B树属于多叉树,也称多路平衡树。有些地方也将B树称为'B-树',这里‘-’不表示减号。
■B树的主要性质:
(1)根节点至少有两个孩子。
(2)每个非根节点为[[M/2], M]个孩子,这里[M/2]表示向上取整。
(3)每个非根节点都有[[M/2], M-1]个关键字,并且以升序排列。
(4)K[i]和k[i+1]之间的孩子节点的值介于k[i]与k[i+1]之间。(5)所有叶子节点都在同一层。

如果想给B树中,插入一个关键字,并且关键字的数目超过,且就需要对树进行调整。那就需要寻找关键字的中位数,那怎样快速的寻找关键字呢?
▲思路一:
将所有的关键字进行排序,然后将中位数寻找出来。
▲思路二:
利用快速排序的思想,选一个key值,如果左边个数等于右边个数,则中位数找到,如果没有,就在个数多的一边找出中间位置的关键字作为key值,直到key的左 = 右,则找到关键字,这样的效率更高。
■下面是插入关键字示例:
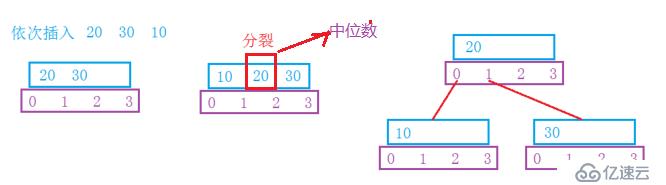
■下面是具体的实现代码:
#pragma once
//实现B树(实际就是多叉树)
/*
性质:(1)根节点至少要2个节点
(2)每个非根节点为[(M/2), M]个孩子
(3)满足左孩子值小于根节点,右孩子值大于根节点
(4)并且每个非根节点有[(M/2)-1, M-1]个关键字,并且以升序排列
(5)key[i]和key[i+1]之间的孩子节点值介于key[i]和key[i+1]之间
(6)所有节点都在同一层
*/
//实现k形式的结构
//如果要实现K,V结构,就需要创建一个结构体,包括K,V
template <class K, int M = 3> //实现M为缺省的,值最好取计数,能够更加方便的求取中位数
struct BTreeNode
{
K _keys[M]; //关键字的至多个数,多预留一个位置是可以更加方便的求取中位数
BTreeNode<K, M>* _subs[M + 1]; //孩子节点的最大数目
BTreeNode<K, M>* _parent; //指向父亲节点
size_t _size; //数组中存在的有效关键字的个数
BTreeNode() //构造B树节点
:_parent(NULL)
, _size(0)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= M; ++i)
{
_subs[i] = NULL;
}
}
};
template <class K, class V> //需要返回两个参数,使用结构体
struct Pair
{
K _first;
V _second;
Pair(const K& key = K(), const V& value = V()) //缺省参数,会调用默认构造函数
:_first(key)
, _second(value)
{ }
};
template <class K, int M = 3>
class BTree
{
typedef BTreeNode<K, M> Node;
public:
BTree() //无参构造
:_root(NULL)
{}
Pair<Node*, int> Find(const K& key) //查找
{
Node* parent = NULL;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
int index = 0;
while (index < cur->_size) //在一个节点中找相同的关键字
{
if (key == cur->_keys[index])
{
return Pair<Node*, int>(cur, index);
}
else if (key < cur->_keys[index])
{
break;
}
else
{
index++;
}
}
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_subs[index];
}
return Pair<Node*, int>(parent, -1);
}
bool Insert(const K& key) //插入节点
{
//没有节点
if (_root == NULL)
{
_root = new Node;
_root->_keys[0] = key;
_root->_size++;
return true;
}
//判断返回值
Pair<Node*, int> cur = Find(key);
if (cur._second != -1)
{
return false;
}
//在节点cur中插入key和sub
Node* str = cur._first;
K InsertKey = key;
Node* sub = NULL;
while (1)
{
_InsertKey(str, InsertKey, sub);
if (str->_size < M) //插入后,节点中的数据个数没有超过规定的
{
return true;
}
//插入数据后,节点的数据个数大于规定的数据个数,需要将节点进行分裂
int mid = (str->_size - 1) / 2;
int index = 0;
Node* tmp = new Node;
//先拷贝key
for (int i = mid + 1; i < str->_size; i++)
{
tmp->_keys[index++] = str->_keys[i];
tmp->_size++;
}
//后拷贝sub
for (int i = mid + 1; i < str->_size; i++)
{
tmp->_subs[index + 1] = str->_subs[i];
if (str->_subs[i])
{
str->_subs[i]->_parent = tmp;
}
}
str->_size = (str->_size - 1) / 2; //更改str的大小
if (str->_parent == NULL)
{
_root = new Node;
_root->_keys[0] = tmp->_keys[mid];
_root->_subs[0] = str;
_root->_subs[1] = tmp;
_root->_size = 1;
str->_parent = _root;
tmp->_parent = _root;
}
else
{
InsertKey = str->_keys[mid];
sub = tmp;
str = str->_parent;
}
}
return true;
}
void _InsertKey(Node* cur, const K& key, Node* sub) //插入key值
{
int index = cur->_size - 1;
while (index >= 0 && cur->_keys[index] > key) //将后面的数据向后移一位
{
cur->_keys[index + 1] = cur->_keys[index];
cur->_subs[index + 2] = cur->_subs[index + 1];
--index;
}
cur->_keys[index + 1] = key; //插入数据及其子节点
cur->_subs[index + 2] = sub;
if (sub)
sub->_parent = cur;
cur->_size++;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < root->_size; i++)
{
cout << root->_keys[i] << " ";
_InOrder(root->_subs[i]);
}
}
protected:
Node* _root;
};
void Test()
{
int a[] = { 53, 75, 139, 49, 145, 36, 101 };
BTree<int, 1023> t;
for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
{
t.Insert(a[i]);
}
t.InOrder();
}亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。