简要概述防火墙:
iptables/netfilter是一种包过滤型的防火墙,主要工作与网络层,对于进出本主机或本网络的报文根据
事先定义的检查规则作匹配检测,对于能够被规则匹配到的报文作出相应处理的组件;
防火墙类型:软件防火墙、硬件防火墙
iptables/netfilter组件:
iptables:iptables 组件是一种工具,也称为用户空间(userspace),用于设置数据过滤与nat规则
netfilter:组件也称为内核空间(kernelspace),是内核的一部分,由一些信息包过滤表组成,这些表包含内核用来控制信息包过滤处理的规则集
链表规则:四表五链
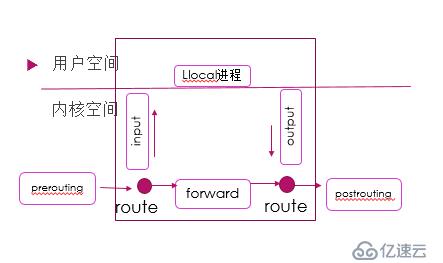
iptables内置有5个 hook functions :input,output,forward,prerouting,postrouting与之对应的5的链
内置的链:PREROUTING ,INPUT, FORWARD, OUTPUT,POSTROUTING
PREROUTING:在进行路由表选择之前处理数据包
INPUT:处理入站的数据包
FORWARD:处理转发的数据包
OUTPUT:处理出站的数据包
POSTROUTING:在进行路由选择后的处理数据包
表及功能:filter, nat, mangle, raw
filter:主要实现过滤功能:能够用于链的有:INPUT,FORWARD,OUTPUT
nat:network address translation 用于修改源IP、目标IP或者端口;PREROUTING ,OUTPUT,POSTROUTING
mangle:为数据包设置标记,拆解报文,做出修改并重新封装起来:PREROUTING ,INPUT, FORWARD, OUTPUT,POSTROUTING
raw:关闭nat表上启用的连接追踪机制:PREROUTING,OUTPUT
如图所示:

规则表的先后顺序:raw--mangle--nat--filter
报文流向:
流入本机:PREROUTING --> INPUT
由本机流出:OUTPUT --> POSTROUTING
转发:PREROUTING --> FORWARD --> POSTROUTING
3.如下图展现了数据包是如何流经本机iptables功能:
4.iptables规则命令参数使用
规则:组成部分根据规则匹配条件来匹配报文,一旦匹配成功后就由规则定义的动作做出处理
匹配条件:基本匹配条件、扩展匹配条件
处理动作:基本处理动作、扩展处理动作、自定义处理机制
格式:iptables [-t bable] COMMAND chain [-m matchname [per-match-options]] -j target [per-target-options]
| 表管理 | -t | raw,mangle,nat,filter,默认表为filter可省略 |
| COMMAND | ||
| 链管理 | -N | Create a new user-defined chain by the given name,自定义新的规则链 |
| -X | Delete the optional user-defined chain specified. 删除自定义规则链 | |
| -P | --policy chain target,设置默认策略,对filter而言:ACCEPT/DROP | |
| -E | --rename-chain old-chain new-chain 重命名 | |
| 规则管理 | -A | -A, --append chain rule-specification ,追加 |
| -I # | --insert chain [rulenum] rule-specification ,插入,可指定位置,省略是表示第一条 | |
| -D | delete删除;可指明规则序号或者指明规则本身 | |
| -R | replace,替换指定链上的指定规则 | |
| -F | flush [chain]清控规则链 | |
| -Z | zero,至零;iptables的每条规则链都有两个计数器:匹配的报文的个数、 匹配到的所有报文的大小之和 | |
| -S | select,以iptables-save命令格式显示链上规则 | |
| 查看 | ||
| -L | --list,列出指定链上的所有规则; -n:numberic,以数字格式显示端口和地址,不反解服务名 -v:verbose -x:显示计数器结果的精确值 --line-number:显示规则的序号 如组合使用:-nvL | |
| 匹配条件选项 | 基本匹配条件,无需加载任何模块,由iptables/netfilter提供 | |
| [!] -s | --source address[/mask][,...] 匹配来源地址ip/mask,[!]表示除了这个IP以外 | |
| [!] -d | --destination address[/mask][,...] 匹配目标地址ip/mask,[!]表示除了这个IP以外 | |
| [!] -i | --in-interface name:数据报文流入的接口;只能应用于数据报文流入的环节,只能应用于PREROUTING,INPUT和FORWARD链; | |
| [!] -o | --out-interface name:数据报文流出的接口;只能应用于数据报文流出的环节,只能应用于FORWARD、OUTPUT和POSTROUTING链; | |
| [!] -p | --protocol protocol匹配协议:tcp, udp, udplite, icmp, icmpv6,esp, ah, sctp, mh or the special keyword "all" | |
| -j target name | 处理动作 | |
| ACCEPT | 允许通过 | |
| LOG | 记录后继续匹配下条规则 | |
| REJECT | 拒绝通过,必要时会给提示 | |
| DROP | 直接丢弃,不给任何回应 | |
| RETURN | 返回调用链 | |
| MASK | 做防火墙标记,不做任何访问控制 | |
| DNAT | 目标 地址转换 | |
| SNAT | 源地址转换 | |
| MASQUERADE | 地址伪装 | |
扩展匹配条件:需要加载扩展模块才生效。
隐式扩展条件:不需手动加载扩展模块,但需要使用-p选项指明协议
-p :--protocol protocol
tcp : 等同于 “-m tcp”/udp
[!] --source-port, --sport port[:port]:匹配报文源 端口,可以是端口连续范围
[!] --destination-port, --dport port[:port]:匹配报文源目标端口,可以是端口连续范围
icmp:
[!] --icmp-type {type[/code]|typename}
echo-request:8/0
echo-reply:0/0
用法:可以单独指定type:允许192.168.0.0/24请求192.168.1.11
iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.1.11 -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j ACCEPT
[!] --tcp-flags mask comp
comp is a comma-separated list of flags which must be set,例如SYN
例如:“--tcp-flags SYN,ACK,FIN,RST SYN”表示,要检查的标志位为SYN,ACK,FIN,RST四个,
其中SYN必须为1,余下的必须为0;
[!] --syn:用于匹配第一次握手,相当于”--tcp-flags SYN,ACK,FIN,RST SYN“;
显示扩展条件:必须指明要加载的扩展模块 [-m matchname [per-match-options]]
1)multiport:以离散的方式定义多端口匹配,最多指定15个端口
[!] --source-ports ,--sports port[,port|,port:port]....指定多个源端口 port:port表示连续端口
[!] --destination-ports,--dports port[,port|,port:port]....指定多个目标端口
[!] --ports port[,port|,port:port]
eg:允许172.16.0.0/16网段的主机访问67主机的22,80端口
iptables -A INPUT -s 172.16.0.0/16 -d 192.168.1.10 -p -m multiport --dport 22,80 -j ACCEPT
2)iprange:This matches on a given arbitrary range of IP addresses.匹配给定的连续IP地址
[!] --src-range from[-to] Match source IP in the specified range.匹配源IP地址
[!] --dst-range from[-to] 匹配目标IP地址
eg:开放192.168.1.80-192.168.1.100对服务器192.168.1.10的80端口访问
iptables -A INPUT -d 192.168.1.10 -p tcp --dport 80 -m iprange --src-range 192.168.1.80-192.168.1.100 -j ACCEPT
3)string: 需要制定--algo
对报文中的应用层数据字符串做模式匹配,应用于响应报文--OUTPUT
--algo {bm|kmp}: Select the pattern matching strategy选择模式匹配策略
(bm = Boyer-Moore, kmp = Knuth-Pratt-Mor‐ ris)
[!] --string pattern: Matches the given pattern.匹配给定的字符串模式
[!] --hex-string pattern: Matches the given pattern in hex notation.16进制格式
eg:iptables -A OUTPUT -s 192.168.1.101 -d 192.168.0.0/24 -p tcp --sport 80 -m string --algo bm --string "bad" -j REJECT
4) time:根据将报文到达的时间与指定的时间范围进行匹配,默认使用UTC时间
--datestart YYYY[-MM[-DD[Thh[:mm[:ss]]]]]
--datestop YYYY[-MM[-DD[Thh[:mm[:ss]]]]]
--timestart hh:mm[:ss]
--timestop hh:mm[:ss]
[!] --monthdays day[,day...]
[!] --weekdays day[,day...] --weekdays Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat, Sun, or values from 1 to 7
eg: iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.1.100 -p tcp --dport 80 -m time --timestart 08:00 --timestop 17:00
--weekdays 1 ,2,3,4,5 -j ACCEPT
5)connlimit :根据每客户端IP做并发连接数数量匹配
Allows you to restrict the number of parallel connections to a server per client IP address (or client address block).
--connlimit-upto n:连接的数量小于等于n时匹配;
--connlimit-above n:连接的数量大于n时匹配;
# iptables -A INPUT -d 172.16.100.67 -p tcp --dport 21 -m connlimit --connlimit-above 2 -j REJECT
iptables -A INPUT -d 172.16.100.67 -p tcp --dport 21 -m connlimit --connlimit-upto 2 -j ACCEPT
6)limit: This module matches at a limited rate using a token bucket filter. 使用令×××桶过滤器做速率匹配
--limit rate[/second|/minute|/hour|/day]
--limit-burst number 速率突发值限制
eg: iptables -I INPUT -d 172.16.100.67 -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -m limit --limit 3/minute --limit-burst 5 -j ACCEPT
7)state
The "state" extension is a subset of the "conntrack" module. "state" allows access to the connection tracking state for this packet.
根据”连接追踪机制“去检查连接的状态,内存中一个存储空间称为连接追踪模板 conntrack template
[!] --state state
conntrack机制:追踪本机上的请求和响应之间的关系;状态有如下几种:
NEW: The packet has started a new connection or otherwise associated with a connection which has not seen packets in both directions.
发出新请求,之间的连接还没有任何数据
ESTABLISHED:NEW状态之后,连接追踪模板中为其建立的条目失效之前期间内所进行的通信状态;
RELATED:The packet is starting a new connection, but is associated with an existing con‐nection
相关联的连接;如ftp协议中的数据连接与命令连接之间的关系;
INVALID:无效的连接;
UNTRACKED:未进行追踪的连接;raw表拆除连接追踪功能
eg: 本地22,80端口只放行新的请求和已建立的连接
iptables -A INPUT -d 192.168.1.100 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 22,80 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -s 192.168.1.100 -p tcp -m multiport --sports 22,80 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
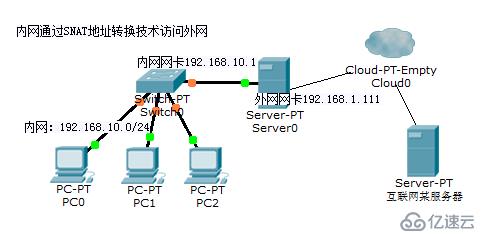
5.SNAT和DNAT
snat:POSTROUTING, OUTPUT 修改IP报文中的源地址
让本地网络中的主机通过某一特定地址访问外部网络时,从而实现地址伪装,可以解决IP资源匮乏;
请求:有内网主机发起,修改源IP,如果修改则由管理员定义
响应:修改目标IP,但由nat自动根据会话表中跟踪机制实现相应修改
nat表的target:
SNAT
--to-source [ipaddr[-ipaddr]][:port[-port]]
--random
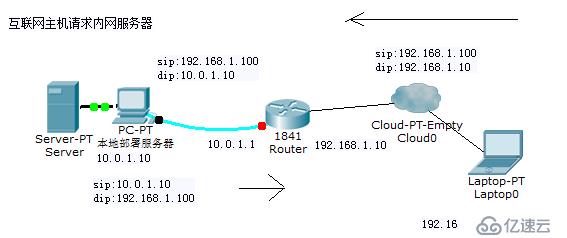
dnat:PREROUTING 修改IP报文中的目标地址
把本地网络中的某一主机上的某服务开放给外部网络中的用户访问时;
请求:由外网主机发起,修改其目标地址,由管理员定义
响应:修改源地址,但由nat自动根据会话表中跟踪机制实现相应修改
DNAT
--to-destination [ipaddr[-ipaddr]][:port[-port]]
如图所示SNAT的实现:
iptables -t nat A POSTROUTING -s 10.0.1.10 -j SNAT --to-source 192.168.1.10
DNAT: iptables -t nat A PREROUTING -d 192.168.1.10 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 10.0.1.10
7.如何开放被动模式的ftp服务?
6.规则的用效期限:
使用iptables命令定义的规则,手动删除之前,其生效期限为kernel存活期限;关机后消失:
保存规则至指定的文件:
CentOS 6:
~]# service iptables save
将规则保存至/etc/sysconfig/iptables文件中;
~]# iptables-save > /PATH/TO/SOME_RULES_FILE
CentOS 7:
~]# iptables -save > /PATH/TO/SOME_RULES_FILE
iptables -S > /PATH/TO/SOME_RULES_FILE
重新载入预存规则文件中规则:
~]# iptables-restore < /PATH/FROM/SOME_RULES_FILE
CentOS 6:
~]# service iptables restart 放在默认的路径/etc/sysconfig/iptables文件重载;
自动生效规则文件中的规则:
(1) 用脚本保存各iptables命令;让此脚本开机后自动运行;
/etc/rc.d/rc.local文件中添加脚本路径;
/PATH/TO/SOME_SCRIPT_FILE
/usr/bin/iptables.sh
(2) 用规则文件保存各规则,开机时自动载入此规则文件中的规则;
/etc/rc.d/rc.local文件添加:
iptables-restore < /PATH/FROM/IPTABLES_RULES_FILE
etc/sysconfig/iptables.v2
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。