жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
еӨ©еҶ·дәҶпјҢиҖҒеӨ«иҰҒжҠҠдјҷйЈҹжҗһдёҠеҺ»пјҢиҝҷдёҚжңҖиҝ‘еңЁиҪҜ件еӣӯдәҢжҘјеҗғпјҢдјҷйЈҹ15еқ—пјҢжқ жқ зҡ„гҖӮ


зҫҺеҢ…еҢ…пјҢдёҚиҜҙдәҶпјҢиҝӣе…ҘжӯЈйўҳгҖӮд»ҠеӨ©иҖҒеӨ«иҰҒи®Ізҡ„жҳҜиҜ»еҸ–иҒ”зі»дәәпјҢе…¶е®һжҲ‘еҒҡиҝҷдёӘзҡ„еҲқиЎ·жҳҜжғіеҒҡдёҖдёӘзҹӯдҝЎжӢҰжҲӘпјҢз”өиҜқжӢҰжҲӘзҡ„еҠҹиғҪгҖӮ
жҲ‘们е…ҲзңӢдёҖдёӢз•ҢйқўпјҢиҝҳжҳҜдёҚй”ҷзҡ„пјҢжҢәз»ҡдёҪзҡ„гҖӮ
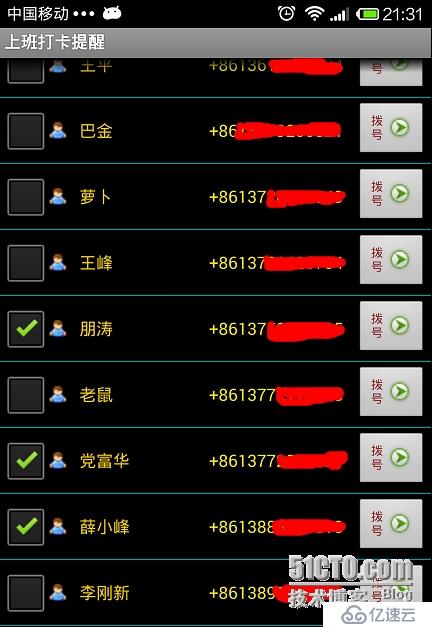
OKпјҢжҲ‘们дёҖзңӢе°ұзҹҘйҒ“пјҢиҝҷеҸҲжҳҜдёҖдёӘListViewгҖӮзӣ®еүҚзҡ„еҠҹиғҪжҳҜеҪ“дҪ еңЁеӨҚйҖүжЎҶжү“й’©пјҢзӮ№еҮ»еҗҺйқўзҡ„жӢЁеҸ·е°ұдјҡе°Ҷз”өиҜқжү“еҮәеҺ»гҖӮеҰӮжһңдёҚжү“й’©пјҢз”өиҜқеҲҷдёҚдјҡжӢЁеҮәеҺ»гҖӮOKпјҢжҲ‘们е…ҲзңӢзңӢйЎөйқўеёғеұҖ
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <ListView android:id="@+id/contactListView" android:descendantFocusability="blocksDescendants" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:divider="@color/teal" android:dividerHeight="1dp"> </ListView> <LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <Button android:id="@+id/btnSelAll" android:text="@string/btnSelAll" android:textColor="@color/teal" android:textSize="14dp" android:textStyle="bold" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"></Button> <Button android:id="@+id/btnInverseSel" android:text="@string/btnSelInverse" android:textColor="@color/teal" android:layout_marginLeft="1dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:textSize="14dp" android:textStyle="bold" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"></Button> <Button android:id="@+id/btnSet" android:text="@string/btnSet" android:layout_weight="1" android:textColor="@color/teal" android:layout_marginLeft="1dp" android:textSize="14dp" android:textStyle="bold" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"></Button> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
жҲ‘们еҶҚзңӢзңӢListViewиҰҒеҠ иҪҪзҡ„жЁЎзүҲ
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/contactTemplate"> <TableLayout android:id="@+id/tabContatMain" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:stretchColumns="2" android:shrinkColumns="2" android:padding="3dip"> <TableRow> <CheckBox android:id="@+id/chkContactUser" android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"></CheckBox> <ImageView android:id="@+id/imgContactPhoto" android:layout_gravity="center_vertical" android:scaleType="fitCenter"></ImageView> <TextView android:id="@+id/txtContactName" android:layout_marginLeft="10dp" android:layout_gravity="center_vertical" android:textColor="@color/teal1"></TextView> <TextView android:id="@+id/txtContactTelNumber" android:layout_marginLeft="4dp" android:gravity="right" android:layout_gravity="center_vertical" android:textColor="@color/yellow"></TextView> <Button android:id="@+id/btnDail" android:text="@string/btnDail" android:textSize="10dp" android:layout_marginLeft="10dp" android:width="60dp" android:drawableRight="@drawable/dail" android:layout_gravity="center_vertical" android:textColor="@color/purplered"></Button> </TableRow> </TableLayout> </LinearLayout>
дҫқ然жҳҜTableLayoutеёғеұҖпјҢжҲ‘们и®ҫзҪ®е®ғзҡ„收缩еҲ—дёә第дәҢеҲ—пјҢдјёеұ•еҲ—д№ҹжҳҜ第дәҢеҲ—гҖӮиҝҷж ·еҰӮжһң第дәҢеҲ—дёҚеӨҹжҳҫзӨәеҲҷдјҡ收缩гҖӮOKпјҢжҲ‘们зңӢдёҖдёӢеҗҺеҸ°д»Јз Ғ
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.punchinalarm);
owner = this;
btnSelAll = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btnSelAll);
btnSelInverse = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btnInverseSel);
btnSet = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btnSet);
contactUserListView = (ListView) this
.findViewById(R.id.contactListView);
dataList = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
this.InitData();
}еңЁOnCreateж–№жі•дёӯпјҢжҲ‘们еҲқе§ӢеҢ–ж•°жҚ®гҖӮ
private void InitData() {
String phoneUserName = null;
String phoneNumber = null;
Long contactId = null;
Long photoId = null;
Map<String, Object> dataMap = null;
ContentResolver resolver = this.getApplicationContext()
.getContentResolver();
/*
* иҺ·еҸ–SimеҚЎиҒ”зі»дәә Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://icc/adn");
*/
Cursor phoneCursor = resolver.query(Phone.CONTENT_URI,
PHONE_PROJECTION, null, null, null);
if (phoneCursor != null) {
while (phoneCursor.moveToNext()) {
dataMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
phoneUserName = phoneCursor.getString(0);
phoneNumber = phoneCursor.getString(1);
photoId = phoneCursor.getLong(2);
contactId = phoneCursor.getLong(3);
if (phoneNumber == null || phoneNumber.trim().length() < 11) {
continue;
}
Bitmap contactPhoto = null;
if (photoId > 0) {
Uri uri = ContentUris.withAppendedId(
ContactsContract.Contacts.CONTENT_URI, contactId);
InputStream input = ContactsContract.Contacts
.openContactPhotoInputStream(resolver, uri);
contactPhoto = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(input);
} else {
contactPhoto = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),
R.drawable.usersmall);
}
dataMap.put("UserName", phoneUserName);
dataMap.put("UserPhoneNumber", phoneNumber);
dataMap.put("UserPhoto", contactPhoto);
dataList.add(dataMap);
}
if (dataList != null && dataList.size() > 0) {
customAdapter simpleAdapter = new customAdapter(this, dataList,
R.layout.contactdetailtemplate, new String[] {
"UserPhoto", "UserName", "UserPhoneNumber" },
new int[] { R.id.chkContactUser, R.id.imgContactPhoto,
R.id.txtContactName, R.id.txtContactTelNumber,
R.id.btnDail });
this.contactUserListView.setAdapter(simpleAdapter);
}
}
}жҲ‘们зҹҘйҒ“еӨ–з•Ңзҡ„зЁӢеәҸйҖҡиҝҮContentResolverжҺҘеҸЈеҸҜд»Ҙи®ҝй—®ContentProviderжҸҗдҫӣзҡ„ж•°жҚ®пјҢеңЁActivityеҪ“дёӯйҖҡиҝҮgetContentResolver()еҸҜд»Ҙеҫ—еҲ°еҪ“еүҚеә”з”Ёзҡ„ ContentResolverе®һдҫӢгҖӮеӣ дёәйҖҡи®ҜеҪ•е’Ңзҹӯж¶ҲжҒҜйғҪеҸҜд»ҘйҖҡиҝҮжҺҘеҸЈи®ҝй—®пјҢжүҖд»ҘжҲ‘们е°ұеҸҜд»ҘйҖҡиҝҮgetContentResolverи®ҝй—®SIMеҚЎе’ҢжүӢжңәдёӯзҡ„иҒ”зі»дәәдҝЎжҒҜгҖӮ
жҲ‘们主иҰҒеҲ°дёӢйқўзҡ„иҝҷеҸҘ
Cursor phoneCursor = resolver.query(Phone.CONTENT_URI, PHONE_PROJECTION, null, null, null);
йҖҡиҝҮжҺҘеҸЈжҹҘиҜўпјҢжҲ‘们дјҡеҫ—еҲ°дёҖдёӘCursorгҖӮйҖҡиҝҮжҹҘзңӢCursorзҡ„е®ҡд№үпјҢжҲ‘们еҸ‘зҺ°е®ғжҳҜдёӘжҠҪиұЎзұ»
public abstract interface android.database.Cursor
жҲ‘们еҸ‘зҺ°е®ғжҸҗдҫӣдәҶдёҖдәӣж–№жі•пјҢеҰӮдёӢ

з”ұжӯӨеҸҜи§ҒпјҢе®ғжҳҜдёҖдёӘж—ўеҸҜд»ҘеүҚиҝӣеҸҲеҸҜд»ҘеҗҺйҖҖзҡ„ж— еҗ‘жёёж ҮпјҢзұ»дјјдәҺSqlServerдёӯзҡ„жёёж ҮгҖӮиҝҷж ·зҡ„иҜқжҲ‘们дёҚи®әжҳҜиҜ»еҸ–иҒ”зі»дәәдҝЎжҒҜпјҢиҝҳжҳҜиҜ»еҸ–зҹӯж¶ҲжҒҜпјҢйғҪеҸҜд»ҘйҡҸж—¶е®ҡдҪҚжёёж ҮгҖӮ
еңЁдёҠйқўжҲ‘们зңӢеҲ°Queryзҡ„еҮ дёӘеҸӮж•°,Phone.Content_URI,иҺ·еҸ–иҒ”зі»дәәзҡ„ж—¶еҖҷйңҖиҰҒеҺ»иҝҷдёӘURIеҺ»еҸ–ж•°жҚ®гҖӮе…¶е®һиҝҷйҮҢзҡ„Phone.Content_URIзҡ„еҖјжҳҜcontent://com.android.contacts/contactsгҖӮе®ғзҡ„е®ҡд№үеҰӮдёӢ
public static final android.net.Uri CONTENT_URI;
okпјҢжҲ‘们жӢҝеҲ°иҒ”зі»дәәд№ӢеҗҺпјҢжҲ‘们иҝӣиЎҢеҫӘзҺҜпјҢжёёж ҮдёӢ移пјҢжӢҝеҮәжүҖжңүзҡ„жңүз”өиҜқеҸ·з Ғзҡ„иҒ”зі»дәәзҡ„ж•°жҚ®гҖӮеӣ дёәжҲ‘д»¬дј е…Ҙзҡ„PHONE_PROJECTIONзҡ„йЎәеәҸжҳҜ姓еҗҚпјҢз”өиҜқеҸ·з ҒпјҢз…§зүҮIDпјҢд»ҘеҸҠдёҖдёӘContactIDгҖӮжүҖд»ҘжҲ‘们зңӢеҲ°еҸ–ж•°жҚ®зҡ„йЎәеәҸеҰӮдёӢ
phoneUserName = phoneCursor.getString(0); phoneNumber = phoneCursor.getString(1); photoId = phoneCursor.getLong(2); contactId = phoneCursor.getLong(3);
жӢҝеҲ°PhotoIDд№ӢеҗҺпјҢжҲ‘们еҲӨж–ӯжҳҜеҗҰеӨ§дәҺ0пјҢеҰӮжһңеӨ§дәҺ0пјҢжҲ‘们дјҡиҺ·еҸ–з”ЁжҲ·еӣҫеғҸгҖӮ
иҺ·еҸ–з”ЁжҲ·еӣҫеғҸзҡ„ж—¶еҖҷпјҢе…ҲйҖҡиҝҮдёӢйқўзҡ„д»Јз Ғе°ҶURIе’ҢеҸӮж•°иҝһжҺҘиө·жқҘ
ContentUris.withAppendedId( ContactsContract.Contacts.CONTENT_URI, contactId)
е…¶е®һиҝҷдёӘзұ»дјјдәҺGetж–№ејҸзҡ„APIпјҢжҜ”еҰӮContactUser/100,ж„ҸжҖқжҳҜиҺ·еҸ–зј–еҸ·дёә100зҡ„дәәзҡ„дҝЎжҒҜгҖӮ
OKпјҢURIжһ„йҖ еҘҪд№ӢеҗҺпјҢжҲ‘们иҺ·еҸ–еӣҫеғҸ
InputStream input = ContactsContract.Contacts .openContactPhotoInputStream(resolver, uri); contactPhoto = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(input);
жңҖеҗҺеҠ е…ҘList<Map<String,Object>>пјҢеҜ№ListViewиҝҗз”ЁйҖӮй…ҚеҷЁгҖӮ
class customAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private List<Map<String, Object>> dataList;
private LayoutInflater mInflater;
private Context context;
private String[] keyString;
private int[] valueViewID;
Holder holder;
public customAdapter(Context context,
List<Map<String, Object>> dataList, int resource,
String[] from, int[] to) {
this.dataList = dataList;
this.context = context;
mInflater = (LayoutInflater) this.context
.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
keyString = new String[from.length];
valueViewID = new int[to.length];
System.arraycopy(from, 0, keyString, 0, from.length);
System.arraycopy(to, 0, valueViewID, 0, to.length);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return dataList.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return dataList.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
public void removeItem(int position) {
dataList.remove(position);
this.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
if (convertView != null) {
holder = (Holder) convertView.getTag();
} else {
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.contactdetailtemplate,
null);
holder = new Holder();
holder.chkContactUser = (CheckBox) convertView
.findViewById(valueViewID[0]);
holder.imgUserPhoto = (ImageView) convertView
.findViewById(valueViewID[1]);
holder.labUserName = (TextView) convertView
.findViewById(valueViewID[2]);
holder.labPhoneNumber = (TextView) convertView
.findViewById(valueViewID[3]);
holder.btnDail = (Button) convertView
.findViewById(valueViewID[4]);
convertView.setTag(holder);
}
Map<String, Object> appInfo = dataList.get(position);
if (appInfo != null) {
String userName = appInfo.get(keyString[1]).toString();
String userPhoneNumber = appInfo.get(keyString[2]) == null ? ""
: appInfo.get(keyString[2]).toString();
Bitmap userPhoto = (Bitmap) appInfo.get(keyString[0]);
holder.labUserName.setText(userName);
holder.labPhoneNumber.setText(userPhoneNumber);
holder.imgUserPhoto.setImageBitmap(userPhoto);
holder.btnDail.setOnClickListener(new ViewButtonListener(
position, holder.chkContactUser));
}
return convertView;
}
}
class Holder {
public TextView labUserName;
public TextView labPhoneNumber;
public ImageView imgUserPhoto;
public Button btnDail;
public CheckBox chkContactUser;
}иҝҷйҮҢпјҢе…¶е®һеҫҲз®ҖеҚ•пјҢжҲ‘们е°ұжҳҜжӢҝеҲ°жҺ§д»¶пјҢ然еҗҺж №жҚ®PositionпјҢжӢҝеҲ°Listдёӯзҡ„жҹҗиЎҢж•°жҚ®пјҢ然еҗҺиөӢеҖјгҖӮ
жңҖеҗҺжҲ‘们зңӢзңӢжҢүй’®зҡ„ClickдәӢ件пјҢжҲ‘д»¬дј е…ҘдәҶPositionе’ҢжҜҸиЎҢзҡ„CheckBoxгҖӮ
class ViewButtonListener implements OnClickListener {
private int position;
Object phoneNumber;
CheckBox chkContactUser;
ViewButtonListener(int position,CheckBox chkContactUser) {
this.position = position;
this.phoneNumber = dataList.get(position).get("UserPhoneNumber");
this.chkContactUser= chkContactUser;
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
int vid = view.getId();
if (vid == R.id.btnDail&&chkContactUser.isChecked()) {
Intent dialIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CALL, Uri
.parse("tel:" + phoneNumber));
startActivity(dialIntent);
}
}
}еңЁOnClickдёӯпјҢжҲ‘们еҲӨж–ӯеҰӮжһңжҳҜжӢЁеҸ·жҢү钮并且еҲ—еӨҙзҡ„CheckBoxжҳҜеӢҫйҖүзҡ„пјҢеҲҷдјҡжӢЁеҸ·пјҢеҗҰеҲҷдёҚдјҡжӢЁеҸ·гҖӮOKпјҢжңҖеҗҺжҲ‘们еёҢжңӣеңЁжҢүеӣһйҖҖй”®зҡ„ж—¶еҖҷпјҢеј№еҮәжҳҜеҗҰйҖҖеҮәзҡ„жҸҗзӨә
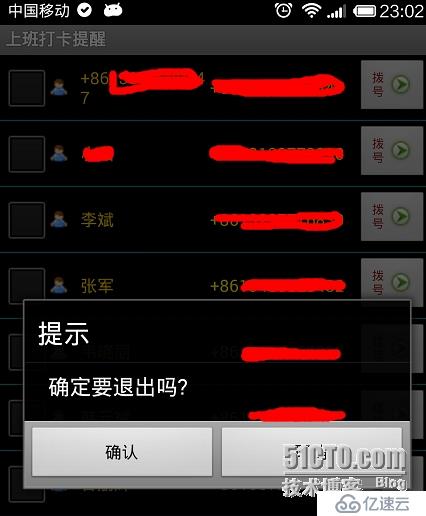
okпјҢд»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢ
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if ((keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK && event.getRepeatCount() == 0)) {
dialog();
return true;
}
return true;
}
protected void dialog() {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new Builder(punchinalarm.this);
builder.setMessage("зЎ®е®ҡиҰҒйҖҖеҮәеҗ—?");
builder.setTitle("жҸҗзӨә");
builder.setPositiveButton("зЎ®и®Ө", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
android.os.Process.killProcess(android.os.Process.myPid());
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("еҸ–ж¶Ҳ",
new android.content.DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
builder.create().show();
}жңҖеҗҺпјҢе“Ҙ们зҡ„еҚҡе®ўжҳҜиҙ§зңҹд»·е®һпјҢе°Ҹзұі3жөӢиҜ•жңәгҖӮ

е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ