一.有关于线程的定义
线程是进程执行的一个分支,运行在进程的内部,是调度的一个基本单元。线程不像进程强调独占,它更多强调的是共享。一个进程可以有多个控制流程即有多个线程,进程是承担和分配系统资源的基本实体。
举个例子:
进程好比是一个大家庭,而线程就相当于是家里的每一个成员,每个成员各司其职,共同让这个大家庭变得更好。这个大家庭的资源,每个成员都可以共享,但这并不是绝对的。因为每个成员都有自己私有的空间或秘密等。所以线程有和进程共同的东西,也有自己私有的。
线程和进程共同的:
1.文件描述符表:描述当前进程所打开的所有文件;
2.当前工作目录;
3.用户id;
4.信号处理方式
线程私有的:(2和3 是重点)
1.线程的id;
2.硬件上下文,包括各寄存器的值,栈指针和程序计数器;
3.栈空间(线程自己的);
4.errno变量;
5.信号屏蔽字;//处理需要处理的,屏蔽不需处理的
6.调度优先级;
二.线程的控制
1.线程的创建
线程的创建是由POSIX 标准定义的,称为POSIX thread 或pthread。在编译的时候要加上_lpthread选项。
线程的创建函数:
pthread_create(pthread _t thread,const pthread_attr _t *attr,void*(*start_routine)(void*),void *arg);//arg 是给第三个传的参数
2.线程的终止
线程在创建退出后,主线程必须进行等待拿到其退出状态。函数原型为:
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread,void ** retval)
这个函数是以阻塞方式进行的。成功返回0,失败返回错误码。
第一个终止方式:
在线程内部直接return 或 用函数 pthread_exit(void *retval);
第二个终止方式:
在线程内部使用pthread _cancel(pthread_t thread);
thread 可以用函数pthread_t pthread_self(void)获得当前线程自己的id。
第三个终止方式:
在主函数内部调用函数 pthread _cancel(pthread_t thread);
三.线程代码
1.只有一个子线程
//thread.c
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<pthread.h>
3
4 void * thread_run(void *arg)
5 {
6
7 while(1)
9 {
10 printf("this is thread\n");
11 sleep(1);
12 }
15 }
16 int main()
17 {
18 pthread_t tid;
19 int ret=pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_run,NULL);
21 while(1)
22 {
23 printf("this is main thread\n");
24 sleep(2);
25 }
26 return 0;
27 }运行结果:
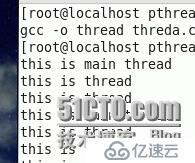
结果分析:
一直在运行着,没有终止。想要终止,调用终止函数。如下:
第一种终止方式:return 或者 pthread_exit()
//thread.c
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<pthread.h>
3
4 void * thread_run(void *arg)
5 {
6 int count=5;
7 while(count-->0) 8 {
9
10 printf("this is thread\n");
11 sleep(1);
12 }
13 //return (void*)1;
14 pthread_exit((void*)1);
15 }
16 int main()
17 {
18 pthread_t tid;
19 int ret=pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_run,NULL);
20 int count=10;
21 while(count-->0)
22 {
23 printf("this is main thread\n");
24 sleep(2);
25 }
26 //pthread_cancel(tid);
27 void *status=0;
28 int retu=pthread_join(tid,&status);
29 if(retu==0)
30 {
31 printf("pthread_join: code:%d\n",(int)status);
32
33 }
34 return 0;
35 }运行结果:

分析:
当在子线程中调用return 或者使用pthread_exit()函数终止子线程。主线程依然在跑。
第二种终止方式:pthread_cancel(pthread_self());
//thread.c
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<pthread.h>
3
4 void * thread_run(void *arg)
5 {
6 int count=5;
7 while(count-->0) 8 {
9
10 printf("this is thread\n");
11 sleep(1);
12 }
13
14 pthread_cancel(pthread_self());
15 }
16 int main()
17 {
18 pthread_t tid;
19 int ret=pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_run,NULL);
20 int count=10;
21 while(count-->0)
22 {
23 printf("this is main thread\n");
24 sleep(2);
25 }
26
27 void *status=0;
28 int retu=pthread_join(tid,&status);
29 if(retu==0)
30 {
31 printf("pthread_join: code:%d\n",(int)status);
32
33 }
34 return 0;
35 }实验结果:

分析:
在子线程中调用pthread_cancel()终止自己,不过要通过pthread_self()来获取自己的id。主线程还在跑,并且拿到子线程退出状态。
第三种终止方式:
//thread.c
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<pthread.h>
3
4 void * thread_run(void *arg)
5 {
6 int count=5;
7 while(count-->0) 8 {
9
10 printf("this is thread\n");
11 sleep(1);
12 }
13
14 pthread_cancel(pthread_self());
15 }
16 int main()
17 {
18 pthread_t tid;
19 int ret=pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_run,NULL);
20 int count=10;
21 while(count-->0)
22 {
23 printf("this is main thread\n");
24 sleep(2);
25 }
26
27 void *status=0;
28 int retu=pthread_join(tid,&status);
29 if(retu==0)
30 {
31 printf("pthread_join: code:%d\n",(int)status);
32
33 }
34 return 0;
35 }实验结果:
与上一个结果一样,只不过是在主函数中调用pthread_cancel()来终止子线程。是被取消的,不是自己主动的。
注:还有一种终止方式,在子线程中通过调用exit()函数,此时进程终止,因为进程终止调用这个函数。一般不会使用其终止线程。将上述代码thread_run()函数中用exit()函数:
4 void * thread_run(void *arg)
5 {
6 int count=5;
7 while(count-->0) 8 {
9
10 printf("this is thread\n");
11 sleep(1);
12 }
13
14 exit(1);
15 }运行结果:

当子线程调用exit时,进程终止,也跑了5次。
2.创建多个线程:
41 void * thread1(void *arg)
42 {
43 int count=5;
44 while(count-->0)
45 {
46
47 printf("this is thread1: %d,thread_t :%u\n",(int)arg,pthread_self());
48 sleep(1);
49 }
50
51
52 }
53
54 void * thread2(void *arg)
55 {
56 int count=5;
57 while(count-->0)
58 {
59
60 printf("this is thread2: %d,thread_t :%u\n",(int)arg,pthread_self());
61 sleep(1);
62 }
63 void * thread2(void *arg)
64 {
65 int count=5;
66 while(count-->0)
67 {
68 int count=5;
69 while(count-->0)
70 {
71
72 printf("this is thread3: %d,thread_t :%u\n",(int)arg,pthread_self());
73 sleep(1);
74 }
75
76
77 }
78 int main()
79 {
80 pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3;
81 pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,thread1,(void*)1);
82 pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,thread2,(void*)2);
83 pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,thread3,(void*)3);
84 sleep(2);
85 pthread_cancel(tid3);
86 void* ret=NULL;
87 pthread_join(tid1,&ret);
88 pthread_join(tid2,&ret);
89 pthread_join(tid3,&ret);
90 return 0;
}运行结果:

四.分离线程
在任意时间点上,线程是可结合的或者是分离的,默认线程创建是可结合的。由于调用pthread_join()函数后,如果该线程没有运行结束,调用者会被阻塞,这时可在子线程中加入代码:
pthread_detach(pthread_self());也可在主函数中调用pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。