作者:MyBug
使用过springboot的同学应该已经知道,springboot通过默认配置了很多框架的使用方式帮我们大大简化了项目初始搭建以及开发过程。
本文的目的就是一步步分析springboot的启动过程,这次主要是分析springboot特性自动装配。
那么首先带领大家回顾一下以往我们的web项目是如何搭建的,通常我们要搭建一个基于Spring的Web应用,我们需要做以下一些工作:
pom文件中引入相关jar包,包括spring、springmvc、redis、mybaits、log4j、mysql-connector-java 等等相关jar …
配置web.xml,Listener配置、Filter配置、Servlet配置、log4j配置、error配置 …
配置数据库连接、配置spring事务
配置视图解析器
开启注解、自动扫描功能
配置完成后部署tomcat、启动调试
……
花在搭建一个初始项目,可能一个小时就过去了或者半天救过了,但是用了SpringBoot之后一切都会变得非常便捷,下面我们首先来分析一下SpringBoot的起步依赖以及自动配置。
1.在我们的pom文件里面引入以下jar:
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.4.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis 开发包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--springboot web模块支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>spring-boot-starter-web包自动帮我们引入了web模块开发需要的相关jar包。
mybatis-spring-boot-starter帮我们引入了dao开发相关的jar包。
spring-boot-starter-xxx是官方提供的starter,xxx-spring-boot-starter是第三方提供的starter。
截图看一下我们的mybatis-spring-boot-starter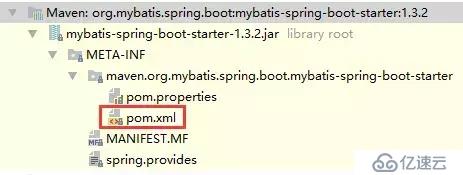
可以看出mybatis-spring-boot-starter并没有任何源码,只有一个pom文件,它的作用就是帮我们引入其它jar。
2.配置数据源
spring:
datasource:
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis_test
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
hikari:
# 最小空闲连接数量
minimum-idle: 5
# 连接池最大连接数,默认是10
maximum-pool-size: 60
# 此属性控制从池返回的连接的默认自动提交行为,默认值:true
auto-commit: true
# 一个连接idle状态的最大时长(毫秒),超时则被释放(retired),缺省:10分钟
idle-timeout: 600000
# 此属性控制池中连接的最长生命周期,值0表示无限生命周期,默认1800000即30分钟
max-lifetime: 1800000
# 数据库连接超时时间,默认30秒,即30000
connection-timeout: 60000stater机制帮我们完成了项目起步所需要的的相关jar包。那问题又来了,传统的spring应用中不是要在application.xml中配置很多bean的吗,比如dataSource的配置,transactionManager的配置 … springboot是如何帮我们完成这些bean的配置的?
下面我们来分析这个过程
1.基于java代码的bean配置
以mybatis为例,在上面的截图中,我们发现mybatis-spring-boot-starter这个包帮我们引入了mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure这个包,如下图: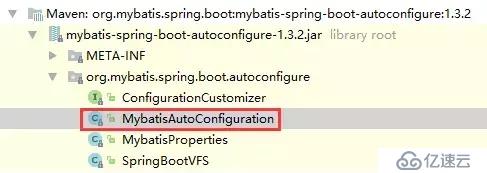
里面有MybatisAutoConfiguration这个类,打开这个类看看有些什么东西。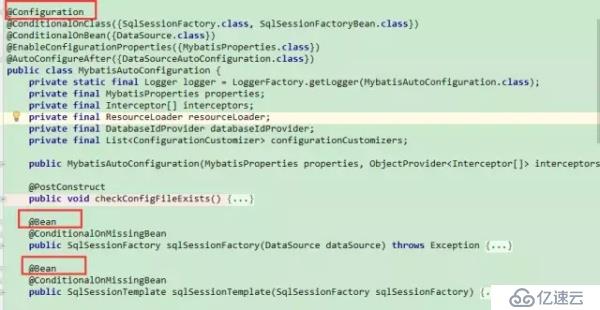
熟悉@Configuration&、@Bean这两个bean的同学或许已经知道了。这两个注解一起使用就可以创建一个基于java代码的配置类,可以用来替代相应的xml配置文件。
@Configuration注解的类可以看作是能生产让Spring IoC容器管理的Bean实例的工厂。@Bean注解告诉Spring,一个带有@Bean的注解方法将返回一个对象,该对象应该被注册到spring容器中。
br/>@Bean注解告诉Spring,一个带有@Bean的注解方法将返回一个对象,该对象应该被注册到spring容器中。
2.自动配置条件依赖
从MybatisAutoConfiguration这个类中使用的注解可以看出,要完成自动配置是有依赖条件的。
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class })
@ConditionalOnBean(DataSource.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MybatisProperties.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
public class MybatisAutoConfiguration {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MybatisAutoConfiguration.class);
private final MybatisProperties properties;
private final Interceptor[] interceptors;
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private final DatabaseIdProvider databaseIdProvider;
private final List<ConfigurationCustomizer> configurationCustomizers;
......首先预习一下Springboot是常用的条件依赖注解有:@ConditionalOnBean,仅在当前上下文中存在某个bean时,才会实例化这个Bean。
br/>@ConditionalOnBean,仅在当前上下文中存在某个bean时,才会实例化这个Bean。
br/>@ConditionalOnExpression,当表达式为true的时候,才会实例化这个Bean。
br/>@ConditionalOnMissingClass,某个class在类路径上不存在的时候,才会实例化这个Bean。
br/>@AutoConfigureAfter,在某个bean完成自动配置后实例化这个bean。
所以要完成Mybatis的自动配置,需要在类路径中存在SqlSessionFactory.class、SqlSessionFactoryBean.class这两个类,需要存在DataSource这个bean且这个bean完成自动注册。
进入DataSourceAutoConfiguration这个类,可以看到这个类属于这个包:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc
这个包又属于spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.0.4.RELEASE.jar这个包,自动配置这个包帮们引入了jdbc、kafka、logging、mail、mongo等包。很多包需要我们引入相应jar后自动配置才生效。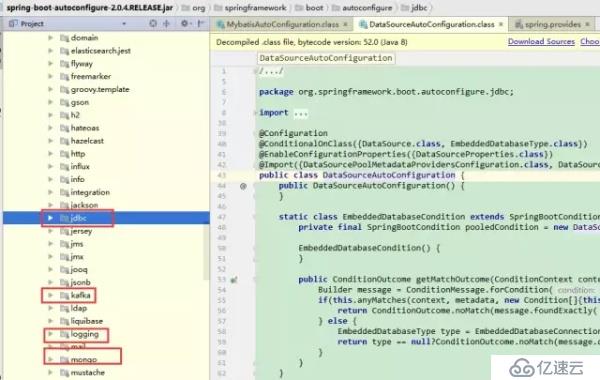
3.Bean参数的获取
到此我们已经知道了bean的配置过程,但是还没有看到springboot是如何读取yml或者properites配置文件的的属性来创建数据源的?
在DataSourceAutoConfiguration类里面,我们注意到使用了EnableConfigurationProperties这个注解。
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ DataSource.class, EmbeddedDatabaseType.class })
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DataSourceProperties.class)
@Import({ DataSourcePoolMetadataProvidersConfiguration.class,
DataSourceInitializationConfiguration.class })
public class DataSourceAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration
@Conditional(EmbeddedDatabaseCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ DataSource.class, XADataSource.class })
@Import(EmbeddedDataSourceConfiguration.class)
protected static class EmbeddedDatabaseConfiguration {
}
......DataSourceProperties中封装了数据源的各个属性,且使用了注解ConfigurationProperties指定了配置文件的前缀。
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public class DataSourceProperties implements BeanClassLoaderAware, InitializingBean {
private ClassLoader classLoader;
/**
* Name of the datasource. Default to "testdb" when using an embedded database.
*/
private String name;
/**
* Whether to generate a random datasource name.
*/
private boolean generateUniqueName;
/**
* Fully qualified name of the connection pool implementation to use. By default, it
* is auto-detected from the classpath.
*/
private Class<? extends DataSource> type;
/**
* Fully qualified name of the JDBC driver. Auto-detected based on the URL by default.
*/
private String driverClassName;
/**
* JDBC URL of the database.
*/
private String url;
/**
* Login username of the database.
*/
private String username;
/**
* Login password of the database.
*/
private String password;
/**
* JNDI location of the datasource. Class, url, username & password are ignored when
* set.
*/
private String jndiName;
/**
* Initialize the datasource with available DDL and DML scripts.
*/
private DataSourceInitializationMode initializationMode = DataSourceInitializationMode.EMBEDDED;
/**
* Platform to use in the DDL or DML scripts (such as schema-${platform}.sql or
* data-${platform}.sql).
*/
private String platform = "all";
/**
* Schema (DDL) script resource references.
*/
private List<String> schema;
/**
* Username of the database to execute DDL scripts (if different).
*/
private String schemaUsername;
/**
* Password of the database to execute DDL scripts (if different).
*/
private String schemaPassword;
/**
* Data (DML) script resource references.
*/
private List<String> data;
......通过以上分析,我们可以得知:@ConfigurationProperties注解的作用是把yml或者properties配置文件转化为bean。
br/>@ConfigurationProperties注解的作用是把yml或者properties配置文件转化为bean。
通过这种方式,把yml或者properties配置参数转化为bean,这些bean又是如何被发现与加载的?
4.Bean的发现
springboot默认扫描启动类所在的包下的主类与子类的所有组件,但并没有包括依赖包的中的类,那么依赖包中的bean是如何被发现和加载的?
我们通常在启动类中加@SpringBootApplication这个注解,点进去看
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
......实际上重要的只有三个Annotation:@Configuration(@SpringBootConfiguration里面还是应用了@Configuration)
br/>@Configuration(@SpringBootConfiguration里面还是应用了@Configuration)
br/>@ComponentScan
br/>@ComponentScan的作用就是自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件,比如@Component和@Repository等,最终将这些bean定义加载到spring容器中。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {};
}如上源码,@EnableAutoConfiguration注解引入了@AutoConfigurationPackage和@Import这两个注解。@AutoConfigurationPackage的作用就是自动配置的包,@Import导入需要自动配置的组件。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
}~
/**
* {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar} to store the base package from the importing
* configuration.
*/
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
register(registry, new PackageImport(metadata).getPackageName());
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new PackageImport(metadata));
}
}new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImport(metadata)).getPackageName()
new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImport(metadata)
这两句代码的作用就是加载启动类所在的包下的主类与子类的所有组件注册到spring容器,这就是前文所说的springboot默认扫描启动类所在的包下的主类与子类的所有组件。
那问题又来了,要搜集并注册到spring容器的那些beans来自哪里?
进入 AutoConfigurationImportSelector类,我们可以发现SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames方法调用loadSpringFactories方法从所有的jar包中读取META-INF/spring.factories文件信息。
下面是spring-boot-autoconfigure这个jar中spring.factories文件部分内容,其中有一个key为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的值定义了需要自动配置的bean,通过读取这个配置获取一组@Configuration类。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener
# Auto Configuration Import Filters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\每个xxxAutoConfiguration都是一个基于java的bean配置类。实际上,这些xxxAutoConfiguratio不是所有都会被加载,会根据xxxAutoConfiguration上的@ConditionalOnClass等条件判断是否加载;通过反射机制将spring.factories中@Configuration类实例化为对应的java实列。
到此我们已经知道怎么发现要自动配置的bean了,最后一步就是怎么样将这些bean加载到spring容器。
5.Bean 加载
如果要让一个普通类交给Spring容器管理,通常有以下方法:
使用 @Configuration与@Bean 注解
使用@Controller @Service @Repository @Component 注解标注该类,然后启用@ComponentScan自动扫描
使用@Import 方法
springboot中使用了@Import 方法@EnableAutoConfiguration注解中使用了@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})注解,AutoConfigurationImportSelector实现了DeferredImportSelector接口,
br/>@EnableAutoConfiguration注解中使用了@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})注解,AutoConfigurationImportSelector实现了DeferredImportSelector接口,
selectImports方法返回一组bean,@EnableAutoConfiguration注解借助@Import注解将这组bean注入到spring容器中,springboot正式通过这种机制来完成bean的注入的。
我们可以将自动配置的关键几步以及相应的注解总结如下:@Configuration&与@Bean------>>>基于java代码的bean配置
br/>@Configuration&与@Bean------>>>基于java代码的bean配置
br/>@EnableConfigurationProperties与@ConfigurationProperties->读取配置文件转换为bean。
欢迎大家一起交流,喜欢文章记得点个赞哟,感谢支持!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。