时长:{t}秒')
if i[0] == '连点':
if i[2] == '连点次数':
clicker_cishu(int(i[3]), int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]), int(i[4]))
print(f'已执行完连点操作,你选择的是{i[2]},连点次数是{i[4]}')
if i[2] == '连点时长':
clicker_time(int(i[3]), int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]), int(i[4]))
print(f'已执行完连点操作,你选择的是{i[2]},连点时长是{i[4]}秒')
if i[0] == '拖拽':
pyautogui.moveTo(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
pyautogui.dragTo(int(i[2][0]), int(i[2][1]), 1, button='left')
print(f'已执行拖拽动作,拖拽起始位置是X:{int(i[1][0])},Y:{int(i[1][1])},拖拽后的位置是X:{int(i[2][0])},Y:{int(i[2][1])}')
if i[0] == '双击':
pyautogui.click(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
pyautogui.click(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
print(f'已执行完点击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{int(i[1][0])},Y:{int(i[1][1])} ')
if i[0] == '输入':
pyautogui.click(int(i[1][0]), int(i[1][1]))
pyperclip.copy(i[2])
time.sleep(0.1)
pyautogui.hotkey('ctrl', 'v')
if i[0] == '按键':
pyautogui.hotkey(*i[1])
if i[0] == '右击':
x = int(i[1][0])
y = int(i[1][1])
pyautogui.rightClick(x, y)
print(f'已执行完右击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{x},Y:{y} ')
if i[0] == '中击':
x = int(i[1][0])
y = int(i[1][1])
pyautogui.middleClick(x, y)
print(f'已执行完中击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{x},Y:{y} ')
if i[0] == '滚动':
import pywinauto.mouse
x, y = pyautogui.position()
pywinauto.mouse.scroll((x, y), i[1]) # (1100,300)是初始坐标,1000是滑动距离(可负)
def cunchu():
yorn = input("执行完毕,是否保存?\n输入'yes'or'no'\n")
while 1:
if yorn == 'yes':
if len(step) == 0:
print('还未记录你任何操作,请添加操作再使用存储功能')
else:
do_name = input('请为以上操作命名吧:')
path = r"{}.txt".format(do_name)
listtotxt(list=step, path=path)
break
if yorn == 'no':
print('你已取消存储')
break
else:
yorn = input("请输入'yes'or'no':\n")
def chakan():
if len(step) == 0:
print('暂未录入操作,请先录入操作再查看')
zizeng = 1
for i in step:
if i[0] == '点击':
x = int(i[1][0])
y = int(i[1][1])
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行点击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{x},Y:{y} ')
if i[0] == '延时':
t = int(i[1])
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行延时动作,延时时长:{t}秒')
if i[0] == '连点':
if i[2] == '连点次数':
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行连点操作,你选择的是{i[2]},连点次数是{i[4]}')
if i[2] == '连点时长':
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行连点操作,你选择的是{i[2]},连点时长是{i[4]}秒')
if i[0] == '拖拽':
print(
f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行拖拽动作,拖拽起始位置是X:{int(i[1][0])},Y:{int(i[1][1])},拖拽后的位置是X:{int(i[2][0])},Y:{int(i[2][1])}')
if i[0] == '双击':
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行点击动作,点击坐标位置:X:{int(i[1][0])},Y:{int(i[1][1])} ')
if i[0] == '按键':
print(f'第{zizeng}步:\n执行按键动作,将同时按下”{i[1]}“键')
zizeng += 1
def daoru():
caozuojiyi = get_caozuo_name()
while True:
xunhuan_choose = input('已存储的操作有:{}\n请输入导入操作的操作名:'.format(caozuojiyi))
if xunhuan_choose in caozuojiyi:
break
else:
print('存储库中并无你想要的操作,请重新输入:')
caozuopath = r'{}.txt'.format(xunhuan_choose)
step1 = txttolist(caozuopath)
print(step1)
return [step1, xunhuan_choose]
def jianshi():
global state, rgb, rgb_xy, xiancheng
while 1:
aa = GetColor(rgb_xy)
if aa == rgb:
try:
stop_thread(xiancheng)
finally:
state = '触发'
print(f'检测到{rgb_xy}位置的RGB值变为{aa}')
break
def zhixingbuzhoukuai(buzhou, bu, xunhuanyn):
global state
print(f'正在执行"{buzhou}"代码块的操作')
state = '未触发'
if bu == '1':
while 1:
if state == '触发':
break
if state == '未触发':
timer(0.1)
elif xunhuanyn == '循环':
while 1:
if state == '触发':
break
if state == '未触发':
zhixing(bu)
elif xunhuanyn == '不循环':
zhixing(bu)
def listtotxt(list, path):
import json
c_list = list
c_list = json.dumps(c_list)
'''将c_list存入文件
'''
a = open(path, "w", encoding='UTF-8')
a.write(c_list)
a.close()
print('已存入txt')
def txttolist(path):
import json
b = open(path, "r", encoding='UTF-8')
out = b.read()
out = json.loads(out)
return out
rgb_xy = []
rgb = []
state = '未触发'
panduans = []
step = []
while True:
choose = input('请输入你需要使用的功能:')
if choose == '点击':
click = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
click.append('点击')
click.append(click_weizhi)
step.append(click)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
if choose == '延时':
while 1:
timerr = []
try:
timex = int(input('请输入延时时间:'))
timerr.append('延时')
timerr.append(timex)
step.append(timerr)
break
except:
print('延时失败/n请输入正确的延时时间')
continue
if choose == '连点':
click_liandian = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
click_liandian.append('连点')
click_liandian.append(click_weizhi)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
click_pinlv = float(input('请输入连点频率:'))
while 1:
click_stop_choose = input('“连点次数”or“连点时长”')
if click_stop_choose == '连点次数':
click_cishu = int(input('请输入连点次数:'))
click_liandian.append('连点次数')
click_liandian.append(click_cishu)
click_liandian.append(click_pinlv)
step.append(click_liandian)
print(click_liandian)
print(step)
break
if click_stop_choose == '连点时长':
click_shichang = int(input('请输入连点时长(秒):'))
click_liandian.append('连点时长')
click_liandian.append(click_shichang)
step.append(click_liandian)
click_liandian.append(click_pinlv)
print(click_liandian)
print(step)
break
else:
continue
if choose == '存储':
if len(step) == 0:
print('还未记录你任何操作,请添加操作再使用存储功能')
else:
do_name = input('请为以上操作命名吧:')
path = r"{}.txt".format(do_name)
listtotxt(list=step, path=path)
if choose == '拖拽':
tuozhuai = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成移动前的位置输入,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
tuozhuai.append('拖拽')
tuozhuai.append(click_weizhi)
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成移动后的位置输入,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
tuozhuai.append(click_weizhi)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
step.append(tuozhuai)
if choose == '循环执行':
while 1:
xunhuan_cishu_zhixing = 0
xunhuan_cishu = input('请输入循环次数(如要无限循环请输入"无限"):')
if xunhuan_cishu == '无限':
while True:
zhixing(step)
if xunhuan_cishu.isdigit():
for i in range(int(xunhuan_cishu)):
xunhuan_cishu_zhixing += 1
zhixing(step)
print(f'已完成{xunhuan_cishu_zhixing}次循环')
break
else:
print('你的输入有误,请重新输入:')
if choose == '导入':
if len(step) == 0:
step = daoru()[0]
else:
baocun_choose = input('此次操作若未保存请先,导入别的操作会覆盖原来的操作,你确定要导入吗?\n请输入“yes”or“no”:\n')
while 1:
if baocun_choose == 'no':
break
if baocun_choose == 'yes':
print('你已取消保存')
step = daoru()[0]
break
else:
yorn = input("请输入'yes'or'no':\n")
if choose == '输入':
shuru = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到你要输入的位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
txt_in = input('请输入你要在该位置输入的文字:\n')
shuru.append('输入')
shuru.append(click_weizhi)
shuru.append(txt_in)
step.append(shuru)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
if choose == '按键':
while 1:
anjian = input('这是模拟操作键盘的操作(例如复制,输入'ctrl‘ + 'c‘):\n')
if anjian != 'q':
anjian = anjian.split('+')
anjians = []
a = []
for an in anjian:
an = an.replace("‘", "").replace("'", "").strip()
if an in pyautogui.KEYBOARD_KEYS:
anjians.append(an)
nihaofan = 0
else:
print('你的输入不合法')
nihaofan = 1
break
if nihaofan == 0:
a.append('按键')
a.append(anjians)
step.append(a)
print('录入成功')
break
if anjian == 'q':
break
if choose == '双击':
click_double = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
click_double.append('双击')
click_double.append(click_weizhi)
step.append(click_double)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
if choose == '滚动':
while 1:
gundong = []
try:
gundong1 = int(input('这里是模拟鼠标滚动,请输入你要滚动距离(正数为向上移动,负数为向下移动):\n'))
gundong.append('滚动')
gundong.append(gundong1)
step.append(gundong)
break
except:
print('你的输入有误,请重新输入')
if choose == '查看':
chakan()
if choose == '右击':
click_r = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
click_r.append('右击')
click_r.append(click_weizhi)
step.append(click_r)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
if choose == '中击':
click_m = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
click_weizhi = get_xy()
click_m.append('中击')
click_m.append(click_weizhi)
step.append(click_m)
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”')
if choose == '执行':
if len(step) == 0:
print('你还未记录任何操作,请至少记录了一个操作再执行')
else:
zhixing(step)
cunchu()
if choose == '判断':
if len(panduans) == 0:
tuichu = 0
panduan = input('此功能的实现是基于颜色的RBG值来判断程序所要要执行的步骤块。\n现在,请选择你的‘先执行步骤块等待条件触发'或是‘直接等待条件触发'的操作:(输入"步骤块"或"等待")\n')
if panduan == '如果':
panduan_if = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上吸取颜色,输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
xy = get_xy()
click_color = GetColor(xy)
panduan_yn = input(f'这个位置的RGB为:{click_color},是否确定为下一步骤块的判断根据?(输入"yes"or"no")\n')
while 1:
if panduan_yn == 'yes':
get_caozuo_name()
print(f'请选择满足当颜色为{click_color}时要执行的步骤包:')
steps, steps_name = daoru()
xunhuan_yn = input('这个步骤块是否循环执行至下一条件触发?(输入"yes"or"no")\n')
while 1:
if xunhuan_yn == 'yes':
panduan_if.append('如果')
panduan_if.append(xy)
panduan_if.append(click_color)
panduan_if.append(steps_name)
panduan_if.append('循环')
panduan_if.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_if)
print('添加成功,该步骤包将会循环')
break
elif xunhuan_yn == 'no':
panduan_if.append('如果')
panduan_if.append(xy)
panduan_if.append(click_color)
panduan_if.append(steps_name)
panduan_if.append('不循环')
panduan_if.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_if)
print('添加成功,该步骤包将只执行一次')
break
else:
xunhuan_yn = input('你的输入有误,请输入"yes"or"no":')
tuichu = 1
break
if panduan_yn == 'no':
print('请重新选择')
break
else:
panduan_yn = input('你的输入有误,请输入"yes"or"no"')
if tuichu == 1:
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”)')
if panduan == '步骤块':
panduan_step = []
steps, steps_name = daoru()
xunhuan_yn = input('这个步骤块是否循环执行直至条件触发?(输入"yes"or"no")\n')
while 1:
if xunhuan_yn == 'yes':
panduan_step.append('步骤块')
panduan_step.append('循环')
panduan_step.append(steps_name)
panduan_step.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_step)
break
elif xunhuan_yn == 'no':
panduan_step.append('步骤块')
panduan_step.append('不循环')
panduan_step.append(steps_name)
panduan_step.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_step)
break
else:
xunhuan_yn = input('你的输入有误,请输入"yes"or"no":')
if panduan == '等待':
panduan_if = []
print('你选择了等待,程序将时刻检测目标位置的颜色以执行接下来的步骤块')
panduan_if.append('等待')
panduans.append(panduan_if)
if panduan != '步骤块' and panduan != '如果' and panduan != '等待':
print('你的输入有误')
if len(panduans) > 0:
print('你一录入了至少一个逻辑判断,请选择继续选择目标位置的颜色来触发接下来你选择的步骤块')
panduan_if = []
while 1:
click_dongzuo = input('请移动鼠标到目标位置上吸取颜色,输入“1”完成动作,输入“0”取消动作')
if click_dongzuo == '1':
xy = get_xy()
click_color = GetColor(xy)
panduan_yn = input(f'这个位置的RGB为:{click_color},是否确定为下一步骤块的判断根据?(输入"yes"or"no")\n')
while 1:
if panduan_yn == 'yes':
get_caozuo_name()
print(f'请选择满足当颜色为{click_color}时要执行的步骤包:')
steps, steps_name = daoru()
xunhuan_yn = input('这个步骤块是否循环执行直至条件触发?(输入"yes"or"no")\n')
while 1:
if xunhuan_yn == 'yes':
panduan_if.append('如果')
panduan_if.append(xy)
panduan_if.append(click_color)
panduan_if.append(steps_name)
panduan_if.append('循环')
panduan_if.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_if)
print('添加成功,该步骤包将会循环')
break
elif xunhuan_yn == 'no':
panduan_if.append('如果')
panduan_if.append(xy)
panduan_if.append(click_color)
panduan_if.append(steps_name)
panduan_if.append('不循环')
panduan_if.append(steps)
panduans.append(panduan_if)
print('添加成功,该步骤包将只执行一次')
break
else:
xunhuan_yn = input('你的输入有误,请输入"yes"or"no":')
tuichu = 1
break
if panduan_yn == 'no':
print('请重新选择')
break
else:
panduan_yn = input('你的输入有误,请输入"yes"or"no"')
if tuichu == 1:
break
elif click_dongzuo == '0':
print('操作已取消')
break
else:
print('请输入正确的操作(输入“0”或“1”)')
if choose == '逻辑执行':
print('这里是逻辑执行库,所有的逻辑判断都会存储到这里')
print(panduans)
xiancheng = threading.Thread(target=zhixingbuzhoukuai, args=('等待', '1', '循环'))
xiancheng.setDaemon(True)
xiancheng.start()
for pan in panduans:
state = '未触发'
if pan[0] == '如果':
print(pan[5])
print(len(pan[5]))
bu = str(pan[5])
print(bu)
bu = readListFromStr(bu)
zhixing(bu)
print(bu)
if state == '未触发':
if pan[4] == '循环':
rgb = pan[2]
rgb_xy = pan[1]
_thread.start_new_thread(jianshi, ())
while 1:
if state == '触发':
xiancheng = threading.Thread(target=zhixingbuzhoukuai, args=(pan[3], pan[5], '循环'))
xiancheng.start()
state = '未触发'
break
if pan[4] == '不循环':
rgb = pan[2]
rgb_xy = pan[1]
_thread.start_new_thread(jianshi, ())
while 1:
if state == '触发':
xiancheng = threading.Thread(target=zhixingbuzhoukuai, args=(pan[3], pan[5], '不循环'))
xiancheng.start()
state = '未触发'
break
if pan[0] == '步骤块':
stop_thread(xiancheng)
if pan[1] == '循环':
xiancheng = threading.Thread(target=zhixingbuzhoukuai, args=(pan[2], pan[3], '循环'))
xiancheng.start()
if pan[1] == '不循环':
xiancheng = threading.Thread(target=zhixingbuzhoukuai, args=(pan[2], pan[3], '不循环'))
xiancheng.start()
if pan[0] == '等待':
print('程序正在监测目标位置RGB值')
print('逻辑执行已全部执行完毕')
break
if choose == '逻辑块存储':
yorn = input("确定保存?\n输入'yes'or'no'\n")
while 1:
if yorn == 'yes':
if len(panduans) == 0:
print('还未记录你任何操作,请添加操作再使用逻辑块存储功能')
else:
do_name = input('请为以上操作命名吧:')
if '逻辑块存储' in do_name:
do_name = input('抱歉,你的命名里不允许包含”逻辑块存储“,请重新命名')
else:
path = r"{}逻辑块存储.txt".format(do_name)
listtotxt(list=panduans, path=path)
break
if yorn == 'no':
print('你已取消存储')
break
else:
yorn = input("请输入'yes'or'no':\n")
if choose == '逻辑块导入':
caozuojiyi = get_caozuokuai_name()
while True:
xunhuan_choose = input('已存储的操作有:{}\n请输入导入操作的操作名:'.format(caozuojiyi))
if xunhuan_choose in caozuojiyi:
break
else:
print('逻辑块存储库中并无你想要的操作,请重新输入:')
caozuopath = r"{}逻辑块存储.txt".format(xunhuan_choose)
panduans = txttolist(path=caozuopath)
if choose == 'q' or choose == 'quit' or choose == '退出' or choose == 'close':
break
if choose == 'tips' or choose == '提示' or choose == 'help' or choose == '帮助':
print(
'''你可以输入'点击', '右击', '中击', '逻辑执行', '判断', '滚动', '延时', '存储', '执行', '循环执行', '拖拽', '连点', '输入', '双击', '查看',
'导入', 'q', 'quit','退出', 'close', 'tips', '提示', 'help', '帮助', '按键'来帮助你完成你的自动化操作''')
if not choose in ['点击', '右击', '中击', '逻辑执行', '判断', '滚动', '延时', '存储', '执行', '循环执行', '拖拽', '连点', '输入', '双击', '查看',
'导入', 'q', 'quit','退出', 'close', 'tips', '提示', 'help', '帮助', '按键']:
print('你的输入有误或暂未开发此功能,请重新输入(输入”help“获得提示)')
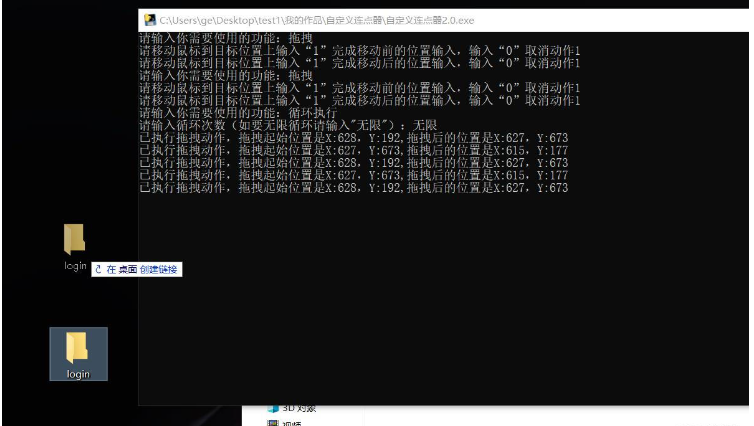
print('代码已全部执行完毕,程序已退出')这是我的2.0版本,之前把逻辑板块之外的功能都写出来了之后迫不及待地玩了一下,帮朋友买了四价,做了微信信息轰炸的程序,看着鼠标把文件夹拖来拖去,做了些拳皇脚本打出超级连招,等会我再试一下盲僧的马氏三角杀哈哈哈,想想就兴奋~~
本来还想做多点功能的,比如:检测目标区域的文字来执行判断操作(这听起来不难);
写个语音输入功能,当执行完什么操作了就让电脑说:“你好厉害啊”、“真的是我的偶像”、“快来看看我抢到四价了”(现在我就能写出来);
import pyttsx3
engine = pyttsx3.init()
engine.say('我抢到了!快来看一下')
engine.runAndWait()以上就是关于“怎么利用Python实现自定义连点器”这篇文章的内容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小编分享的内容对大家有帮助,若想了解更多相关的知识内容,请关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。