这篇“Vue cli及Vue router怎么搭建”文章的知识点大部分人都不太理解,所以小编给大家总结了以下内容,内容详细,步骤清晰,具有一定的借鉴价值,希望大家阅读完这篇文章能有所收获,下面我们一起来看看这篇“Vue cli及Vue router怎么搭建”文章吧。
先安装nodejs
配置环境变量
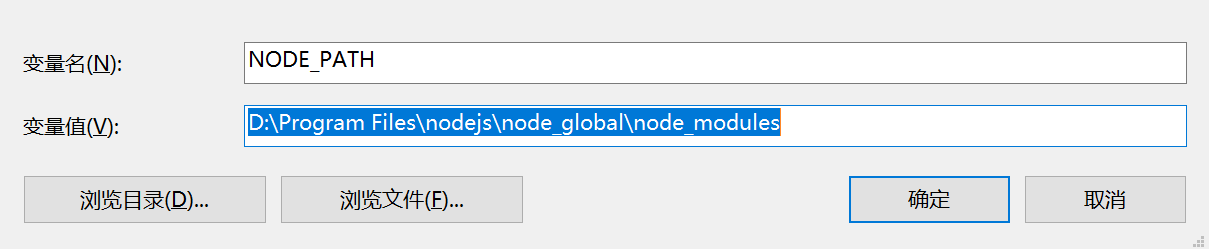
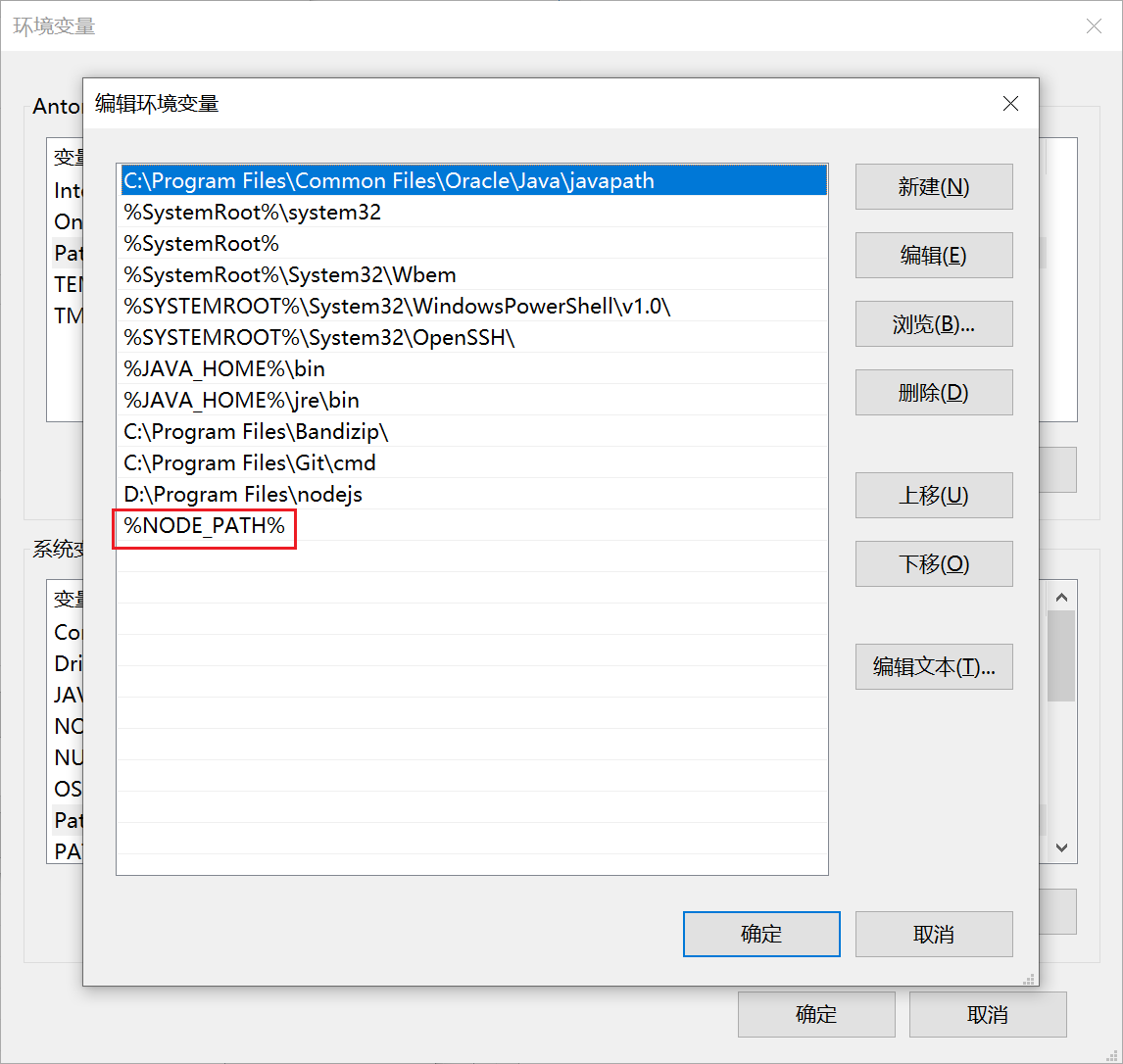
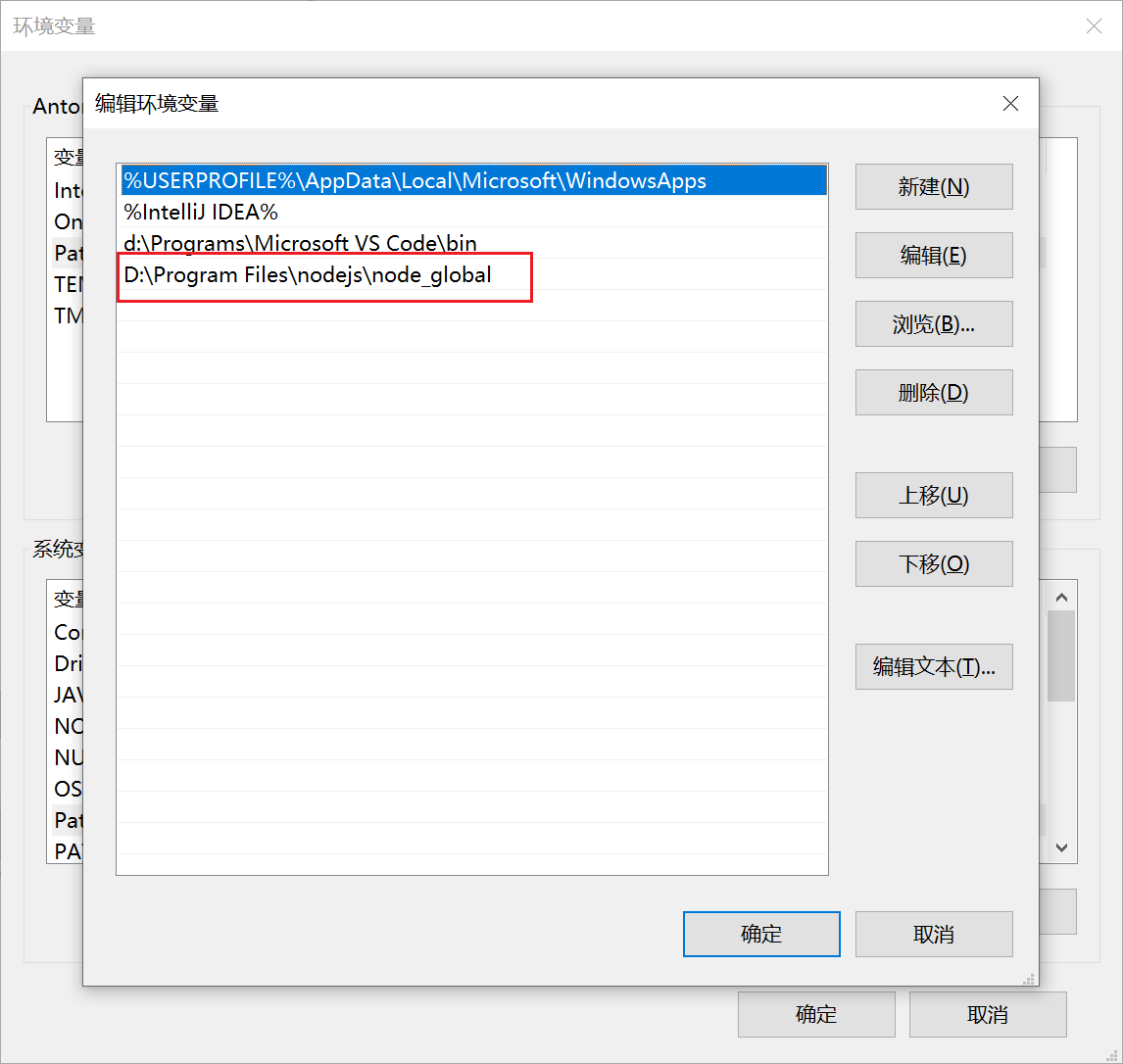
安装vue-cli的前提是你已经安装了npm,在命令行工具中输入npm -v 命令来检测npm的安装以及版本情况。
node下载地址:下载 | Node.js 中文网
安装成功提示:npm -v
配置淘宝镜像
npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org全局安装vue-cli,命令行:
npm install vue-cli -g
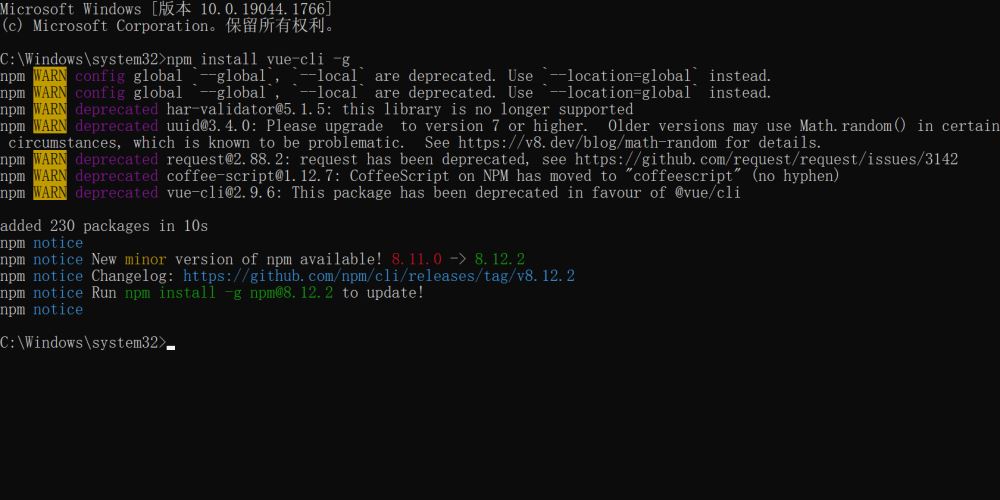
PS:-g代表全局安装,然后查看版本:
vue -V
PS: 注意这里的V是大写
用vue init命令来初始化项目,具体使用方法如下:
vue init <template-name> <project-name>init:表示要用vue-cli来初始化项目
<template-name>:表示模板名称,vue-cli官方提供的5种模板:
webpack:一个全面的webpack+vue-loader的模板,功能包括热加载,linting,检测和CSS扩展。
webpack-simple:一个简单webpack+vue-loader的模板,不包含其他功能,让你快速的搭建vue的开发环境。
browserify:一个全面的Browserify+vueify 的模板,功能包括热加载,linting,单元检测。
browserify-simple:一个简单Browserify+vueify的模板,不包含其他功能,让你快速的搭建vue的开发环境。
simple:一个最简单的单页应用模板。
<project-name>:标识项目名称,用户根据自己的项目来起名字。
在实际开发中,一般都会使用webpack这个模板,命令使用如下:
vue init webpack my-vue-demo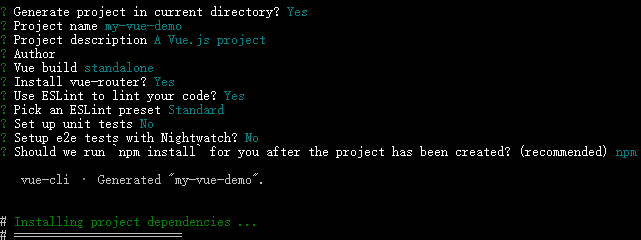
Project name:项目名称 ,默认为初始化建项目的名称my-vue-demo,不需要直接回车
Project description:项目描述,默认为A Vue.js project,不需要直接回车
Author:作者,如果有配置git的作者,自动会读取。直接回车
Install vue-router? 是否安装vue的路由插件,需要安装,选择Y
Use ESLint to lint your code? 是否用ESLint来限制你的代码错误和风格。不需要输入n,需要选择y,如果是大型团队开发,最好是进行配置
setup unit tests with Karma + Mocha? 是否需要安装单元测试工具,不需要输入n,需要选择y
Setup e2e tests with Nightwatch? 是否安装e2e来进行用户行为模拟测试,不需要输入n,需要选择y
初始化完成之后会出现以下信息,表示操作成功。
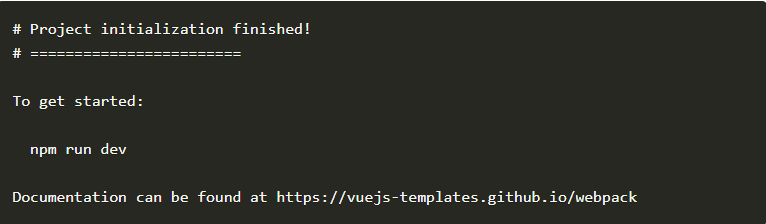
cd my-vue-demo,使用cd命令进入到项目目录
npm run dev
以上命令为开发模式下运行项目
npm run build
以上命令为项目发布打包
一个vue-cli的项目结构如下,其中src文件夹是需要掌握,其余了解即可。
文件夹目录如下:
每个文件夹目录详细说明如下:
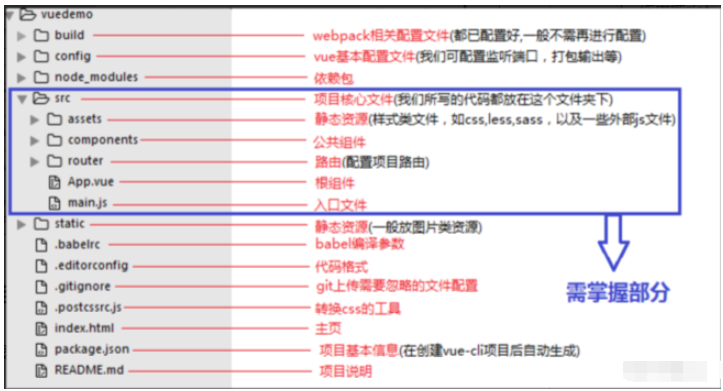
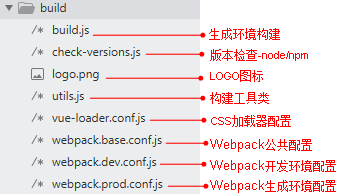
1. build目录(webpack配置)
build文件主要是webpack的配置,目录详情如下:
2. config目录(vue项目配置目录)
config文件主要是项目相关配置,常用的就是当端口冲突时配置监听端口,打包输出路径及命名等,目录详情如下:

3. node_modules(项目依赖包)
node_modules里面是项目依赖包,其中包括很多基础依赖,自己也可以根据需要安装其他依赖。安装方法打开命令工具,进入项目目录,输入npm install [依赖包名称],回车
在两种情况下我们会自己去安装依赖:
》项目运行缺少该依赖包
》安装插件:如vuex
PS:有时会安装指定依赖版本,需在依赖包名称后加上版本号信息,如npm install vue-loader@11.1.4
核心文件目录前面已经说明了,下面重点讲解index.html,main.js,App.vue,router的index.js,HelloWorld.vue
1. index.html(主页)
index.html为项目的主页,跟其他html一样,但一般只定义一个空的根节点,在main.js里面定义的实例将挂载在根节点下,内容都通过vue组件来填充。说明如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<title>my-vue-demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 定义的vue实例将挂载在#app节点下 -->
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
</html>2. main.js(入口文件)
main.js为项目的入口文件,即单入口,主要是引入vue框架,根组件及路由设置,并且定义vue实例,说明如下:
// 引入vue框架
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入根组件
import App from './App'
// 引入路由配置
import router from './router'
// 关闭生产模式下给出的提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 定义实例
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})3. App.vue(根组件)
一个vue页面通常由三部分组成:模板(template)、js(script)、样式(style),说明如下:
<!-- 模板 -->
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<!-- js代码 -->
<script>
export default {
name: 'App'
}
</script>
<!-- css样式 -->
<style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>[template-模板]
(1) 模板只能包含一个父节点,也就是说顶层的div只能有一个(如上图,父节点为#app的div,其没有兄弟节点)
(2)<router-view/>是子路由视图插槽,后面的路由页面都显示在此处,相当于iframe
【script-JS代码】
vue通常用es6来写,用export default导出,其下面可以包含数据data,生命周期(mounted等),方法(methods)等。
【style-CSS样式】
样式通过style标签<style></style>包裹,默认是影响全局的,如需定义作用域只在该组件下起作用,需在标签上加scoped,<style scoped></style>
引入外部CSS示例:
<style>
import './assets/css/public.css'
</style>4. router(路由配置)
router文件夹下,有一个index,js的路由配置文件,说明如下:
// 引入vue框架
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入vue-router路由依赖
import Router from 'vue-router'
// 引入页面组件,命名为HelloWorld
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld'
// 使用路由依赖
Vue.use(Router)
// 定义路由配置
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'HelloWorld',
component: HelloWorld
}
]
})5. HelloWorld.vue(页面组件)
最熟悉的HelloWorld输出,说明如下:
<template>
<div>
<!-- 输出变量 -->
<h2>{{ msg }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// 定义页面名称,可以不要
name: 'HelloWorld',
data () {
return {
// 定义变量
msg: 'HelloWorld'
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
h2 {
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: normal;
}
</style>官方文档
Vue Router 是 Vue.js 官方的路由管理器。它和 Vue.js 的核心深度集成,让构建单页面应用变得易如反掌。
包含的功能有:
嵌套的路由/视图表
模块化的、基于组件的路由配置
路由参数、查询、通配符
基于 Vue.js 过渡系统的视图过渡效果
细粒度的导航控制
带有自动激活的 CSS class 的链接
HTML5 历史模式或 hash 模式,在 IE9 中自动降级
自定义的滚动条行为
安装
vue-router是一个插件包,需要用npm来进行安装的。如果采用vue-cli构建初始化项目会提示安装,也可以自己使用命令安装:
npm install vue-router --save解读核心文件
用vue-cli构建项目之后,在src/router/index.js文件中,看到以下的路由核心文件:
// 引入vue框架
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入vue-router路由依赖
import Router from 'vue-router'
// 引入页面组件,命名为HelloWorld
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld'
// Vue全局使用Router
Vue.use(Router)
// 定义路由配置
export default new Router({
routes: [ //配置路由,这里是个数组
{ //每一个链接都是一个对象
path: '/', //链接路径
name: 'HelloWorld', //路由名称,
component: HelloWorld //对应的组件模板
}
]
})使用
在系统入口文件main.js中注入router,代码如下:
// 引入vue框架
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入根组件
import App from './App'
// 引入路由配置
import router from './router'
// 关闭生产模式下给出的提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 定义实例
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router, // 注入框架中
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})1.router-link标签跳转
在html标签内使用router-link跳转,相应于超链接a标签,使用方式如下:
<router-link to="/">[显示字段]</router-link>to:导航路径
使用示例如下:
<p>导航 :
<router-link to="/">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/hello">hello</router-link>
</p>2.编程式导航-JS代码内部跳转
实际项目中,很多时候都是通过在JS代码内部进行导航的跳转,使用方式如下:
this.$router.push('/xxx')具体的简单用法:
(1)先编写一个按钮,在按钮上绑定goHome( )方法。
<button @click="goHome">回到首页</button>(2)在<script>模块里加入goHome方法,并用this.$router.push(‘/’)导航到首页
export default {
name: 'app',
methods: {
goHome(){
this.$router.push('/home');
}
}
}3. 其它常用方法
// 后退一步记录,等同于 history.back()
this.$router.go(-1)
// 在浏览器记录中前进一步,等同于 history.forward()
this.$router.go(1)子路由,也叫路由嵌套,采用在children后跟路由数组来实现,数组里和其他配置路由基本相同,需要配置path和component,然后在相应部分添加<router-view/>来展现子页面信息,相当于嵌入iframe。具体看下面的示例:
1.src/components/Home.vue(父页面)
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h2>{{ msg }}</h2>
<!-- 添加子路由导航 -->
<p>导航 :
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link> |
<router-link to="/home/one">-子页面1</router-link> |
<router-link to="/home/two">-子页面2</router-link>
</p>
<!-- 子页面展示部分 -->
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Home',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Home Page!'
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>2.src/components/One.vue(子页面1)
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h2>{{ msg }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'One',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Hi, I am One Page!'
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>3.src/components/Two.vue(子页面2)
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h2>{{ msg }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Two',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Hi, I am Two Page!'
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>4.src/router/index.js(路由配置)
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Home from '@/components/Home'
import One from '@/components/One'
import Two from '@/components/Two'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/', // 默认页面重定向到主页
redirect: '/home'
},
{
path: '/home', // 主页路由
name: 'Home',
component: Home,
children:[ // 嵌套子路由
{
path:'one', // 子页面1
component:One
},
{
path:'two', // 子页面2
component:Two
},
]
}
]
})5. 效果图

PS:各部分代码都很简单,也有注释,在采用vue-cli初始化项目完成之后直接复制到相应目录即可查看效果。
1.通过<router-link> 标签中的to传参
基本语法:
<router-link :to="{name:xxx, params:
{key:value}}">valueString</router-link>PS:上面to前边是带冒号,后边跟的是一个对象形势的字符串
name:在路由配置文件中起的name值。叫做命名路由,下一节会讲到。
params:要传的参数,它是对象形式,在对象里可以传递多个值。
具体实例如下:
(1)在src/components/Home.vue里面导航中添加如下代码:
<router-link :to="{name: 'one', params:{username:'test123'}}">子页面1</router-link>(2)在src/router/indes.js中添加如下代码,重点是name:\
{
path:'one', // 子页面1
name: 'one', // 路由名称-命名路由
component:One
}(3)在src/components/One.vue里面接受参数,代码如下:
<h3>{{$route.params.username}}</h3>2. url中传递参数
(1)在路由中以冒号传递,在src/router/index.js中加入如下代码:
{
path:'/home/two/:id/:name', // 子页面2
component:Two
},(2)接受参数,在src/components/Two.vuez中加入如下代码:
<p>ID:{{ $route.params.id}}</p>
<p>名称:{{ $route.params.name}}</p>(3)路由跳转,在src/components/Home.vue中加入如下代码:
<router-link to="/home/two/1/张三">子页面2</router-link>PS:to前没有冒号为字符串路由,必须全部匹配。
(4)如果路由参数需要有特定的规则,就需要加入正则表达式了,示例如下:
{
path:'/home/two/:id(\\d+)/:name', // 子页面2
component:Two
}3.编程式导航-params传递参数
(1)在src/router/index.js页面加入如下代码:
{
path:'/home/three', // 子页面3
name: 'three',
component:Three
}(2)在src/components/Three.vue页面加入如下代码:
<p>ID:{{ $route.params.id}}</p>
<p>名称:{{ $route.params.name}}</p>(3)在src/components/Home.vue中加入如下代码:
// template
<button @click="toThreePage">页面3-params传参</button>
// script
methods: {
toThreePage() {
this.$router.push({name: 'three', params: {id: 1, name: 'zhangsan'}})
}
}说明:
A、动态路由使用params传递参数,在this.$router.push() 方法中path不能和params一起使用,否则params将无效。需要用name来指定页面。
B、以上方式参数不会显示到浏览器的地址栏中,如果刷新一次页面,就获取不到参数了,改进方式将第一部中的代码改成如下:
{
path:'/home/three/:id/:name', // 子页面3
name: 'three',
component:Three
}4. 编程式导航-query传递参数
(1)在src/router/index.js页面加入如下代码:
{
path:'/home/three', // 子页面3
name: 'three',
component:Three
}(2)在src/components/Three.vue页面加入如下代码:
<p>ID:{{ $route.query.id}}</p>
<p>名称:{{ $route.query.name}}</p>(3)在src/components/Home.vue中加入如下代码:
// template
<button @click="toThreePage">页面3-params传参</button>
// script
methods: {
toThreePage() {
this.$router.push({path: '/home/three', query: {id: 1, name: 'zhangsan'}})
}
}PS:动态路由使用query传递参数,会显示到浏览器地址栏中,以上链接为
/home/three?id=1&name=zhangsan
1. 命名路由
给一个路由命一个唯一的名称,然后跳转调用这个名称即可。
(1)在src/router/index.js中加一个带name的路由,代码如下:
{
path: 'one', // 子页面1
name: 'one', // 路由名称-命名路由
component: One // 页面组件
}(2)在src/component/Home.vue页面中调用,代码如下:
// template跳转调用
<router-link :to="{name: 'one'}">子页面1</router-link>
// router.push函数跳转调用
router.push({ name: 'user'}})2.命名视图
在同一个页面展示多个视图,如果不用嵌套,只能采用命名视图来实现了,代码如下:
(1)在src/router/index.js中,代码如下:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
// 创建页面组件
const Header = { template: '<div>Header</div>' }
const Left = { template: '<div>Left</div>' }
const Right = { template: '<div>Right</div>' }
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/', // 主页路由
components: {
default: Header,
a: Left,
b: Right
}
}
]
})(2)在src/App.vue中,代码如下:
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view />
<router-view name="a" class="left" />
<router-view name="b" class="right" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App'
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
width: 500px;
border: 1px solid red;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.left,.right{
float: left;
width:48%;
text-align: center;
border:1px solid red
}
</style>PS:经过实践,命名视图只能放在最顶级的页面中,即第一步中的代码不能放在其他页面中。
3.重定向
重定向是通过route的配置中关键词redirect来实现的,具体代码如下:
(1)在src/router/index.js中,代码如下:
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/', // 默认页面重定向到主页
redirect: '/home' // 重定向
},
{
path: '/home', // 主页路由
component: Home,
children:[ // 嵌套子路由
{
path:'/home/two/:id/:name', // 子页面2
component:Two
},
{
path:'/home/three/:id/:name', // 子页面3
name: 'three', // 路由名称-命名路由
redirect: '/home/two/:id/:name' // 重定向-传递参数
},
]
}
]
})(2)在src/components/Home.vue中,代码如下:
<router-link to="/">首页</router-link> |
<router-link to="/home/two/1/lisi">子页面2</router-link> |
<router-link :to="{name: 'three', params: {id: 1, name: 'zhangsan'}}">子页面3</router-link>说明1-不带参数的重定向:
redirect: '/home' // 重定向-不带参数说明2-带参数的重定向:
redirect: '/home/two/:id/:name' // 重定向-传递参数4. 别名
重定向是通过route的配置中关键词alias来实现的,具体代码如下:
(1)在src/router/index.js中,代码如下:
{
path:'/one', // 子页面1
component:One,
alias: '/oneother'
}(2)在src/components/Home.vue中,代码如下:
<router-link to="/oneother">子页面1</router-link>说明1:redirect和alias的区别
redirect:直接改变了url的值,把url变成了真实的path路径。\
alias:url路径没有别改变,这种更友好,让用户知道自己访问的路径,只是改变了<router-view>中的内容。
说明2:
别名请不要用在path为’/’中,如下代码的别名是不起作用的。
{
path: '/',
component: Hello,
alias:'/home'
}以上就是关于“Vue cli及Vue router怎么搭建”这篇文章的内容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小编分享的内容对大家有帮助,若想了解更多相关的知识内容,请关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。