这篇文章给大家分享的是有关python和c++怎么实现旋转矩阵到欧拉角的变换方式的内容。小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,一起跟随小编过来看看吧。
在摄影测量学科中,国际摄影测量遵循OPK系统,即是xyz转角系统,而工业中往往使用zyx转角系统。
旋转矩阵的意义:描述相对地面的旋转情况,yaw-pitch-roll对应zyx对应k,p,w
#include <iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<eigen3/Eigen/Core>
#include<eigen3/Eigen/Dense>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
Eigen::Matrix3d rotationVectorToMatrix(Eigen::Vector3d theta)
{
Eigen::Matrix3d R_x=Eigen::AngleAxisd(theta(0),Eigen::Vector3d(1,0,0)).toRotationMatrix();
Eigen::Matrix3d R_y=Eigen::AngleAxisd(theta(1),Eigen::Vector3d(0,1,0)).toRotationMatrix();
Eigen::Matrix3d R_z=Eigen::AngleAxisd(theta(2),Eigen::Vector3d(0,0,1)).toRotationMatrix();
return R_z*R_y*R_x;
}
bool isRotationMatirx(Eigen::Matrix3d R)
{
int err=1e-6;//判断R是否奇异
Eigen::Matrix3d shouldIdenity;
shouldIdenity=R*R.transpose();
Eigen::Matrix3d I=Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
return (shouldIdenity-I).norm()<err?true:false;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Eigen::Matrix3d R;
Eigen::Vector3d theta(rand() % 360 - 180.0, rand() % 360 - 180.0, rand() % 360 - 180.0);
theta=theta*M_PI/180;
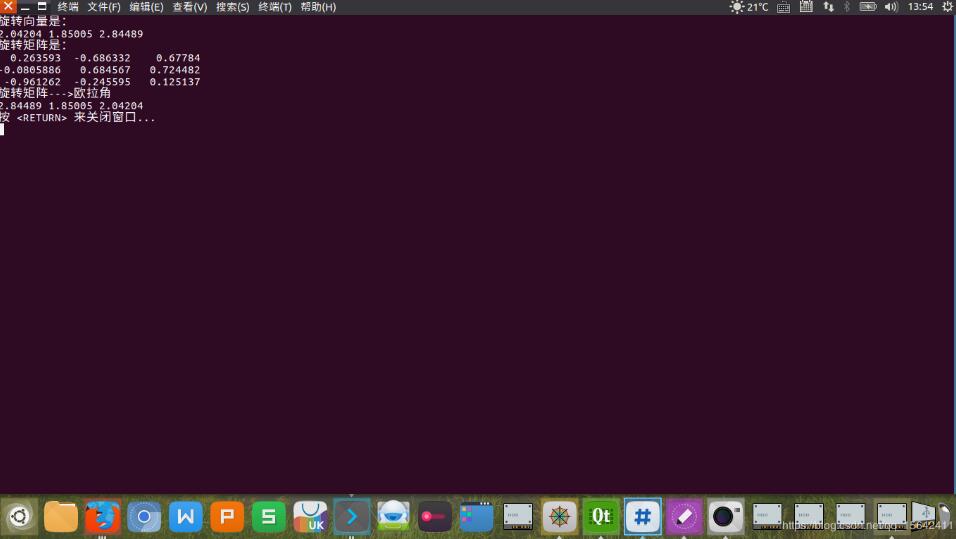
cout<<"旋转向量是:\n"<<theta.transpose()<<endl;
R=rotationVectorToMatrix(theta);
cout<<"旋转矩阵是:\n"<<R<<endl;
if(! isRotationMatirx(R)){
cout<<"旋转矩阵--->欧拉角\n"<<R.eulerAngles(2,1,0).transpose()<<endl;//z-y-x顺序,与theta顺序是x,y,z
}
else{
assert(isRotationMatirx(R));
}
return 0;
}
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
import random
def isRotationMatrix(R) :
Rt = np.transpose(R)
shouldBeIdentity = np.dot(Rt, R)
I = np.identity(3, dtype = R.dtype)
n = np.linalg.norm(I - shouldBeIdentity)
return n < 1e-6
def rotationMatrixToEulerAngles(R) :
assert(isRotationMatrix(R))
sy = math.sqrt(R[0,0] * R[0,0] + R[1,0] * R[1,0])
singular = sy < 1e-6
if not singular :
x = math.atan2(R[2,1] , R[2,2])
y = math.atan2(-R[2,0], sy)
z = math.atan2(R[1,0], R[0,0])
else :
x = math.atan2(-R[1,2], R[1,1])
y = math.atan2(-R[2,0], sy)
z = 0
return np.array([x, y, z])
def eulerAnglesToRotationMatrix(theta) :
R_x = np.array([[1, 0, 0 ],
[0, math.cos(theta[0]), -math.sin(theta[0]) ],
[0, math.sin(theta[0]), math.cos(theta[0]) ]
])
R_y = np.array([[math.cos(theta[1]), 0, math.sin(theta[1]) ],
[0, 1, 0 ],
[-math.sin(theta[1]), 0, math.cos(theta[1]) ]
])
R_z = np.array([[math.cos(theta[2]), -math.sin(theta[2]), 0],
[math.sin(theta[2]), math.cos(theta[2]), 0],
[0, 0, 1]
])
R = np.dot(R_z, np.dot( R_y, R_x ))
return R
if __name__ == '__main__' :
e = np.random.rand(3) * math.pi * 2 - math.pi
R = eulerAnglesToRotationMatrix(e)
e1 = rotationMatrixToEulerAngles(R)
R1 = eulerAnglesToRotationMatrix(e1)
print ("\nInput Euler angles :\n{0}".format(e))
print ("\nR :\n{0}".format(R))
print ("\nOutput Euler angles :\n{0}".format(e1))
print ("\nR1 :\n{0}".format(R1))感谢各位的阅读!关于“python和c++怎么实现旋转矩阵到欧拉角的变换方式”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,让大家可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到吧!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。