本篇内容主要讲解“Jetpack Android新一代导航管理Navigation怎么使用”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“Jetpack Android新一代导航管理Navigation怎么使用”吧!
不知道小伙伴们是否注意到,用AS创建一个默认的新项目后,MainActivity已经有了很大的不同,最大的区别就是新增加了两个Fragment,同时我们注意到这两个Fragment之间跳转的时候并没有使用之前FragmentTransaction这种形式,而是使用了NavController和NavHostFragment,这就是新一代导航管理Navigation。
项目中依赖Navigation:
implementation 'androidx.navigation:navigation-fragment-ktx:2.3.5'
implementation 'androidx.navigation:navigation-ui-ktx:2.3.5'新建一个Android Resource File,类型选择Navigation即可,输入名称后我们就创建了一个导航视图。
在导航试图中,我们可以通过添加activity/fragment等标签手动添加页面,也支持在Design页面中通过界面添加,如下:
注意:这样添加后手动修改一下label。如果我们将Navigation与ToolBar连接,会在标题栏这个label。
示例中添加了两个页面,添加后代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/FirstFragment"
android:name="com.xxx.xxx.FirstFragment"
android:label="@string/first_fragment_label"
tools:layout="@layout/fragment_first">
</fragment>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/SecondFragment"
android:name="com.xxx.xxx.SecondFragment"
android:label="@string/second_fragment_label"
tools:layout="@layout/fragment_second">
</fragment>
</navigation>除了添加Fragment和Activity,Google还提供了一个占位符placeholder,添加加完代码如下:
<fragment android:id="@+id/placeholder" />用于暂时占位以便后面可以替换为Fragment和Activity
添加完页面后,我们还需要添加页面之间的导航,可以手动添加action标签,当然也可以通过拖拽来实现,如下:
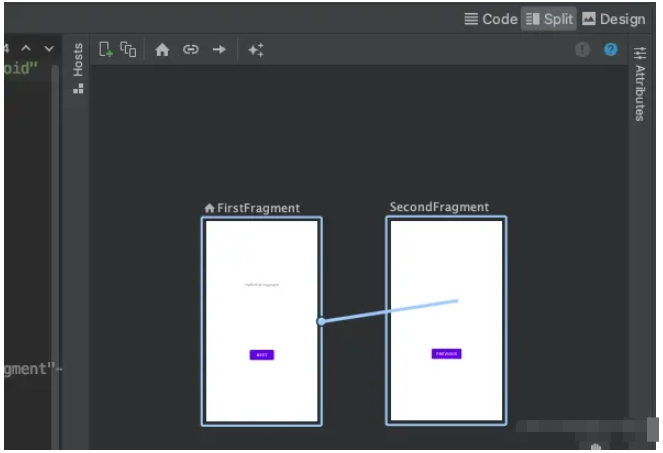
这样我们就添加了一个从FirstFragment导航到SecondFragment的动作,我们再添加一个逆向的动作,最终的代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/FirstFragment"
android:name="com.xxx.xxx.FirstFragment"
android:label="@string/first_fragment_label"
tools:layout="@layout/fragment_first">
<action
android:id="@+id/action_FirstFragment_to_SecondFragment"
app:destination="@id/SecondFragment" />
</fragment>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/SecondFragment"
android:name="com.xxx.xxx.SecondFragment"
android:label="@string/second_fragment_label"
tools:layout="@layout/fragment_second">
<action
android:id="@+id/action_SecondFragment_to_FirstFragment"
app:destination="@id/FirstFragment" />
</fragment>
</navigation>注意占位符placeholder同样支持添加导航。
这样就实现了两个页面间的导航,最后还需要为这个navigation设置id和默认页面startDestination,如下:
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/nav_graph"
app:startDestination="@id/FirstFragment">这样导航视图就创建完成了。可以看到Google力图通过可视化工具来简化开发工作,这对我们开发者来说非常有用,可以省去大量编写同质化代码的时间。
下一步我们需要向Activity中添加导航宿主,导航宿主是一个空页面,必须实现NavHost接口,我们使用Navigation提供的默认NavHost————NavHostFragment即可。如下:
<fragment
android:id="@+id/nav_host_fragment_content_main"
android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:defaultNavHost="true"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:navGraph="@navigation/nav_graph" />在Activity的视图中添加一个fragment标签,android:name设置为实现类,即NavHostFragment;app:navGraph设置为刚才新建的导航视图。
注意app:defaultNavHost="true",设置为true后表示将这个NavHostFragment设置为默认导航宿主,这样就会拦截系统的返回按钮事件。同一布局中如果有多个导航宿主(比如双窗口)则必须制定一个为默认的导航宿主。
这时候我们运行应用,就可以发现Activity中已经可以展示FirstFragment了。
我们还需要为两个fragment添加按钮,是其点击跳转到另外一个页面,代码如下:
binding.buttonFirst.setOnClickListener {
findNavController().navigate(R.id.action_FirstFragment_to_SecondFragment)
}示例中是FirstFragment中的一个按钮,点击时执行了id为action_FirstFragment_to_SecondFragment的动作,这个是我们之前在导航视图中配置好的,会导航到SecondFragment。
注意首先通过findNavController()来获取一个NavController对象,然后调用它的navigate函数即可,当然这个函数有多种重载,比如可以传递参数,如下:
public void navigate(@IdRes int resId, @Nullable Bundle args) {这里不一一列举了,大家自行查看源码即可。
可以看到使用Navigation代码精简了很多,只需要一行代码执行一个函数即可。
我们重点来看看findNavController(),它是一个扩展函数,如下:
fun Fragment.findNavController(): NavController =
NavHostFragment.findNavController(this)实际上是NavHostFragment的一个静态函数findNavController:
@NonNull
public static NavController findNavController(@NonNull Fragment fragment) {
...
View view = fragment.getView();
if (view != null) {
return Navigation.findNavController(view);
}
// For DialogFragments, look at the dialog's decor view
Dialog dialog = fragment instanceof DialogFragment
? ((DialogFragment) fragment).getDialog()
: null;
if (dialog != null && dialog.getWindow() != null) {
return Navigation.findNavController(dialog.getWindow().getDecorView());
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Fragment " + fragment
+ " does not have a NavController set");
}通过源码可以看到最终是执行了Navigation的findNavController函数,它的代码如下:
@NonNull
public static NavController findNavController(@NonNull View view) {
NavController navController = findViewNavController(view);
...
return navController;
}这里是通过findViewNavController函数来获取NavController的,它的代码如下:
@Nullable
private static NavController findViewNavController(@NonNull View view) {
while (view != null) {
NavController controller = getViewNavController(view);
if (controller != null) {
return controller;
}
ViewParent parent = view.getParent();
view = parent instanceof View ? (View) parent : null;
}
return null;
}这里可以看到通过view来获取NavController,如果没有则向上层查找(父view)直到找到或到根结点。getViewNavController代码如下:
@Nullable
private static NavController getViewNavController(@NonNull View view) {
Object tag = view.getTag(R.id.nav_controller_view_tag);
NavController controller = null;
if (tag instanceof WeakReference) {
controller = ((WeakReference<NavController>) tag).get();
} else if (tag instanceof NavController) {
controller = (NavController) tag;
}
return controller;
}看到这里获取view中key为R.id.nav_controller_view_tag的tag,这个tag就是NavController,那么这个tag又从哪来的?
其实就是上面我们提到导航宿主————NavHostFragment,在他的onViewCreated中可以看到如下代码:
@Override
public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
if (!(view instanceof ViewGroup)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("created host view " + view + " is not a ViewGroup");
}
Navigation.setViewNavController(view, mNavController);
// When added programmatically, we need to set the NavController on the parent - i.e.,
// the View that has the ID matching this NavHostFragment.
if (view.getParent() != null) {
mViewParent = (View) view.getParent();
if (mViewParent.getId() == getId()) {
Navigation.setViewNavController(mViewParent, mNavController);
}
}
}这里的mNavController是在NavHostFragment的onCreate中创建出来的,是一个NavHostController对象,它继承NavController,所以就是NavController。
可以看到onViewCreated中调用了Navigation的setViewNavController函数,它的代码如下:
public static void setViewNavController(@NonNull View view,
@Nullable NavController controller) {
view.setTag(R.id.nav_controller_view_tag, controller);
}这样就将NavController加入tag中了,通过findNavController()就可以得到这个NavController来执行导航了。
注意在onViewCreated中不仅为Fragment的View添加了tag,同时还为其父View也添加了,这样做的目的是在Activity中也可以获取到NavController,这点下面就会遇到。
Google提供了Navigation与ToolBar连接的功能,代码如下:
val navController = findNavController(R.id.nav_host_fragment_content_main)
appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph)
setupActionBarWithNavController(navController, appBarConfiguration)上面我们提到,如果Navigation与ToolBar连接,标题栏会自动显示在导航视图中设定好的label。
注意这里的findNavController是Activity的扩展函数,它最终一样会调用Navigation的对应函数,所以与Fragment的流程是一样的。而上面我们提到了,在NavHostFragment中给上层View也设置了tag,所以在这里才能获取到NavController。
除了这个,我们还可以发现当在切换页面的时候,标题栏的返回按钮也会自动显示和隐藏。当导航到第二个页面SecondFragment,返回按钮显示;当回退到首页时,返回按钮隐藏。
但是此时返回按钮点击无效,因为我们还需要重写一个函数:
override fun onSupportNavigateUp(): Boolean {
val navController = findNavController(R.id.nav_host_fragment_content_main)
return navController.navigateUp(appBarConfiguration)
|| super.onSupportNavigateUp()
}这样当点击标题栏的返回按钮时,会执行NavController的navigateUp函数,就会退回到上一页面。
到此,相信大家对“Jetpack Android新一代导航管理Navigation怎么使用”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://juejin.cn/post/7208711636496400439