什么是特性,我自己的理解是:
特性是一种允许我们向程序集增加元数据的语言结构。它是用于保存程序结构信息的特殊的类。特性有2个基本概念:“目标”,“消费者”,就拿特殊性DebuggerStepThrough来说,编译器就是消费者,当它遇到被此特性注册过的Mothed时,就不会进入此Mothed执行(断点时)会直接得到此Methed的运行结果,而次Method就是目标了。总而言之,应用了特性的语言结构叫“目标”;设计用来获取和使用此特性的就叫“消费者”。
下面讲解.Net自带的几个比较著名的特性
1,Obsolete : 提示Method过时
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace AtrributeTest.com
{
/// <summary>
/// 用于测试Obsolete特性
/// 目标:Method
/// 消费者 : IDE
/// </summary>
public sealed class ObsoleteTest
{
[Obsolete("这个方法已经过时,请使用MyNewMethod方法",false)]
public void MyOldMethd()
{
Console.WriteLine("这是一个过时的方法");
}
public void MyNewMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("这是一个新方法");
}
}
}测试:
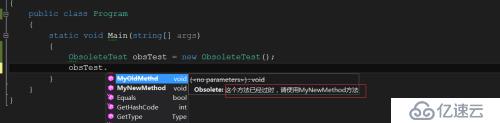
可以看出当IDE跳出提示时,会自动在有“Obsolete”标志的Method上划一横线(表示不提倡使用),我在Obsolete的构造函数中提示“这个方法已经过时,请使用MyNewMethod方法”也只IDE提示中显示出来。关于Obsolete的第二个参数(Boolean),它表是“是否不能使用”。如果为true,当使用了MyOldMethd方法后,编译会报错;反之(False的情况),只是不提倡使用。
2,Conditional : 取消Method的任何调用
这个的话我认为并没有编译参数好用。我先放测试代码,再给出解释
1,此内中有一个方法“MyTestMethod”被Conditional特性修饰
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace AtrributeTest.com
{
/// <summary>
/// 用于测试Condition特性
/// 目标:Method
/// 消费者 : IDE(将影响编译)
/// </summary>
public sealed class ConditionalTest
{
[Conditional("IsTest")]
public void MyTestMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("这是我的测试方法,请在正式上线后注释掉");
}
}
}此方法在2处调用
①:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace AtrributeTest.com
{
/// <summary>
/// 用于测试Obsolete特性
/// 目标:Method
/// 消费者 : IDE
/// </summary>
public sealed class ObsoleteTest
{
[Obsolete("这个方法已经过时,请使用MyNewMethod方法",false)]
public void MyOldMethd()
{
Console.WriteLine("这是一个过时的方法");
}
public void MyNewMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("这是一个新方法");
ConditionalTest contTest = new ConditionalTest();
contTest.MyTestMethod();
}
}
}②:Main函数
#define IsTest
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using AtrributeTest.com;
namespace AtrributeTest
{
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("ObsoleteTest..........................");
ObsoleteTest obsTest = new ObsoleteTest();
obsTest.MyNewMethod();
Console.WriteLine("Program..........................");
ConditionalTest conTest = new ConditionalTest();
conTest.MyTestMethod();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
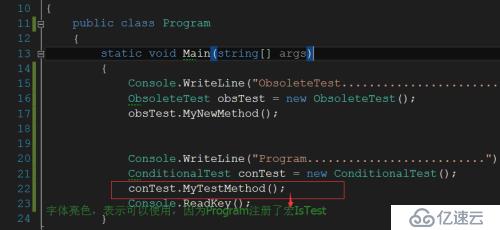
}在Program中我定义了一个宏 IsTest , 所以在此类的Main函数中MyTestMethod是可以被执行的。但是在ObsoleteTest内中没有定义此宏,所以此类的方法MyNewMethod中的MyTestMethod是不会被执行的。这点值得注意。实际上在IDE中已经给予了提示:
在注册过IsTest宏的Program类,如下图:
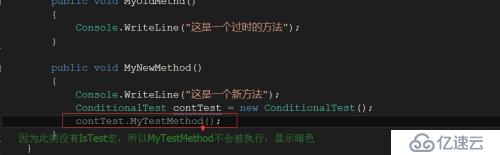
在没有注册过宏IsTest宏的ObsoleteTest类,如下图:
值得注意注意的是 ,① 宏一定要放在所有using的前面 ; ②宏的定义要与[Conditional("IsTest")]后面的参数一样,但是不能要“”(引号)
但是如果整个项目的此Method都能/不能调用 , 单单一个个在Class中加/删宏会累死你的 。这里本人有个好方法“预处理指令”在本人的博客《C#的预处理指令的全局设计》中有,但是还有一个此特性还有一个缺点:
所有引用(调用)此Method的地方不会被编译,但是定义它的地方会被编译。建议还是使用#if / #endif
自定义特性:(要注意三点)
一:需要继承Attribute类
二:需要以Attribute单词作为后缀名
三:最好申明为sealed,需要申明此特性的消费着
好,现在来整一个Demo,现在一步步实现
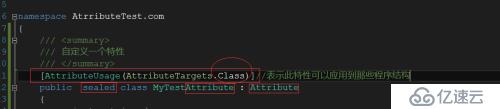
①建立第一个自定义特性,如下图
②完整代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace AtrributeTest.com
{
/// <summary>
/// 自定义一个特性
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class)]//表示此特性可以应用到那些程序结构
public sealed class MyTestAttribute : Attribute
{
private string des;
public int Id { get; set; }
public MyTestAttribute(string @des)
{
this.des = des;
}
}
}③使用自定义特性
注意 : 使用反射获取特性信息
using System;
using AtrributeTest.com;
namespace AtrributeTest
{
[MyTest("我的第一个特性",Id = 1)]
public class Program
{
private static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type @ty = typeof (Program);
object[] arr = ty.GetCustomAttributes(false);//是否搜索父类上的特性
MyTestAttribute my = arr[0] as MyTestAttribute;
Console.WriteLine("特性类的des : {0}" , my.des);
Console.WriteLine("特性类的ID号 : {0}" ,my.Id);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。