本篇内容介绍了“Android ViewBinding如何使用”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
在使用ViewBinding之前,我们一直使用的是kotlin-android-extensions,使用kotlin-android-extensions可以节约很多写findViewById的时间。不过这个kotlin-android-extensions插件已经废弃了,简单说一下kotlin-android-extensions存在的问题:
1.通过反编译kotlin-android-extensions的代码,发现会创建一个HashMap,用来存放所有的id和对应的View的缓存,如果缓存中没有View,那么就通过findViewById去创建并存入缓存,否则就直接获取。所以会存在内存问题。
private HashMap _$_findViewCache;
public View _$_findCachedViewById(int var1) {
if (this._$_findViewCache == null) {
this._$_findViewCache = new HashMap();
}
View var2 = (View)this._$_findViewCache.get(var1);
if (var2 == null) {
View var10000 = this.getView();
if (var10000 == null) {
return null;
}
var2 = var10000.findViewById(var1);
this._$_findViewCache.put(var1, var2);
}
return var2;
}
public void _$_clearFindViewByIdCache() {
if (this._$_findViewCache != null) {
this._$_findViewCache.clear();
}
}
// $FF: synthetic method
public void onDestroyView() {
super.onDestroyView();
this._$_clearFindViewByIdCache();
}2.由于kotlin-android-extensions是通过view的id名直接引用的,如果多个布局间的同名id,就需要手动对import进行重命名处理,如果引用错误的布局文件,就会出现crash。所以存在资源重名的问题。
3.只有Kotlin才可以使用。
所以ViewBinding优势有:java,kotlin都可以使用,可以有效避免NullPointerException。
buildFeatures {
viewBinding true
}
开启ViewBinding之后,在编译时,AGP会自动帮我们给每个xml布局创建一个Binding类,位于build/generated/data_binding_base_class_source_out/目录下。
public final class FragmentLoginBinding implements ViewBinding {
@NonNull
private final ConstraintLayout rootView;
@NonNull
public final ConstraintLayout container;
@NonNull
public final ProgressBar loading;
@NonNull
public final Button login;
@NonNull
public final EditText password;
@NonNull
public final EditText username;
private FragmentLoginBinding(@NonNull ConstraintLayout rootView,
@NonNull ConstraintLayout container, @NonNull ProgressBar loading, @NonNull Button login,
@NonNull EditText password, @NonNull EditText username) {
this.rootView = rootView;
this.container = container;
this.loading = loading;
this.login = login;
this.password = password;
this.username = username;
}
@Override
@NonNull
public ConstraintLayout getRoot() {
return rootView;
}
@NonNull
public static FragmentLoginBinding inflate(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater) {
return inflate(inflater, null, false);
}
@NonNull
public static FragmentLoginBinding inflate(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater,
@Nullable ViewGroup parent, boolean attachToParent) {
View root = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_login, parent, false);
if (attachToParent) {
parent.addView(root);
}
return bind(root);
}
@NonNull
public static FragmentLoginBinding bind(@NonNull View rootView) {
// The body of this method is generated in a way you would not otherwise write.
// This is done to optimize the compiled bytecode for size and performance.
int id;
missingId: {
ConstraintLayout container = (ConstraintLayout) rootView;
id = R.id.loading;
ProgressBar loading = rootView.findViewById(id);
if (loading == null) {
break missingId;
}
id = R.id.login;
Button login = rootView.findViewById(id);
if (login == null) {
break missingId;
}
id = R.id.password;
EditText password = rootView.findViewById(id);
if (password == null) {
break missingId;
}
id = R.id.username;
EditText username = rootView.findViewById(id);
if (username == null) {
break missingId;
}
return new FragmentLoginBinding((ConstraintLayout) rootView, container, loading, login,
password, username);
}
String missingId = rootView.getResources().getResourceName(id);
throw new NullPointerException("Missing required view with ID: ".concat(missingId));
}
}注意:
1.因为这些类编译时就生成了,就不会占用运行时内存。
2.未使用的Binding文件会在混淆时被删除,所以对包大小影响很小。
3.编译器生成Binding文件是增量更新的。
那么如何不生成Binding类呢?tools:viewBindingIgnore="true"
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:viewBindingIgnore="true"
tools:context=".MainActivity">class TestViewBindingActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var bindding: ActivityTestViewBindingBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
bindding = ActivityTestViewBindingBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(bindding.root)
changeText()
}
private fun changeText() {
bindding.titleTv.text = "哈哈,在Activity中使用ViewBinding了"
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".testviewbinding.TestViewBindingActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/titleTv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="在Activity中使用ViewBinding"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>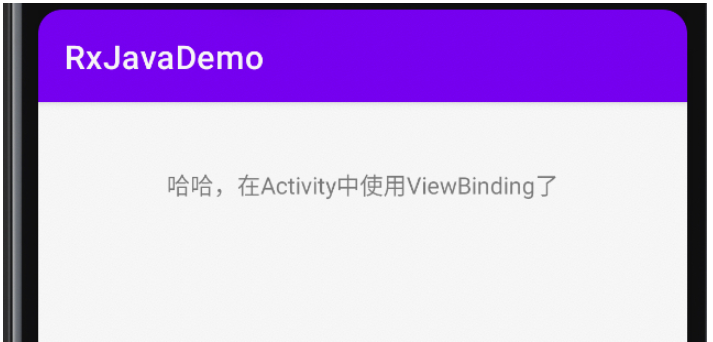
class TextViewBindingFragment : Fragment() {
private var param1: String? = null
private var param2: String? = null
private var _binding: FragmentTextViewBindingBinding? = null
private val binding get() = _binding!!
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
arguments?.let {
param1 = it.getString(ARG_PARAM1)
param2 = it.getString(ARG_PARAM2)
}
}
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
_binding = FragmentTextViewBindingBinding.inflate(layoutInflater, container, false)
return binding.root
}
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState)
changeText()
}
private fun changeText() {
binding.tvTitle.text = "哈哈,在Fragment中使用ViewBinding"
}
override fun onDestroyView() {
super.onDestroyView()
_binding = null
}
companion object {
@JvmStatic
fun newInstance(param1: String, param2: String) =
TextViewBindingFragment().apply {
arguments = Bundle().apply {
putString(ARG_PARAM1, param1)
putString(ARG_PARAM2, param2)
}
}
@JvmStatic
fun newInstance() = TextViewBindingFragment()
}
}class TestViewBindingActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var bindding: ActivityTestViewBindingBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
bindding = ActivityTestViewBindingBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(bindding.root)
val newInstance = TextViewBindingFragment.newInstance()
addFragment(
supportFragmentManager,
newInstance,
isAllowStateLoss = true,
frameId = R.id.fragmentFrame
)
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".testviewbinding.TextViewBindingFragment">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvTitle"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="在Fragment中" />
</FrameLayout>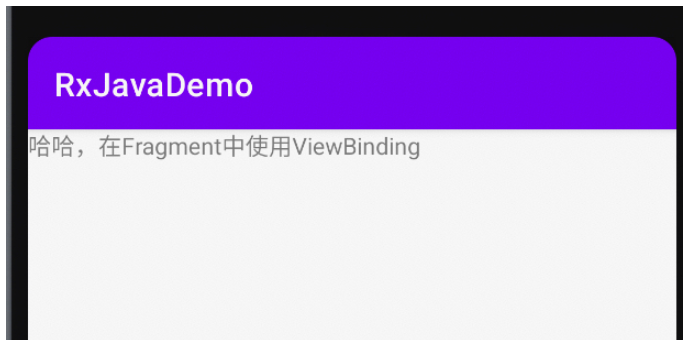
class TestAdapterActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var binding: ActivityTestAdapterBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityTestAdapterBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
initView()
}
companion object {
val ITEMS = mutableListOf<String>("1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6")
}
private fun initView() {
with(binding.contentRcycler) {
layoutManager = GridLayoutManager(context, 4)
adapter = TestRecyclerViewAdapter(ITEMS)
}
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".testviewbinding.TestAdapterActivity">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/contentRcycler"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>class TestRecyclerViewAdapter(private val values: List<String>) :
RecyclerView.Adapter<TestRecyclerViewAdapter.ViewHolder>() {
inner class ViewHolder(binding: RecyclerItemLayoutBinding) :
RecyclerView.ViewHolder(binding.root) {
val textTv = binding.contentTv
}
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): ViewHolder {
return ViewHolder(
RecyclerItemLayoutBinding.inflate(
LayoutInflater.from(parent.context),
parent,
false
)
)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ViewHolder, position: Int) {
val item = values[position]
holder.textTv.text = item
}
override fun getItemCount(): Int = values.size
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/contentTv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="16dp"
tools:text="99" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
class CommonDialog(context: Context) : Dialog(context) {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(DialogLayoutBinding.inflate(layoutInflater).root)
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/dialogContent"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:text="This is Dialog"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
class TestIncludeActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var binding: ActivityTestIncludeBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityTestIncludeBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
initView()
}
private fun initView() {
binding.itemInclude.itemContentTv.text = "哈哈, this is include"
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".testviewbinding.TestIncludeActivity">
<include
android:id="@+id/itemInclude"
layout="@layout/item_layout" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout><?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/itemContentTv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:text="Test include"
android:textSize="30sp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>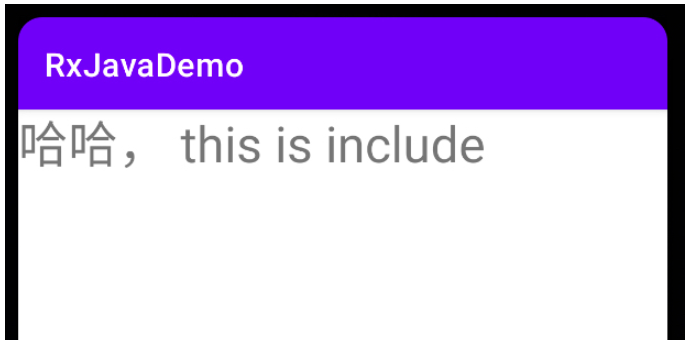
abstract class BaseViewBindingActivity<T : ViewBinding> : AppCompatActivity() {
protected val binding by lazy {
getViewBinding()
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(binding.root)
}
protected abstract fun getViewBinding(): T
}class ChildViewBindingMainActivity :
BaseViewBindingActivity<ActivityChildViewBindingMainBinding>() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding.titleTv.text = "哈哈,this is child binding activity"
}
override fun getViewBinding(): ActivityChildViewBindingMainBinding {
return ActivityChildViewBindingMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".encapsulatviewbinding.ChildViewBindingMainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/titleTv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="36sp" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
class TestViewBindingMainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val binding by inflate<ActivityTestViewBindingMainBinding>()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding.titleTv.text = "哈哈,通过反射封装ViewBinding"
}
}
inline fun <reified T : ViewBinding> inflateByViewBinding(layoutInflater: LayoutInflater) =
T::class.java.getMethod("inflate", LayoutInflater::class.java).invoke(null, layoutInflater) as T
inline fun <reified T : ViewBinding> Activity.inflate() = lazy {
inflateByViewBinding<T>(layoutInflater).apply {
setContentView(root)
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".encapsulatviewbinding.TestViewBindingMainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/titleTv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="36sp" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
abstract class BaseBindingMainActivity2<T : ViewBinding> : AppCompatActivity() {
protected lateinit var binding: T
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
val type = javaClass.genericSuperclass
if (type is ParameterizedType) {
val clazz = type.actualTypeArguments[0] as Class<T>
val method = clazz.getMethod("inflate", LayoutInflater::class.java)
binding = method.invoke(null, layoutInflater) as T
}
setContentView(binding.root)
}
}class ChildViewBindingMainActivity2 :
BaseBindingMainActivity2<ActivityChildViewBindingMain2Binding>() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding.titleTv.text = "哈哈,这是反射+基类的方式"
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".encapsulatviewbinding.ChildViewBindingMainActivity2">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/titleTv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>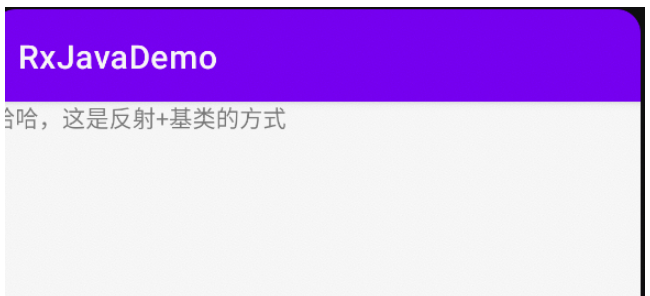
abstract class BaseBindingViewFragment<T : ViewBinding> : Fragment() {
private var _binding: T? = null
protected val binding get() = _binding!!
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
val type = javaClass.genericSuperclass
val clazz = (type as ParameterizedType).actualTypeArguments[0] as Class<T>
val method = clazz.getMethod(
"inflate",
LayoutInflater::class.java,
ViewGroup::class.java,
Boolean::class.java
)
_binding = method.invoke(null, layoutInflater, container, false) as T
this.viewLifecycleOwner.lifecycle.addObserver(object : LifecycleEventObserver {
override fun onStateChanged(source: LifecycleOwner, event: Lifecycle.Event) {
if (event == Lifecycle.Event.ON_DESTROY) {
Log.v(TAG, "onDestroy binding be null")
_binding = null
}
}
})
return binding.root
}
companion object {
const val TAG = "BaseBindingViewFragment"
}
}class ChildBindingFragment : BaseBindingViewFragment<FragmentChildBindingBinding>() {
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
return super.onCreateView(inflater, container, savedInstanceState)
}
companion object {
@JvmStatic
fun newInstance() = ChildBindingFragment()
}
}class TestBindingMainActivity3 : BaseBindingMainActivity2<ActivityTestBindingMain3Binding>() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
val newInstance = ChildBindingFragment.newInstance()
addFragment(
supportFragmentManager,
newInstance,
isAllowStateLoss = true,
frameId = R.id.frame
)
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".encapsulatviewbinding.ChildBindingFragment">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/hello_blank_fragment" />
</FrameLayout>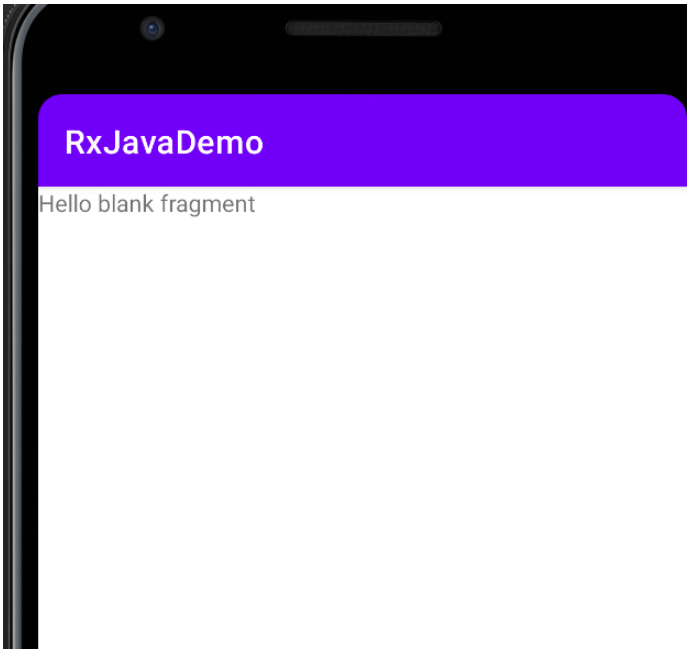
class TestViewBindingFragment2 : Fragment(R.layout.fragment_test_view_binding2) {
private val binding by inflate<FragmentTestViewBinding2Binding>()
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState)
binding.root
}
companion object {
@JvmStatic
fun newInstance() = TestViewBindingFragment2()
}
}
inline fun <reified T : ViewBinding> Fragment.inflate() =
FragmentViewBindingDelegate(T::class.java)
class FragmentViewBindingDelegate<T : ViewBinding>(private val clazz: Class<T>) :
ReadOnlyProperty<Fragment, T> {
private var binding: T? = null
override fun getValue(thisRef: Fragment, property: KProperty<*>): T {
if (binding == null) {
binding =
clazz.getMethod("bind", View::class.java).invoke(null, thisRef.requireView()) as T
thisRef.viewLifecycleOwner.lifecycle.addObserver(object : LifecycleEventObserver {
override fun onStateChanged(source: LifecycleOwner, event: Lifecycle.Event) {
if (event == Lifecycle.Event.ON_DESTROY) {
binding = null
}
}
})
}
return binding!!
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".encapsulatviewbinding.TestViewBindingFragment2">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="8888888" />
</FrameLayout>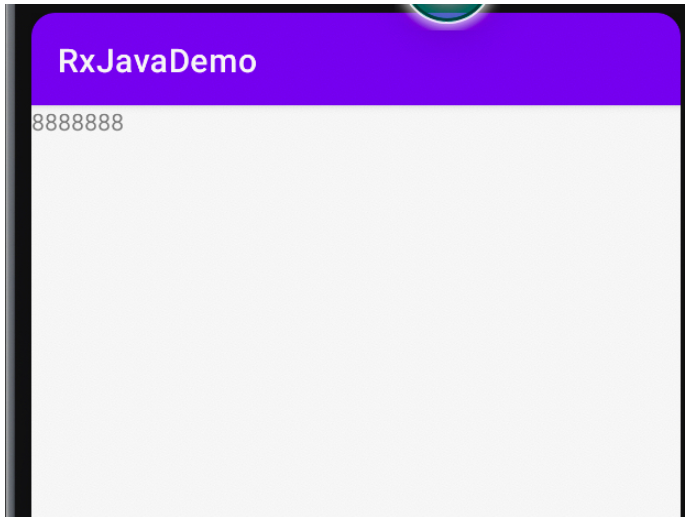
“Android ViewBinding如何使用”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注亿速云网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。