这篇文章主要讲解了Windows怎么配置VSCode+CMake+Ninja+Boost.Test的C++开发环境,内容清晰明了,对此有兴趣的小伙伴可以学习一下,相信大家阅读完之后会有帮助。
平时习惯了在Linux环境写C++,有时候切换到Windows想继续在同一个项目上工作,重新配置环境总是很麻烦。虽然Windows下用Visual Studio写C++只需要双击个图标,但我还是想折腾一下VS Code的环境配置。原因主要有两点:一是个人习惯上各种语言都在VS Code里面写,利用Git同步代码可以很方便地在不同平台开发同一个项目;二是有些情形下无法使用图形化界面,比如为Git配置CI(持续性集成)时显然不能用Visual Studio这个图形化的IDE来执行Windows环境的测试。
本文涉及的环境和工具版本:
主要内容
1 创建C++项目
2 安装Visual Studio
3 安装CMake和Ninja
4 下载和编译Boost
4.1 Command Prompt的使用
4.2 编译Boost
5 命令行编译和测试
6 配置VS Code
6.1 settings.json
6.2 c_cpp_properties.json
6.3 tasks.json
6.4 launch.json
6.5 CMakeLists.txt
6.6 编译、测试和调试
创建C++项目
VSCode及插件的安装过程本文暂不介绍,这里直接给出项目的文件结构和代码。
项目结构如下。 .vscode 文件夹里面的3个json文件用来配置VS Code,第二个文件夹里面包含对LeetCode某一个问题的解答( solution.hpp 和 solution.cpp ), solution_test.cpp 用来执行单元测试。最下面的 CMakeLists.txt 文件用来配置CMake,给出项目的编译规则。

这里先给出C++部分的代码,其他文件的内容会在后面给出。
solution.hpp
#ifndef SOLUTION_HEADER
#define SOLUTION_HEADER
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2);
};
#endif
solution.cpp
#include "solution.hpp"
static auto x = []() {
// turn off sync
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// untie in/out streams
cin.tie(NULL);
return 0;
}();
vector<int> Solution::intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
if (nums1.size() > nums2.size())
swap(nums1, nums2);
unordered_set<int> A(nums1.begin(), nums1.end()), C;
for (auto& i : nums2) {
if (A.find(i) != A.end())
C.insert(i);
}
return vector<int>(C.begin(), C.end());
}solution.cpp
#include "solution.hpp"
static auto x = []() {
// turn off sync
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// untie in/out streams
cin.tie(NULL);
return 0;
}();
vector<int> Solution::intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
if (nums1.size() > nums2.size())
swap(nums1, nums2);
unordered_set<int> A(nums1.begin(), nums1.end()), C;
for (auto& i : nums2) {
if (A.find(i) != A.end())
C.insert(i);
}
return vector<int>(C.begin(), C.end());
}solution_test.cpp
#define BOOST_TEST_MODULE SolutionTest
#include "solution.hpp"
#include <boost/test/unit_test.hpp>
BOOST_AUTO_TEST_SUITE(SolutionSuite)
BOOST_AUTO_TEST_CASE(PlainTest1)
{
vector<int> nums1{1,2,2,1};
vector<int> nums2{2,2};
vector<int> results = Solution().intersection(nums1, nums2);
vector<int> expected{2};
sort(results.begin(), results.end());
sort(expected.begin(), expected.end());
BOOST_CHECK_EQUAL_COLLECTIONS(results.begin(), results.end(), expected.begin(), expected.end());
}
BOOST_AUTO_TEST_CASE(PlainTest2)
{
vector<int> nums1{4,9,5};
vector<int> nums2{9,4,9,8,4};
vector<int> results = Solution().intersection(nums1, nums2);
vector<int> expected{9,4};
sort(results.begin(), results.end());
sort(expected.begin(), expected.end());
BOOST_CHECK_EQUAL_COLLECTIONS(results.begin(), results.end(), expected.begin(), expected.end());
}
BOOST_AUTO_TEST_SUITE_END()安装Visual Studio
这里不详述VS的安装过程,只是提示一下需要安装的组件。
需要注意Visual Studio Community 2019 Preview版本在编译Boost不能被正确识别,需要安装正式版。Visual Studio Community 2017/2019 两个版本我都试验过,这里以2019版本为例。
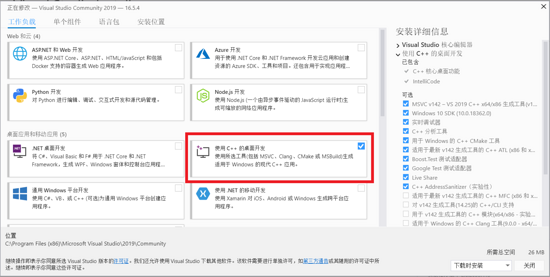
只需要安装“使用C++的桌面开发”这一套组件就可以了。
安装CMake和Ninja
CMake可以下载名为cmake-3.17.2-win64-x64.msi 的安装包来安装,Ninja 下载之后只有一个可执行文件,可以随意放在一个目录下。
安装过程暂不详述,只需要注意安装完成之后要设置一下环境变量。
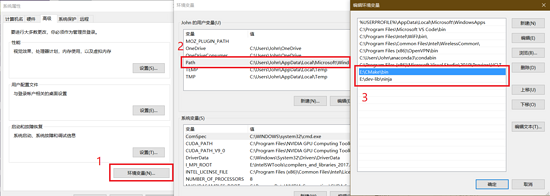
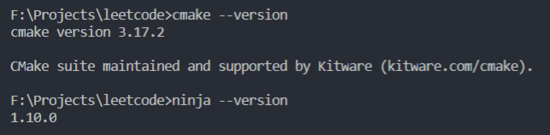
设置好环境变量之后,可以重新打开命令行工具或终端,检查一下CMake和Ninja的版本,看是否设置成功。
下载和编译Boost
Boost可以从这个链接下载: https://dl.bintray.com/boostorg/release/1.73.0/source/ ,然后解压到某个目录下。
Boost本身是header-only的,即大部分情况下只需要包含其头文件就能直接调用。但为了便于把我们自己的程序链接到Boost的单元测试模块(Boost.Test),这里需要编译一下Boost,产生静态库文件。
Command Prompt的使用
由于我们之前已经安装了Visual Studio以及在Windows平台编译C++所需的编译工具和依赖库,所以我们可以直接利用VS提供的环境来编译Boost。
在开始菜单的“Visual Studio 2019”目录下可以发现几个命令行工具,我们可以打开一个名为“x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2019”的命令行工具,这个图标在硬盘上对应到 C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat 这个脚本。该脚本的作用是把MSVC和Windows SDK的包含路径、库路径等添加到环境变量,然后打开一个cmd命令行。所以在这个cmd运行期间能够直接检测到编译C++所需的所有依赖项。
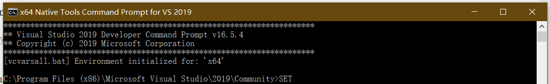
我们可以试着在这个cmd当中输入 SET ,查看已经生效的所有环境变量。
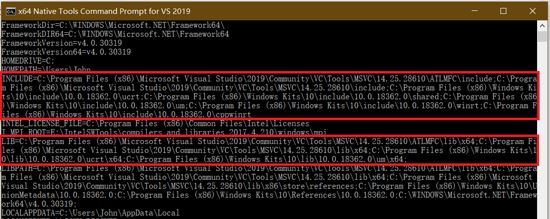
利用这些信息,我们在常规的cmd或PowerShell里也能正常编译C++代码。具体的过程会在后面介绍。
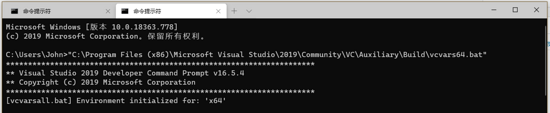
默认cmd的字体有点难看,我个人习惯在Windows Terminal 里面开一个cmd终端,然后执行下面的命令:
> "C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat"
这就可以让我们的新终端也能够检测到MSVC环境,如下图所示。
编译Boost
然后, cd 到Boost的根目录,执行下面的命令:
> bootstrap.bat > b2 --prefix=build install
等待编译完成之后,在 build\lib 目录下会出现一大堆 .lib 文件,我们只会用到 libboost_unit_test_framework-vc142-mt-gd-x64-1_73.lib 这一个文件。
当然,如果只想编译单元测试模块,可以用下面的命令:
> b2 address-model=64 architecture=x86 --with-test link=static --prefix=build install
命令行编译和测试
这里我们先在命令行里编译C++项目,并运行单元测试。 cd 到项目目录下,然后执行以下命令:
> mkdir build > cd build > cmake -G "Ninja" .. > ninja test_main > test_main.exe
在Windows平台上,生成工具可以选择VS提供的NMAKE,也可以用Ninja。微软的NMAKE类似于Linux平台的make工具。按照这个 视频 的介绍,Ninja的编译速度要比NMAKE快一些。

可以发现,在 vcvars64.bat 所提供的环境下,使用的是VS所安装的CMake和Ninja,版本号比我们自己安装都要老一些。下面我们介绍如何在VS Code中配置C++的编译和测试环境。
配置VS Code
settings.json
打开VS Code的设置,在 settings.json 中添加下面几行内容,可以起到类似 vcvars64.bat 的作用:
{
"terminal.integrated.shell.windows": "C:\\Windows\\System32\\cmd.exe",
"terminal.integrated.env.windows": {
"PATH" : "C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio\\2017\\Community\\VC\\Tools\\MSVC\\14.16.27023\\bin\\Hostx64\\x64;C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Windows Kits\\10\\bin\\10.0.18362.0\\x64;E:\\CMake\\bin;E:\\dev-lib\\ninja",
"INCLUDE": "C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio\\2017\\Community\\VC\\Tools\\MSVC\\14.16.27023\\include;C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Windows Kits\\10\\Include\\10.0.18362.0\\ucrt",
"LIB": "C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio\\2017\\Community\\VC\\Tools\\MSVC\\14.16.27023\\ATLMFC\\lib\\x64;C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio\\2017\\Community\\VC\\Tools\\MSVC\\14.16.27023\\lib\\x64;C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Windows Kits\\10\\lib\\10.0.18362.0\\ucrt\\x64;C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Windows Kits\\10\\lib\\10.0.18362.0\\um\\x64"
},
"cmake.cmakePath": "E:\\CMake\\bin\\cmake.exe"
}c_cpp_properties.json
这里给出Linux和Windows两个平台的配置。
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Linux",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**"
],
"defines": [],
"compilerPath": "/usr/bin/clang++",
"cStandard": "c11",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "clang-x64"
},
{
"name": "Win32",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**",
"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio\\2017\\Community\\VC\\Tools\\MSVC\\14.16.27023\\include",
"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio\\2017\\Community\\VC\\Tools\\MSVC\\14.16.27023\\ATLMFC\\include",
"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Windows Kits\\10\\Include\\10.0.18362.0\\ucrt",
"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Windows Kits\\10\\include\\10.0.18362.0\\shared",
"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Windows Kits\\10\\include\\10.0.18362.0\\um",
"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Windows Kits\\10\\include\\10.0.18362.0\\winrt",
"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Windows Kits\\10\\include\\10.0.18362.0\\cppwinrt",
"E:\\dev-lib\\boost_1_73_0"
],
"defines": ["_DEBUG", "UNICODE", "_UNICODE"],
"windowsSdkVersion": "10.0.18362.0",
"compilerPath": "C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio\\2017\\Community\\VC\\Tools\\MSVC\\14.16.27023\\bin\\Hostx64\\x64\\cl.exe",
"cStandard": "c11",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "msvc-x64"
}
],
"version": 4
}tasks.json
前两个 task 是Linux环境的(第一个是清空build目录,第二个是配置CMake),第三个 task 是Windows下配置CMake的。
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "clean",
"type": "shell",
"command": "rm -r build/*"
},
{
"label": "configure",
"type": "shell",
"command": "cmake",
"args": [
"--no-warn-unused-cli",
"-DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=/usr/bin/clang",
"-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=/usr/bin/clang++",
"-DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=TRUE",
"-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug",
"-H${workspaceFolder}",
"-B${workspaceFolder}/build",
"-G'Unix Makefiles'"
]
},
{
"label": "MSVC configure",
"type": "shell",
"command": "cmake",
"args": [
"-H${workspaceFolder}",
"-B${workspaceFolder}/build",
"-GNinja"
]
}
]
}launch.json
第一个是在Linux用 gdb 调试,第二个是在Linux下用 lldb 调试,第三个是在Windows用MSVC的 cl.exe 调试。
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/build/test_main",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": true,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
},
{
"name": "(lldb) Launch",
"type": "lldb",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/build/test_main",
"args": [],
},
{
"name": "(cl) Launch",
"type": "cppvsdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}\\build\\test_main.exe",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
}
]
}CMakeLists.txt
这个CMake脚本也是跨平台的,自动识别Linux或Windows,然后执行相应的链接。
cmake_minimum_required (VERSION 3.5)
project(leetcode)
set(PROBLEM_NAME "349-Intersection-of-Two-Arrays-set")
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
set(SOLUTION_SOURCES ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/${PROBLEM_NAME}/solution.cpp)
add_library(solution STATIC ${SOLUTION_SOURCES})
enable_testing()
set(TEST_SOURCES ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/${PROBLEM_NAME}/solution_test.cpp)
set(TEST_LIBS solution)
add_executable(test_main ${TEST_SOURCES})
if(WIN32)
message(STATUS "Detected Windows platform")
set(BOOST_ROOT E:\\dev-lib\\boost_1_73_0)
set(BOOST_LIBRARYDIR E:\\dev-lib\\boost_1_73_0\\build\\lib)
set(Boost_USE_STATIC_LIBS ON)
find_package(Boost REQUIRED COMPONENTS unit_test_framework)
target_link_libraries(test_main PRIVATE ${TEST_LIBS} Boost::boost Boost::unit_test_framework)
elseif(UNIX)
message(STATUS "Detected UNIX platform")
find_package(Boost REQUIRED COMPONENTS unit_test_framework)
add_library(boost_unit_test_framework STATIC IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(boost_unit_test_framework PROPERTIES
IMPORTED_LOCATION /usr/lib/libboost_unit_test_framework.a)
target_link_libraries(test_main ${TEST_LIBS} boost_unit_test_framework)
else()
message(FATAL_ERROR "Unsupported platform")
endif()
add_test(solution_test test_main COMMAND test_main)编译、测试和调试
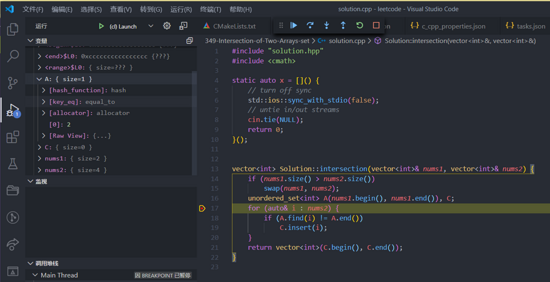
按快捷键 Ctrl + Shift + P ,然后就可以输入我们之前定义的不同命令了:
单元测试的效果如下图所示:

调试的效果如下图所示:
看完上述内容,是不是对Windows怎么配置VSCode+CMake+Ninja+Boost.Test的C++开发环境有进一步的了解,如果还想学习更多内容,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。