1、树、森林为什么向二叉树转换?
因为在实际的处理问题中,大多数情况都是一对多,就向树、森林这样的数据结构!
而对于二叉树我们已经很熟悉了,所以转向我们所熟悉的结构,好处理。
2、孩子兄弟树的方法
把握左孩子右兄弟的原则:
(1)、树与二叉树的转换:
i>以树的根结点为二叉树的根节点;
ii>左孩子指针指向该根节点的第一个子结点;
iii>右孩子指针指向"兄弟结点"
(2)、二叉树表示森林:
i>二叉树的根结点是森林中第一棵树的根结点
ii>根结点的右孩子为森林中其它树的根结点
3、图形表示法

4、树的创建----->化二叉树
应具有的存储结构:树结点和树
template<typename Type>
class TreeNode{
friend class Tree<Type>;
public:
TreeNode() : data(Type()), firstChild(NULL), nextSibling(NULL){}
TreeNode(Type d, TreeNode *first = NULL, TreeNode *next = NULL) :
data(d), firstChild(first), nextSibling(next){}
~TreeNode(){}
private:
Type data;
TreeNode *firstChild; //第一个孩子
TreeNode *nextSibling; //下一个兄弟
};
template<typename Type>
class Tree{
public:
Tree() : root(NULL){}
Tree(Type ref) : root(NULL), refval(ref){}
~Tree(){}
private:
TreeNode<Type> *root;
Type refval; //'#'
};5、应该实现的方法:
public: void createTree(const char *str); //创建树 int size()const; //求树的结点个数 int height()const; //求树高 TreeNode<Type>* root_1()const; //返回根结点 bool isEmpty()const; //判树空 TreeNode<Type> *firstChild()const; //返回第一个孩子结点 TreeNode<Type> *nextSibling()const; //返回第一个兄弟结点 TreeNode<Type>* find(Type key)const; //查找当前结点 TreeNode<Type>* parent(TreeNode<Type> *cur)const; //查找当前结点的父
(1)、创建树(化二叉树)----->在我们的思想中就是二叉树的创建。
(2)、求结点个数--->根二叉树的一样
(3)、查找当前结点----->跟二叉树一样
(4)、求树高(森林的也可以求出):
int height(TreeNode<Type> *t)const{
TreeNode<Type> *p;
int m;
int max = 0;
if(t == NULL){
return 0; //空树,高0
}else if(t->firstChild == NULL){
return 1; //只有根,为1
}else{
p = t->firstChild; //先为第一个孩子
while(p != NULL){
m = height(p); //求高
if(max < m){
max = m; //遍历所有的分支,每次求最高的
}
p = p->nextSibling; //每次往右分支走,但还是求的左边树高;
}
return max+1; //返回时加上根的高度
}
}(5)、查找当前结点的父(自己画图多多跟踪)
TreeNode<Type>* parent(TreeNode<Type> *t, TreeNode<Type> *cur)const{
if(t == NULL || cur == NULL || t == cur){ //父为NULL
return NULL;
}
TreeNode<Type> *p = t->firstChild;
while(p != NULL && p != cur){
TreeNode<Type> *tmp = parent(p, cur); //递归查找其父结点,将找的结果给了tmp;
if(tmp != NULL){
return tmp;
}
p = p->nextSibling; //在往右找
}
if(p != NULL && p == cur){
return t; //找到了
}else{
return NULL;
}
}6、全部代码、测试代码,测试结果
(1)、因为少,所以都在类内实现:
#ifndef _TREE_H_
#define _TREE_H_
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename Type>
class Tree;
template<typename Type>
class TreeNode{
friend class Tree<Type>;
public:
TreeNode() : data(Type()), firstChild(NULL), nextSibling(NULL){}
TreeNode(Type d, TreeNode *first = NULL, TreeNode *next = NULL) :
data(d), firstChild(first), nextSibling(next){}
~TreeNode(){}
private:
Type data;
TreeNode *firstChild;
TreeNode *nextSibling;
};
template<typename Type>
class Tree{
public:
Tree() : root(NULL){}
Tree(Type ref) : root(NULL), refval(ref){}
~Tree(){}
public:
void createTree(const char *str){
createTree(root, str);
}
int size()const{
return size(root);
}
int height()const{
return height(root);
}
TreeNode<Type>* root_1()const{
return root;
}
bool isEmpty()const{
return root == NULL;
}
TreeNode<Type> *firstChild()const{
if(root != NULL){
return root->firstChild;
}
return NULL;
}
TreeNode<Type> *nextSibling()const{
if(root != NULL){
return root->nextSibling;
}
return NULL;
}
TreeNode<Type>* find(const Type &key)const{
return find(root, key);
}
TreeNode<Type>* parent(TreeNode<Type> *cur)const{
return parent(root, cur);
}
protected:
void createTree(TreeNode<Type> *&t, const char *&str){
if(*str == refval){
t = NULL;
}else{
t = new TreeNode<Type>(*str);
createTree(t->firstChild, ++str);
createTree(t->nextSibling, ++str);
}
}
int size(TreeNode<Type> *t)const{
if(t == NULL){
return 0;
}
return size(t->firstChild) + size(t->nextSibling) + 1;
}
TreeNode<Type>* parent(TreeNode<Type> *t, TreeNode<Type> *cur)const{
if(t == NULL || cur == NULL || t == cur){
return NULL;
}
TreeNode<Type> *p = t->firstChild;
while(p != NULL && p != cur){
TreeNode<Type> *tmp = parent(p, cur);
if(tmp != NULL){
return tmp;
}
p = p->nextSibling;
}
if(p != NULL && p == cur){
return t;
}else{
return NULL;
}
}
TreeNode<Type>* find(TreeNode<Type> *t, const Type &key)const{
if(t == NULL){
return NULL;
}
if(t->data == key){
return t;
}
TreeNode<Type>* p = find(t->firstChild, key);
if(p != NULL){
return p;
}
return find(t->nextSibling, key);
}
int height(TreeNode<Type> *t)const{
TreeNode<Type> *p;
int m;
int max = 0;
if(t == NULL){
return 0;
}else if(t->firstChild == NULL){
return 1;
}else{
p = t->firstChild;
while(p != NULL){
m = height(p);
if(max < m){
max = m;
}
p = p->nextSibling;
}
return max+1;
}
}
private:
TreeNode<Type> *root;
Type refval; //'#'
};
#endif(2)、测试代码:

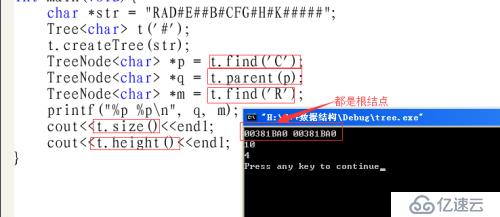
#include"tree.h"
int main(void){
char *str = "RAD#E##B#CFG#H#K#####"; //先根序的二叉树序列;
Tree<char> t('#');
t.createTree(str);
TreeNode<char> *p = t.find('C');
TreeNode<char> *q = t.parent(p);
TreeNode<char> *m = t.find('R');
printf("%p %p\n", q, m);
cout<<t.size()<<endl;
cout<<t.height()<<endl;
return 0;
}(3)、测试结果
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。