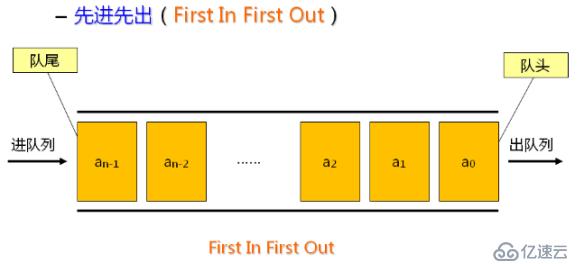
队列是一种特殊的线性表,仅能在线性表的两端进行操作。
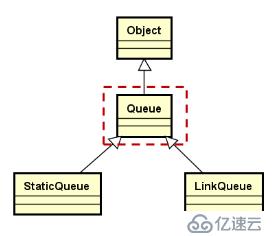
template < typename T >
class Queue
{
public:
virtual void enqueue(const T& e) = 0;
virtual void dequeue() = 0;
virtual T front() const = 0;
virtual void clear() = 0;
virtual int length() const = 0;
};顺序队列的实现: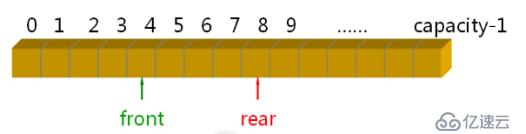
设计要点:
类模板,使用原生数组作为队列 存储空间,使用模板参数决定队列的最大容量;
template < typename T, int N >
class StaticQueue : public Queue<T>
{
protected:
T m_space[N];
int m_front;
int m_rear;
int m_length;
public:
StaticQueue()
void enqueue(const T& e)
void dequeue()
T front() const
void clear()
int length() const
int capacity() const
};注意事项:
StaticQueue实现要点:(循环计数法) 提高队列操作的效率(本质上时循环队列)
关键操作:
队满:(m_length == N) && (m_front == m_rear)
StaticQueue最终实现:
template < typename T, int N >
class StaticQueue : public Queue<T>
{
protected:
T m_space[N];
int m_front;
int m_rear;
int m_length;
public:
StaticQueue() //O(1)
{
m_front = 0;
m_rear = 0;
m_length = 0;
}
void enqueue(const T& e) //O(1)
{
if(m_length < N)
{
m_space[m_rear] = e;
m_rear = (m_rear + 1) % N;
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "no space in current staticqueue...");
}
}
void dequeue() //O(1)
{
if(m_length > 0)
{
m_front = (m_front + 1) % N;
m_length--;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "no element in current staticqueue...");
}
}
T front() const //O(1)
{
if(m_length > 0)
{
return m_space[m_front];
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "no element in current staticqueue...");
}
}
void clear() //O(1)
{
m_front = 0;
m_rear = 0;
m_length = 0;
}
int length() const //O(1)
{
return m_length;
}
int capacity() const //O(1)
{
return N;
}
bool is_empty() //O(1)
{
return (m_length == 0) && (m_front == m_rear);
}
bool is_full() //O(1)
{
return (m_length == N) && (m_front == m_rear);
}
};顺序队列的缺陷:当数据为类类型时,StaticQueue的对象在创建时,会多次调用元素类型的构造函数,影响效率。所以我们采用链式存储结构来实现队列。
设计要点:
1.类模板,继承自抽象父类Queue;
2.在内部使用链式结构实现元素的存储
3.只在链表的头部和尾部进行操作。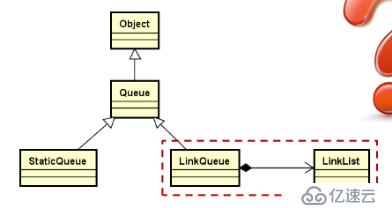
LinkQueue声明:
template <typename T>
class LinkQueue : public Queue<T>
{
protected:
LinkList<T> m_list;
public:
LinkQueue(){}
void enqueue(const T& e) //O(n)
void dequeue() //O(1)
T front() const //O(1)
void clear() //O(n)
int length() const //O(1)
};LinkQueue最终实现:
template <typename T>
class LinkQueue : public Queue<T>
{
protected:
LinkList<T> m_list;
public:
LinkQueue(){}
void enqueue(const T& e) //O(n)
{
m_list.insert(e);
}
void dequeue() //O(1)
{
if(m_list.length() > 0)
{
m_list.remove(0);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "no elemet in current LinkQueue...");
}
}
T front() const //O(1)
{
if(m_list.length() > 0)
{
return m_list.get(0);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "no elemet in current LinkQueue...");
}
}
void clear() //O(n)
{
while (m_list.length() > 0)
{
m_list.remove(0);
}
}
int length() const //O(1)
{
return m_list.length();
}
};LinkQueue中,入队操作由于只能操作队列的尾部(链表的最后位置),要进行遍历操作,所以时间复杂度为O(n),可以使用双向循环链表代替单链表来解决这个问题。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。