红黑树:首先是一棵二叉搜索树,它在每个节点上增加了一个存储位来表示节点的颜色,可以是Red或Black。通过对任何一条从根到叶子简单路径上的颜色来约束,红黑树保证最长路径不超过最短路径的两倍,因而近似于平衡。
红黑树满足的性质:
根节点是黑色的
如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个子节点是黑色的(没有连续的红节点)
每条路径的黑色节点的数量相等
红黑树保证最长路径不超过最短路径的两倍,如下图所示
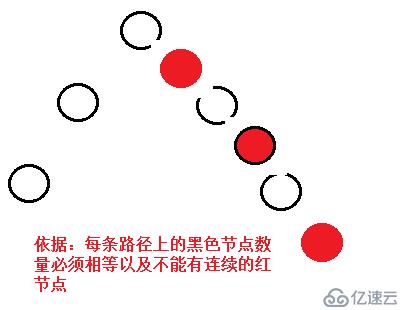
插入节点时的三种情况
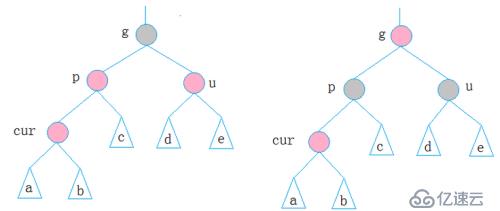
cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u存在且为红
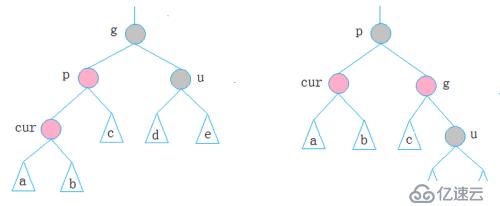
cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u为黑,p为g的左孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则进行右单旋转;相反,p为g的右孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则进行左单旋转
p、g变色--p变黑,g变红
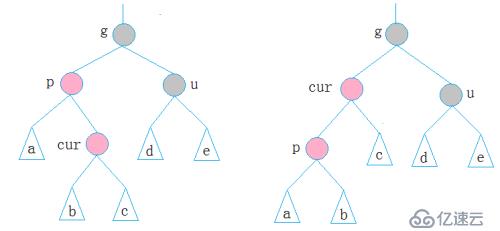
cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u为黑,p为g的左孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则针对p做左单旋转;相反,p为g的右孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则针对p做右单旋转
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
enum Color
{
RED,
BALCK
};
template<class K,class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
K _key;
V _value;
Color _col;
RBTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value)
:_left(NULL)
, _right(NULL)
, _parent(NULL)
, _key(key)
, _value(value)
, _col(RED)
{}
};
template<class K,class V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
RBTree()
:_root(NULL)
{}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_root == NULL)
return NULL;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key == key)
return cur;
else if (cur->_key < key)
cur = cur->_right;
else
cur = cur->_left;
}
return NULL;
}
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (_root == NULL)
{
_root = new Node(key, value);
_root->_col = BALCK;
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = NULL;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key>key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
cout << "该节点已存在" << endl;
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key, value);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//调整节点颜色
while (cur != _root&&parent->_col == RED)
{//规定根节点必须为黑色,若parent的颜色为红色,则它一定不为根节点,它的父节点也一定存在
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;//不用判空
Node* uncle = NULL;
if (parent == ppNode->_left)
{//parent为它的父节点的左孩子,则叔节点若存在,肯定在右边
uncle = ppNode->_right;
if (uncle&&uncle->_col == RED)
{//1.cur为红,parent为红,ppNode为黑,u存在且为红
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BALCK;
ppNode->_col = RED;
cur = ppNode;
ppNode = cur->_parent;
}
else
{//2.cur为红,parent为红,uncle不存在或者为黑
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(parent);
swap(cur, parent);
}
parent->_col = BALCK;
ppNode->_col = RED;
RotateR(ppNode);
}
}
else
{//另一边
uncle = ppNode->_left;
if (uncle&&uncle->_col == RED)
{//1.cur为红,parent为红,ppNode为黑,u存在且为红
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BALCK;
ppNode->_col = RED;
cur = ppNode;
ppNode = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(parent);
swap(cur, parent);
}
parent->_col = BALCK;
ppNode->_col = RED;
RotateL(ppNode);
}
}
}
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
{
subLR->_parent = parent;
}
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
if (parent == _root || ppNode == NULL)//若要调整的节点为根节点
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = NULL;
}
else
{
if (parent == ppNode->_left)
{
ppNode->_left = subL;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = ppNode;
}
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
{
subRL->_parent = parent;
}
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
if (parent == _root || ppNode == NULL)//若要调整的节点为根节点
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = NULL;
}
else
{
if (parent == ppNode->_left)
{
ppNode->_left = subR;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = ppNode;
}
}
bool IsBalance()
{
int BlackNodeCount = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BALCK)
{
BlackNodeCount++;
}
cur = cur->_left;
}
int count = 0;
return _IsBalance(_root, BlackNodeCount, count);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
~RBTree()
{}
protected:
bool _IsBalance(Node* root, const int BlackNodeCount, int count)
{
if (root == NULL)
return false;
if (root->_parent)
{
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED)
{
cout << "不能有两个连续的红节点" << endl;
return false;
}
}
if (root->_col == BALCK)
++count;
if (root->_left == NULL&&root->_right == NULL&&count != BlackNodeCount)
{
cout << "该条路径上黑色节点数目与其它不相等" << endl;
return false;
}
return _IsBalance(root->_left, BlackNodeCount,count) &&
_IsBalance(root->_right, BlackNodeCount,count);
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
protected:
Node* _root;
};
void Test()
{
RBTree<int,int> bt;
int arr[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); ++i)
{
bt.Insert(arr[i], i);
}
bt.IsBalance();
bt.InOrder();
cout << bt.Find(6) << endl;;
cout<<bt.Find(9) << endl;
}红黑树与AVL树的异同:
红黑树和AVL树都是高效的平衡二叉树,增删查改的时间复杂度都是O(lg(N))
红黑树的不追求完全平衡,保证最长路径不超过最短路径的2倍,相对而言,降低了旋转的要求,所以性能跟AVL树差不多,但是红黑树实现更简单,所以实际运用中红黑树更多。
红黑树的应用:
STL库中的map、set
多路复用epoll模式在linux内核的实现
JAVA的TreeMap实现
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。