1、图
(1)、图是一种非线性结构;主要由顶点和边构成;
(2)、<> 代表有向图,( )代表无向图
(3)、无向图有N个顶点时,最多有N*(N-1)/2条边;有向图最多有N*(N-1)条边;
(4)、权:边上具有相关的数,带权图叫做网络;
(5)、邻接顶点: 与其接触边上的顶点;
(6)、度:与顶点V关联的边数;有向图中度 = 出度 + 入度;
(7)、简单路径:路径上各顶点互不重复,
(8)、回路/环:路径上第一个顶点与最后一个顶点重合;
(9)、连通图/强连通图:各顶点之间有边联系,有向图,双路径存在叫做强连通图;
(10)、生成树:是无向连通图的极小连通子图,若有N个顶点,则生成树由N-1条边构成!
2、图的邻接矩阵
(1)、邻接矩阵模型如下:
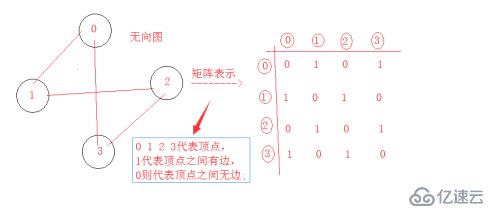
就是将图的多对多的非线性结构用矩阵的方式表示;
我们必须知道:
(1)、会由矩阵来恢复图;
(2)、第一个邻接顶点:从列开始处,第一个边
(3)、下一个邻接顶点:给2个参数,第一个参数表示是谁的下一个邻接顶点,第二个表示从当前顶点开始其后的第一条边;
(4)、其顶点存放在数组空间中;
(5)、顶点之间的关系通过矩阵来表示边;
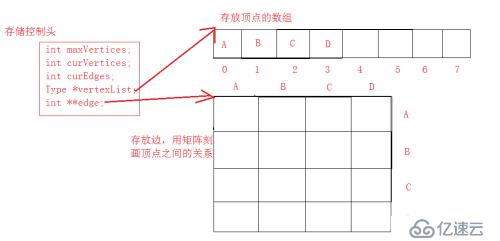
存储结构:
int maxVertices; //最大顶点数 int curVertices; //当前顶点数 int curEdges; //当前边数 //用的是C++的继承 Type *vertexList; //存放顶点的数组 int **edge; //存放顶点关系的矩阵用边表示
存储模型如下:
3、图的实现方法
均用C++实现;并且父类给了接口,子类继承实现即可;方便对不同的存储结构的编写;
核心方法,删除顶点:
(1)、第一种方法实现:
bool removeVertex(const Type &v){
int i = getVertexIndex(v);
if(i == -1){
return false;
}
for(int k = i; k < curVertices-1; ++k){
vertexList[k] = vertexList[k+1];
}
int edgeCount = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; ++j){
if(edge[i][j] != 0)
edgeCount++;
}
//删除行
for(int k = i; k < curVertices-1; ++k)
{
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; ++j)
{
edge[k][j] = edge[k+1][j];
}
}
//删除列
for(int k = i; k < curVertices-1; ++k)
{
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; ++j)
{
edge[j][k] = edge[j][k+1];
}
}
curVertices--;
curEdges -= edgeCount;
return true;
} 以上存在数组的大量移动,效率太低;
(2)、第二种方法的实现:
bool removeVertex(const Type &v){
int i = getVertexIndex(v);
if(i == -1){
return false;
}
vertexList[i] = vertexList[curVertices-1];
int edgeCount = 0;
for(int k = 0; k < curVertices; k++){
if(edge[i][k] != 0){ //统计删除该行的边数
edgeCount++;
}
}
//删除行
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; j++){
edge[i][j] = edge[curVertices-1][j];
}
//删除列
for(j = 0; j < curVertices; j++){
edge[j][i] = edge[j][curVertices-1];
}
curVertices--;
curEdges -= edgeCount;
return true;
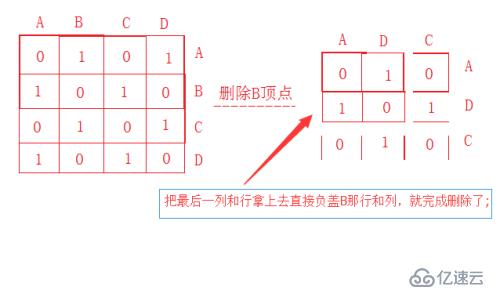
}第二种方法甚好,将要删除的顶点(连边一起删除),用最后一个元素(行/列)去覆盖删除的那个即可,之间的关系不变,但是就避免了大量移动,一次覆盖就好,效率极大!!!
模型如下:
4、图的方法实现完整代码、测试代码、测试结果
(1)、完整代码(用的是继承,方便写其它的存储结构代码):
#ifndef _GRAPH_H_
#define _GRAPH_H_
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE 10
template<typename Type>
class Graph{
public:
bool isEmpty()const{
return curVertices == 0;
}
bool isFull()const{
if(curVertices >= maxVertices || curEdges >= curVertices*(curVertices-1)/2)
return true; //图满有2种情况:(1)、当前顶点数超过了最大顶点数,存放顶点的空间已满
return false; //(2)、当前顶点数并没有满,但是当前顶点所能达到的边数已满
}
int getCurVertex()const{
return curVertices;
}
int getCurEdge()const{
return curEdges;
}
public:
virtual bool insertVertex(const Type &v) = 0; //插入顶点
virtual bool insertEdge(const Type &v1, const Type &v2) = 0; //插入边
virtual bool removeVertex(const Type &v) = 0; //删除顶点
virtual bool removeEdge(const Type &v1, const Type &v2) = 0; //删除边
virtual int getFirstNeighbor(const Type &v) = 0; //得到第一个相邻顶点
virtual int getNextNeighbor(const Type &v, const Type &w) = 0; //得到下一个相邻顶点
public:
virtual int getVertexIndex(const Type &v)const = 0; //得到顶点下标
virtual void showGraph()const = 0; //显示图
protected:
int maxVertices; //最大顶点数
int curVertices; //当前顶点数
int curEdges; //当前边数
};
template<typename Type>
class GraphMtx : public Graph<Type>{ //邻接矩阵继承父类矩阵
#define maxVertices Graph<Type>::maxVertices //因为是模板,所以用父类的数据或方法都得加上作用域限定符
#define curVertices Graph<Type>::curVertices
#define curEdges Graph<Type>::curEdges
public:
GraphMtx(int vertexSize = VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE){ //初始化邻接矩阵
maxVertices = vertexSize > VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE ? vertexSize : VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE;
vertexList = new Type[maxVertices]; //申请顶点空间
for(int i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //都初始化为0
vertexList[i] = 0;
}
edge = new int*[maxVertices]; //申请边的行
for(i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //申请列空间
edge[i] = new int[maxVertices];
}
for(i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //赋初值为0
for(int j = 0; j < maxVertices; j++){
edge[i][j] = 0;
}
}
curVertices = curEdges = 0; //当前顶点和当前边数
}
GraphMtx(Type (*mt)[4], int sz){ //通过已有矩阵的初始化
int e = 0; //统计边数
maxVertices = sz > VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE ? sz : VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE;
vertexList = new Type[maxVertices]; //申请顶点空间
for(int i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //都初始化为0
vertexList[i] = 0;
}
edge = new int*[maxVertices]; //申请边的行
for(i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //申请列空间
edge[i] = new Type[maxVertices];
}
for(i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //赋初值为矩阵当中的值
for(int j = 0; j < maxVertices; j++){
edge[i][j] = mt[i][j];
if(edge[i][j] != 0){
e++; //统计列的边数
}
}
}
curVertices = sz;
curEdges = e/2;
}
~GraphMtx(){}
public:
bool insertVertex(const Type &v){
if(curVertices >= maxVertices){
return false;
}
vertexList[curVertices++] = v;
return true;
}
bool insertEdge(const Type &v1, const Type &v2){
int maxEdges = curVertices*(curVertices-1)/2;
if(curEdges >= maxEdges){
return false;
}
int v = getVertexIndex(v1);
int w = getVertexIndex(v2);
if(v==-1 || w==-1){
cout<<"edge no exit"<<endl; //要插入的顶点不存在,无法插入
return false;
}
if(edge[v][w] != 0){ //当前边已经存在,不能进行插入
return false;
}
edge[v][w] = edge[w][v] = 1; //因为是无向图,对称的,存在边赋为1;
return true;
} //删除顶点的高效方法
bool removeVertex(const Type &v){
int i = getVertexIndex(v);
if(i == -1){
return false;
}
vertexList[i] = vertexList[curVertices-1];
int edgeCount = 0;
for(int k = 0; k < curVertices; k++){
if(edge[i][k] != 0){ //统计删除该行的边数
edgeCount++;
}
}
//删除行
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; j++){
edge[i][j] = edge[curVertices-1][j];
}
//删除列
for(j = 0; j < curVertices; j++){
edge[j][i] = edge[j][curVertices-1];
}
curVertices--;
curEdges -= edgeCount;
return true;
}
/* //删除顶点用的是数组一个一个移动的方法,效率太低。
bool removeVertex(const Type &v){
int i = getVertexIndex(v);
if(i == -1){
return false;
}
for(int k = i; k < curVertices-1; ++k){
vertexList[k] = vertexList[k+1];
}
int edgeCount = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; ++j){
if(edge[i][j] != 0)
edgeCount++;
}
for(int k = i; k < curVertices-1; ++k)
{
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; ++j)
{
edge[k][j] = edge[k+1][j];
}
}
for(int k = i; k < curVertices-1; ++k)
{
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; ++j)
{
edge[j][k] = edge[j][k+1];
}
}
curVertices--;
curEdges -= edgeCount;
return true;
}
*/
bool removeEdge(const Type &v1, const Type &v2){
int v = getVertexIndex(v1);
int w = getVertexIndex(v2);
if(v==-1 || w==-1){ //判断要删除的边是否在当前顶点内
return false; //顶点不存在
}
if(edge[v][w] == 0){ //这个边根本不存在,没有必要删
return false;
}
edge[v][w] = edge[w][v] = 0; //删除这个边赋值为0,代表不存在;
curEdges--;
return true;
}
int getFirstNeighbor(const Type &v){
int i = getVertexIndex(v);
if(i == -1){
return -1;
}
for(int col = 0; col < curVertices; col++){
if(edge[i][col] != 0){
return col;
}
}
return -1;
}
int getNextNeighbor(const Type &v, const Type &w){
int i = getVertexIndex(v);
int j = getVertexIndex(w);
if(i==-1 || j==-1){
return -1;
}
for(int col = j+1; col < curVertices; col++){
if(edge[i][col] != 0){
return col;
}
}
return -1;
}
public:
void showGraph()const{
if(curVertices == 0){
cout<<"Nul Graph"<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < curVertices; i++){
cout<<vertexList[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
for(i = 0; i < curVertices; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; j++){
cout<<edge[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<vertexList[i]<<endl;
}
}
int getVertexIndex(const Type &v)const{
for(int i = 0; i < curVertices; i++){
if(vertexList[i] == v){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
private:
Type *vertexList; //存放顶点的数组
int **edge; //存放顶点关系的矩阵用边表示
};
#endif(2)、测试代码:
#include"Graph.h"
#define VERTEX_SIZE 4
int main(void){
GraphMtx<char> gm;
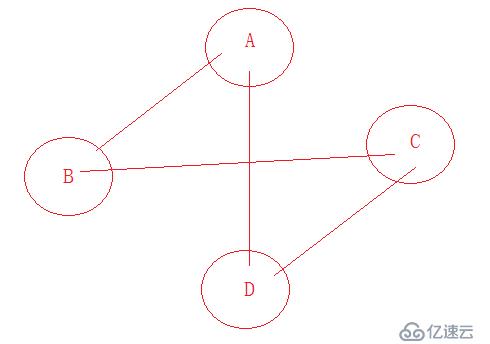
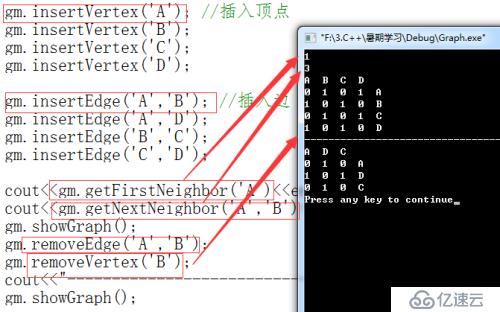
gm.insertVertex('A'); //插入顶点
gm.insertVertex('B');
gm.insertVertex('C');
gm.insertVertex('D');
gm.insertEdge('A','B'); //插入边
gm.insertEdge('A','D');
gm.insertEdge('B','C');
gm.insertEdge('C','D');
cout<<gm.getFirstNeighbor('A')<<endl; //B
cout<<gm.getNextNeighbor('A','B')<<endl;//D
gm.showGraph();
gm.removeEdge('A','B');
gm.removeVertex('B');
cout<<"-----------------------------------------------------------------"<<endl;
gm.showGraph();
/* 用矩阵关系直接初始化图,没啥意思
int mtx[VERTEX_SIZE][VERTEX_SIZE] = {
{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0},
};
GraphMtx<int> gm(mtx, VERTEX_SIZE);
gm.showGraph();
*/
return 0;
}(3)测试结果:
测试的图:
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。