1、类型转换
static_cast<>():静态类型转换,编译时C++编译器会做类型检查,在C语言中,隐式类型转换的地方,均可以使用static_cast<>()进行类型转换;
reinterpret_cast<>():强制类型转换;编译器重新解释;
dynamic_cast<Cat *>(base):父类对象===>子类对象,向下转型,一般用在继承中;
const_cast<>():const char *---> char *,把常量属性去掉;
(1)、代码如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal{
public:
virtual void cry() = 0;
};
class Dog : public Animal{
public:
virtual void cry(){
cout<<"汪王"<<endl;
}
void doHome(){
cout<<"看家"<<endl;
}
private:
};
class Cat : public Animal{
public:
virtual void cry(){
cout<<"喵喵"<<endl;
}
void doThing(){
cout<<"抓老鼠"<<endl;
}
private:
};
void playObj(Animal *base){
base->cry(); //1、有继承 2、有虚函数的重写 3、有父类指针指向子类对象; ===>发生多态
//dynamic_cast能识别子类对象,运行时类型识别;
Dog *pDog = dynamic_cast<Dog *>(base); //是自己类型的,将转换成功,否则返回为NULL;
if(pDog){
pDog->doHome(); //让狗做自己特有的工作;
}
Cat *pCat = dynamic_cast<Cat *>(base);//父类对象===>子类对象,向下转型;
if(pCat){
pCat->doThing(); //让猫做自己特有的工作;
}
}
int main(void){
Dog d1;
Cat c1;
playObj(&d1);
playObj(&c1);
//Animal *base = NULL;
//base = static_cast<Animal *>(&d1);
return 0;
}
/*
int main(void){
double pi = 3.14;
int num2 = static_cast<int>(pi); //静态类型转换,编译时C++编译器会做类型检查,在C语言中,隐式类型转换
的地方,均可以使用static_cast<>()进行类型转换;
char *p1 = "abcdef";
int *p2 = NULL;
//p2 = static_cast<int*>(p1); //使用static_cast,编译器编译时,会做类型检查,若有错误,提示错误;
p2 = reinterpret_cast<int *>(p1);// 强制类型转换;编译器重新解释
cout<<p1<<endl;
cout<<p2<<endl; //%d
return 0;
}
*/运行结果:
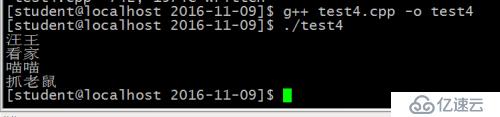
(2)、针对const_cast<char *>(p)的类型转换代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void printBuf(const char *p){
//p[1] = '1';
char *p1 = NULL;
p1 = const_cast<char *>(p);//const char *---> char *,把常量属性去掉;
p1[0] = 'Z';
cout<<p<<endl;
}
int main(void){
const char buf[] = "abcdefg";
//程序员要确保p所指向的空间确实能修改,如果不能修改将会带来灾难性的后果;
//const char *buf = "abcdef";//会发生断错误;因为其所指向的空间本身不可修改
printBuf(buf);
return 0;
}运行结果:
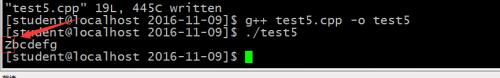
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。